Abstract
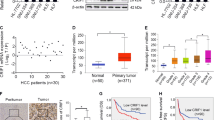
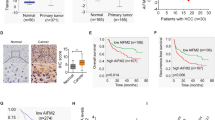
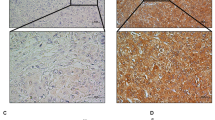
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most malignant tumors with high rate of recurrence and metastasis. Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 178 (CCDC178) has been reported to be mutated in HCC, whereas its role in physiological and pathologic process, including in human cancer, remains largely unknown. Here, we found that CCDC178 is upregulated in HCC tissues and its overexpression is correlated with pathological stage (P=0.003). CCDC178 deficiency reduced the anchorage-independent growth and anoikis resistance of HCC cells, and inhibited the HCC metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, CCDC178 associated with BRCA1-associated protein 2 (BRAP2), a negative regulator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, and promoted its degradation. Moreover, CCDC178 deficiency impaired the ERK activation, which is dependent on BRAP2. In conclusion, we identify CCDC178 as a novel candidate oncogene involved in anoikis resistance and HCC metastasis, and raise the possibility that CCDC178 may be a new therapeutic target for HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCDC178:
-
coiled-coil domain-containing 178
- BRAP2:
-
BRCA1-associated protein
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide.
References
Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016; 2: 16018.
Torre LA1 Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A . Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87–108.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL . Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 2557–2576.
Eccles SA, Welch DR . Metastasis: recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet 2007; 369: 1742–1757.
Geiger TR, Peeper DS . Metastasis mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1796: 293–308.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC . Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 563–572.
Frisch SM, Francis H . Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 619–626.
Gilmore A . Anoikis. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 1473–1477.
Frisch SM, Screaton RA . Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 555–562.
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P . Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1833: 3481–3498.
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Chiarugi P . Anoikis: an emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J Pathol 2012; 226: 380–393.
Liotta LA, Kohn E . Anoikis: cancer and the homeless cell. Nature 2004; 430: 973–974.
Howe AK, Aplin AE, Juliano RL . Anchorage-dependent ERK signaling—mechanisms and consequences. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2002; 12: 30–35.
Hübner A, Barrett T, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . Multisite phosphorylation regulates Bim stability and apoptotic activity. Mol Cell 2008; 30: 415–425.
Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Paulus JK, Lynch DK, Sgroi DC, Debnath J et al. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 733–740.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA . Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7: 169–181 Review.
Galante JM, Mortenson MM, Bowles TL, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ . ERK/BCL-2 pathway in the resistance of pancreatic cancer to anoikis. J Surg Res 2009; 152: 18–25.
Zhou F, Yang Y, Xing D . Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. FEBS J 2011; 278: 403–413.
Kairouz-Wahbe R, Biliran H, Luo X, Khor I, Wankell M, Besch-Williford C et al. Anoikis effector Bit1 negatively regulates Erk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 1528–1532.
Malin D, Strekalova E, Petrovic V, Rajanala H, Sharma B, Ugolkov A et al. ERK-regulated αB-crystallin induction by matrix detachment inhibits anoikis and promotes lung metastasis in vivo. Oncogene 2015; 34: 5626–5634.
Hauck CR, Hsia DA, Schlaepfer DD . Focal adhesion kinase facilitates platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated ERK2 activation required for chemotaxis migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 41092–41099.
Lassus P, Roux P, Zugasti O, Philips A, Fort P, Hibner U . Extinction of Rac1 and Cdc42Hs signalling defines a novel p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2377–2385.
Huang J, Deng Q, Wang Q, Li KY, Dai JH, Li N et al. Exome sequencing of hepatitis B virus–associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 2012; 44: 1117–1121.
Zhang J, Huang JY, Chen YN, Yuan F, Zhang H, Yan FH et al. Whole genome and transcriptome sequencing of matched primary and peritoneal metastatic gastric carcinoma. Sci Rep UK 2015; 5: 13750.
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013; 339: 819–823.
Li S1, Ku CY, Farmer AA, Cong YS, Chen CF, Lee WH . Identification of a novel cytoplasmic protein that specifically binds to nuclear localization signal motifs. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 6183–6189.
Matheny SA, Chen C, Kortum RL, Razidlo GL, Lewis RE, White MA . Ras regulates assembly of mitogenic signalling complexes through the effector protein IMP. Nature 2004; 427: 256–260.
Matheny SA, White MA, Ras-sensitive IMP . modulation of the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade through KSR1. Methods Enzymol 2006; 407: 237–247.
Chen C, Lewis RE, White MA . IMP modulates KSR1-dependent multivalent complex formation to specify ERK1/2 pathway activation and response thresholds. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 12789–12796.
Matheny SA, White MA . Signaling threshold regulation by the Ras effector IMP. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 11007–11011.
Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME et al. Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 1999; 286: 1358–1362.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Takashima O, Tsuruta F, Kigoshi Y, Nakamura S, Kim J, Katoh MC et al. Brap2 regulates temporal control of NF-kappaB localization mediated by inflammatory response. PLoS One 2013; 8: e58911.
Yan SR, Joseph RR, Rosen K, Reginato MJ, Jackson A, Allaire N et al. Activation of NF-kappaB following detachment delays apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 6482–6491.
Karin M, Lin A . NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 221–227.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yongjun Dang at School of Basic Medical Science, Fudan University for fruitful scientific discussions and sharing some reagents. This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFC0902401to JW); the National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China (2013ZX10002010-08 to JW) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272250 and 81472619 to JW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author contributions
XH performed most experiments. YZ, LW, BZ, DS, JJW and LY provided technical support for various assays. JW designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Zhao, Y., Wei, L. et al. CCDC178 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through modulation of anoikis. Oncogene 36, 4047–4059 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.10
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.10
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals CCDC58 as a carcinogenic factor related to immune infiltration
Apoptosis (2024)
-
Homeobox Protein BarH-like 1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Activating Coiled-Coil Domain-Containing Protein 178
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2024)
-
Characterization of the Immune Infiltration Landscape and Identification of Prognostic Biomarkers for Esophageal Cancer
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
EGFR/MET promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by stabilizing tumor cells and resisting to RTKs inhibitors in circulating tumor microemboli
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Decorin-mediated suppression of tumorigenesis, invasion, and metastasis in inflammatory breast cancer
Communications Biology (2021)