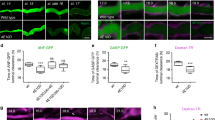
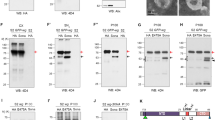
Abstract
Regulation of actin assembly and depolymerization is important for the organization of epithelia. Recent studies have shown that the actin-capping proteins are required to prevent cell extrusion and inappropriate activation of Yorkie (Yki) activity in Drosophila, implicating the importance of actin regulation for epithelial integrity and Yki-dependent tissue growth. However, the role of Twinstar (Tsr), the Drosophila homolog for cofilin/actin depolymerization factor (ADF), in epithelial integrity and Hippo signaling is unknown. Here we demonstrate that reduction of Tsr by RNA interference (RNAi) or mutant clones in wing imaginal disc induces not only F-actin accumulation but also ectopic expression of Wingless (Wg) and Yki target gene expanded (ex). Knockdown of Yki in Tsr-depleted cells reduced the level of ectopic Wg expression. Reduced Tsr also led to downregulation of cell junction proteins and extrusion of affected cells from the basal part of the epithelium. Rho GTPase 1 was upregulated in Tsr-depleted tissue, supporting the Tsr function in the inhibition of cell extrusion from the epithelium. Tsr is also required for blocking cell death and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling. Ectopic JNK activation induced caspase activation but did not cause cell extrusion. Further, the invasiveness of Tsr-depleted cells was not suppressed by inhibition of cell death or JNK signaling. In contrast, Yki upregulation was significantly suppressed by cell death inhibition. Taken together, our data suggest that Tsr is required for cell survival and tissue growth by regulating JNK and Yki signaling while maintaining the epithelial integrity by controlling cell junctions. This study provides an insight into potential roles of ADF/cofilin in invasive cell migration and tumor suppression in higher animals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamburg JR . Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1999; 15: 185–230.
Maloney MT, Bamburg JR . Cofilin-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other amyloidopathies. Mol Neurobiol 2007; 35: 21–43.
Tsai CH, Chiu SJ, Liu CC, Sheu TJ, Hsieh CH, Keng, Peter C et al. Regulated expression of cofilin and the consequent regulation of p27kip1 are essential for G1 phase progression. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 2365–2374.
Hsu FF, Lin TY, Chen JY, Shieh SY . p53-Mediated transactivation of LIMK2b links actin dynamics to cell cycle checkpoint control. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2864–2876.
Lee YJ, Mazzati DJ, Yun Z, Keng, Peter C . Inhibition of invasiveness of human lung cancer cell line H1299 by over-expression of cofilin. Cell Biol Intern 2005; 29: 877–883.
Tahtamouni LH, Shaw AE, Hasan MH, Yasin SR, Bamburg JR . Non-overlapping activities of ADF and cofilin-1 during the migration of metastatic breast tumor cells. BMC Cell Biol 2013; 14: 45.
Hotulainen P, Paunola E, Vartianen MK, Lappalainen P . Actin-depolymerizing factor and cofilin-1 play overlapping roles in promoting rapid F-Actin depolymerization in mammalian nonmuscle cells. Mol Biol Cell 2004; 16: 649–664.
Nagai S, Moreno O, Smith CA, Ivanchuk S, Romagnuolo R, Golbourn B et al. Role of the cofilin activity cycle in astrocytoma migration and invasion. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 859–869.
Edwards KA, Montague RA, Shepard S, Edgar BA, Erikson RL, Kiehart DP . Identification of Drosophila cytoskeletal proteins by induction of abnormal cell shape in fission yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 4589–4593.
Gunsalus KC, Bonaccorsi S, Williams E, Verni F, Gatti M, Goldberg ML . Mutations in twinstar, a Drosophila gene encoding a cofilin/ADF homologue, result in defects in centrosome migration and cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 1995; 131: 1243–1259.
Chen J, Godt D, Gunsalus K, Kiss I, Goldberg M, Laski FA . Cofilin/ADF is required for cell motility during Drosophila ovary development and oogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 204–209.
Niwa R, Nagata-Ohashi K, Takeichi M, Mizuno K, Uemura T . Control of actin reorganization by Slingshot, a family of phosphatases that dephosphorylate ADF/cofilin. Cell 2002; 108: 233–246.
Ng J, Luo L . Rho GTPases regulate axon growth through convergent and divergent signaling pathways. Neuron 2004; 44: 779–793.
Blair A, Tomlinson A, Pham H, Gunsalus KC, Goldberg ML, Laski FA . Twinstar, the Drosophila homolog of cofilin/ADF, is required for planar cell polarity patterning. Development 2006; 133: 1789–1797.
Rogers EM, Hsiung F, Rodrigues AB, Moses K . Slingshot cofilin phosphatase localization is regulated by receptor tyrosine kinases and regulates cytoskeletal structure in the developing Drosophila eye. Mech Dev 2005; 122: 1194–1205.
Pham H, Yu H, Laski FA . Cofilin/ADF is required for retinal elongation and morphogenesis of the Drosophila rhabdomere. Dev Biol 2008; 318: 82–91.
Boggiano JC, Fehon RG . Growth control by committee: intercellular junctions, cell polarity, and the cytoskeleton regulate Hippo signaling. Dev Cell 2012; 22: 695–702.
