Abstract
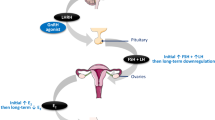
We present a case report of a patient with prostate cancer who failed to demonstrate consistent testosterone suppression to castration levels and incomplete suppression of serum prostate-specific antigen, although treated with gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists for 48 months. Serum dehydroepiandrosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate, as well as the androgen metabolite, androsterone glucuronide, were elevated compared to the other patients. The present data suggest that those prostate cancer patients who have even marginally elevated adrenal androgens may especially benefit from combined androgen blockade.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huggins C, Hodges CV . Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res 1941; 1: 293–296.
Labrie F, Belanger A, Luu-The V, Labrie C, Simard J, Cusan L et al. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists in the treatment of prostate cancer. Endocr Rev 2005; 26: 361–379.
Crawford ED, DeAntoni EP . Current status of combined androgen blockade: optimal therapy for advanced prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995; 80: 1062–1066.
Crawford ED, Eisenberger MA, McLeod DG, Spaulding JT, Benson R, Dorr FA et al. A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 419–424.
Labrie F, Cusan L, Seguin C, Bélanger A, Pelletier G, Reeves J et al. Antifertility effects of LHRH agonists in the male rat and inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis in man. Int J Fertil 1980; 25: 157–170.
Maximum androgen blockade in advanced prostate cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Prostate Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet 2000; 355: 1491–1496.
Schlegel PN, Kuzma P, Frick J, Farkas A, Gomahr A, Spitz I et al. Effective long-term androgen suppression in men with prostate cancer using a hydrogel implant with the GnRH agonist histrelin. Urology 2001; 58: 578–582.
Chertin B, Spitz I M, Lindenberg T, Algur N, Zer T, Kuzma P et al. An implant releasing the gonadotropin hormone-releasing hormone agonist histrelin maintains medical castration for up to 30 months in metastatic prostate cancer. J Urol 2000; 163: 838–844.
Belanger A, Candas B, Dupont A, Cusan L, Diamond P, Gomez JL et al. Changes in serum concentrations of conjugated and unconjugated steroids in 40–80-year-old men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 79: 1086–1090.
Labrie F, Belanger A, Belanger P, Bérubé R, Martel C, Cusan L et al. Androgen glucuronides, instead of testosterone, as the new markers of androgenic activity in women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2006; 99: 182–188.
Oefelein MG, Cornum R . Failure to achieve castrate levels of testosterone during luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist therapy: the case for monitoring serum testosterone and a treatment decision algorithm. J Urol 2000; 164: 726–729.
Ogan K, Berger M, Ball R . Gonadotropin releasing hormone analogue antiandrogen failure secondary to a pituitary adenoma. J Urol 1998; 160: 497–498.
Mostaghel EA, Page ST, Lin DW, Fazli L, Coleman IM, True LD et al. Intraprostatic androgens and androgen-regulated gene expression persist after testosterone suppression: therapeutic implications for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5033–5041.
Heracek J, Richard H, Martin H, Luboslav S, Jana S, Jitka K et al. Tissue and serum levels of principal androgens in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Steroids 2007; 72: 375–380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spitz, I., Chertin, B., Fridmans, A. et al. Partial androgen suppression consequent to increased secretion of adrenal androgens in a patient with prostate cancer treated with long-acting GnRH agonists. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12, 100–103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.15
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.15