Janody F, Treisman JE . Actin capping protein alpha maintains vestigial-expressing cells within the Drosophila wing disc epithelium. Development 2006; 133: 3349–3357.
Fernandez BG, Gaspar P, Bras-Pereira C, Jezowska B, Rebelo SR, Janody F . Actin-capping protein and the Hippo pathway regulate F-actin and tissue growth in Drosophila. Development 2011; 138: 2337–2346.
Lin CM, Lin PY, Li YC, Hsu JC . Capulet and Slingshot share overlapping functions during Drosophila eye morphogenesis. J Biomed Sci 2012; 19: 46.
Sansores-Garcia L, Bossuyt W, Wada K, Yonemura S, Tao C, Sasaki H et al. Modulating F-actin organization induces organ growth by affecting the Hippo pathway. EMBO J 2011; 30: 2325–2335.
Reddy BVVG, Irvine KD . The Fat and Warts signaling pathways: new insights into their regulation, mechanism and conservation. Development 2008; 135: 2827–2838.
Cho E, Irvine KD . Action of fat, four-jointed, dachsous and dachs in distal-to-proximal wing signaling. Development 2004; 131: 4489–4500.
Badouel C, Gardano L, Amin N, Garg A, Rosenfeld R, Le Bihan T et al. The FERM-domain protein Expanded regulates Hippo pathway activity via direct interactions with the transcriptional activator Yorkie. Dev Cell 2009; 16: 411–420.
Genevet A, Tapon N . The Hippo pathway and apico–basal cell polarity. Biochem J 2011; 436: 213–224.
Hamaratoglu F, Willecke M, Kango-Singh M, Nolo R, Hyun E, Tao C et al. The tumour-suppressor genes NF2/Merlin and Expanded act through Hippo signalling to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 27–36.
Xu T, Rubin GM . Analysis of genetic mosaics in developing and adult Drosophila tissues. Development 1993; 117: 1223–1237.
Miles WO, Dyson NJ, Walker JA . Modeling tumor invasion and metastasis in Drosophila. Dis Model Mech 2011; 4: 753–761.
Vidal M, Larson DE, Cagan RL . Csk-deficient boundary cells are eliminated from normal Drosophila epithelia by exclusion, migration, and apoptosis. Dev Cell 2006; 10: 33–44.
Humbert P, Russell S, Richardson H . Dlg, Scribble and Lgl in cell polarity, cell proliferation and cancer. BioEssays 2003; 25: 542–553.
Speck O, Hughes SC, Noren NK, Kulikauskas RM, Fehon RG . Moesin functions antagonistically to the Rho pathway to maintain epithelial integrity. Nature 2003; 421: 83–87.
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP . JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6245–6251.
Sun G, Irvine KD . Regulation of Hippo signaling by Jun kinase signaling during compensatory cell proliferation and regeneration, and in neoplastic tumors. Dev Biol 2011; 350: 139–151.
Liu X, Grammont M, Irvine KD . Roles for scalloped and vestigial in regulating cell affinity and interactions between the wing blade and the wing hinge. Dev Biol 2000; 228: 287–303.
Neumann CJ, Cohen SM . Distinct mitogenic and cell fate specification functions of wingless in different regions of the wing. Development 1996; 122: 1781–1789.
Jezowska B, Fernández BG, Amândio AR, Duarte P, Mendes C, Brás-Pereira C et al. A dual function of Drosophila capping protein on DE-cadherin maintains epithelial integrity and prevents JNK-mediated apoptosis. Dev Biol 2011; 360: 143–159.
Rudrapatna VA, Bangi E, Cagan RL . A Jnk–Rho–Actin remodeling positive feedback network directs Src-driven invasion. Oncogene 2014; 33: 2801–2806.
Nakajima Y, Meyer EJ, Kroesen A, McKinney SA, Gibson MC . Epithelial junctions maintain tissue architecture by directing planar spindle orientation. Nature 2013; 500: 359–362.
Backhaus B, Sulkowski E, Schlote FW . A semi-synthetic, general-purpose medium for Drosophila melanogaster. Drosophila Inform Ser 1984; 60: 210–212.
Lee YS, Carthew RW . Making a better RNAi vector for Drosophila: use of intron spacers. Methods 2003; 30: 322–329.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs David Helfman and Kyung-Ok Cho for critical comments on the manuscript. We thank Drs Florence Janody, Jongkyeong Chung and Kenneth Irvine for providing flies and antibodies mentioned in the text. We acknowledge the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, DGGC, the NIG-Fly Stock Center and the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank for fly stocks and antibodies. We thank the TRiP at Harvard Medical School (NIH/NIGMS R01-GM084947) for providing transgenic RNAi fly stocks. This research was supported by a National Research Laboratory Grant (NRF-2011-0028326) and a Global Research Laboratory Grant (2014K1A1A2042982) through the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Korean, Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, C., Kim, YG., Le, T. et al. Twinstar/cofilin is required for regulation of epithelial integrity and tissue growth in Drosophila. Oncogene 35, 5144–5154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.46
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.46
This article is cited by
-
The spectraplakin Dystonin antagonizes YAP activity and suppresses tumourigenesis
Scientific Reports (2019)