Abstract
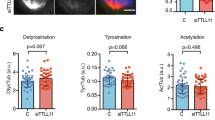
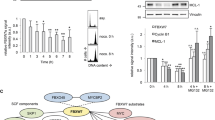
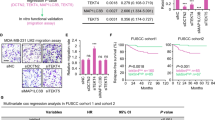
Deregulation of mitotic microtubule (MT) dynamics results in defective spindle assembly and chromosome missegregation, leading further to chromosome instability, a hallmark of tumor cells. RBP-J interacting and tubulin-associated protein (RITA) has been identified as a negative regulator of the Notch signaling pathway. Intriguingly, deregulated RITA is involved in primary hepatocellular carcinoma and other malignant entities. We were interested in the potential molecular mechanisms behind its involvement. We show here that RITA binds to tubulin and localizes to various mitotic MT structures. RITA coats MTs and affects their structures in vitro as well as in vivo. Tumor cell lines deficient of RITA display increased acetylated α-tubulin, enhanced MT stability and reduced MT dynamics, accompanied by multiple mitotic defects, including chromosome misalignment and segregation errors. Re-expression of wild-type RITA, but not RITA Δtub ineffectively binding to tubulin, restores the phenotypes, suggesting that the role of RITA in MT modulation is mediated via its interaction with tubulin. Mechanistically, RITA interacts with tubulin/histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and its suppression decreases the binding of the deacetylase HDAC6 to tubulin/MTs. Furthermore, the mitotic defects and increased MT stability are also observed in RITA−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts. RITA has thus a novel role in modulating MT dynamics and its deregulation results in erroneous chromosome segregation, one of the major reasons for chromosome instability in tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RITA:
-
RBP-J interacting and tubulin-associated protein
- HDAC6:
-
histone deacetylase 6
- MT:
-
microtubule
- dSTORM:
-
direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy.
References
Desai A, Mitchison TJ . Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1997; 13: 83–117.
Mitchison T, Kirschner M . Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature 1984; 312: 237–242.
Hyman AA, Salser S, Drechsel DN, Unwin N, Mitchison TJ . Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule dynamics: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue, GMPCPP. Mol Biol Cell 1992; 3: 1155–1167.
Howard J, Hyman AA . Dynamics and mechanics of the microtubule plus end. Nature 2003; 422: 753–758.
Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO . Microtubule +TIPs at a glance. J Cell Sci 2010; 123 (Pt 20): 3415–3419.
Manning AL, Compton DA . Structural and regulatory roles of nonmotor spindle proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2008; 20: 101–106.
Yount AL, Zong H, Walczak CE . Regulatory mechanisms that control mitotic kinesins. Exp Cell Res 2015; 334: 70–77.
Goshima G, Scholey JM . Control of mitotic spindle length. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2010; 26: 21–57.
Brouhard GJ, Rice LM . The contribution of alphabeta-tubulin curvature to microtubule dynamics. J Cell Biol 2014; 207: 323–334.
Bakhoum SF, Compton DA . Chromosomal instability and cancer: a complex relationship with therapeutic potential. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 1138–1143.
Penela P, Nogues L, Mayor F Jr . Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2014; 27: 10–17.
Wacker SA, Alvarado C, von WG, Knippschild U, Wiedenmann J, Clauss K et al. RITA, a novel modulator of Notch signalling, acts via nuclear export of RBP-J. EMBO J 2011; 30: 43–56.
Tamura K, Taniguchi Y, Minoguchi S, Sakai T, Tun T, Furukawa T et al. Physical interaction between a novel domain of the receptor Notch and the transcription factor RBP-J kappa/Su(H). Curr Biol 1995; 5: 1416–1423.
Wang H, Chen G, Wang H, Liu C . RITA inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction of apoptosis. Oncol Res 2013; 20: 437–445.
Wang H, Yang Z, Liu C, Huang S, Wang H, Chen Y et al. RBP-J-interacting and tubulin-associated protein induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the p53-Fbxw7 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014; 454: 71–77.
Forbes SA, Beare D, Gunasekaran P, Leung K, Bindal N, Boutselakis H et al. COSMIC: exploring the world's knowledge of somatic mutations in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 2015; 43: D805–D811.
Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang X . Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods 2006; 3: 793–795.
Hoogendoorn E, Crosby KC, Leyton-Puig D, Breedijk RM, Jalink K, Gadella TW et al. The fidelity of stochastic single-molecule super-resolution reconstructions critically depends upon robust background estimation. Sci Rep 2014; 4: 3854.
Heilemann M, van de Linde S, Schuttpelz M, Kasper R, Seefeldt B, Mukherjee A et al. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2008; 47: 6172–6176.
Bates M, Huang B, Dempsey GT, Zhuang X . Multicolor super-resolution imaging with photo-switchable fluorescent probes. Science 2007; 317: 1749–1753.
Pakala SB, Nair VS, Reddy SD, Kumar R . Signaling-dependent phosphorylation of mitotic centromere-associated kinesin regulates microtubule depolymerization and its centrosomal localization. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 40560–40569.
Ritter A, Sanhaji M, Steinhauser K, Roth S, Louwen F, Yuan J . The activity regulation of the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin by Polo-like kinase 1. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 6641–6655.
Sanhaji M, Ritter A, Belsham HR, Friel CT, Roth S, Louwen F et al. Polo-like kinase 1 regulates the stability of the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin in mitosis. Oncotarget 2014; 5: 3130–3144.
Luders J, Patel UK, Stearns T . GCP-WD is a gamma-tubulin targeting factor required for centrosomal and chromatin-mediated microtubule nucleation. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 137–147.
Meunier S, Vernos I . K-fibre minus ends are stabilized by a RanGTP-dependent mechanism essential for functional spindle assembly. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 1406–1414.
Janke C, Bulinski JC . Post-translational regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton: mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011; 12: 773–786.
Akella JS, Wloga D, Kim J, Starostina NG, Lyons-Abbott S, Morrissette NS et al. MEC-17 is an alpha-tubulin acetyltransferase. Nature 2010; 467: 218–222.
Shida T, Cueva JG, Xu Z, Goodman MB, Nachury MV . The major alpha-tubulin K40 acetyltransferase alphaTAT1 promotes rapid ciliogenesis and efficient mechanosensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21517–21522.
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Nixon A et al. HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature 2002; 417: 455–458.
Matsuyama A, Shimazu T, Sumida Y, Saito A, Yoshimatsu Y, Seigneurin-Berny D et al. In vivo destabilization of dynamic microtubules by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J 2002; 21: 6820–6831.
North BJ, Marshall BL, Borra MT, Denu JM, Verdin E . The human Sir2 ortholog, SIRT2, is an NAD+-dependent tubulin deacetylase. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 437–444.
Gadde S, Heald R . Mechanisms and molecules of the mitotic spindle. Curr Biol 2004; 14: R797–R805.
L'Hernault SW, Rosenbaum JL . Chlamydomonas alpha-tubulin is posttranslationally modified by acetylation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysine. Biochemistry 1985; 24: 473–478.
Piperno G, LeDizet M, Chang XJ . Microtubules containing acetylated alpha-tubulin in mammalian cells in culture. J Cell Biol 1987; 104: 289–302.
Soppina V, Herbstman JF, Skiniotis G, Verhey KJ . Luminal localization of alpha-tubulin K40 acetylation by cryo-EM analysis of fab-labeled microtubules. PLoS One 2012; 7: e48204.
Maruta H, Greer K, Rosenbaum JL . The acetylation of alpha-tubulin and its relationship to the assembly and disassembly of microtubules. J Cell Biol 1986; 103: 571–579.
Cambray-Deakin MA, Burgoyne RD . Acetylated and detyrosinated alpha-tubulins are co-localized in stable microtubules in rat meningeal fibroblasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 1987; 8: 284–291.
Webster DR, Borisy GG . Microtubules are acetylated in domains that turn over slowly. J Cell Sci 1989; 92 (Pt 1): 57–65.
Song Y, Brady ST . Post-translational modifications of tubulin: pathways to functional diversity of microtubules. Trends Cell Biol 2015; 25: 125–136.
Giustiniani J, Daire V, Cantaloube I, Durand G, Pous C, Perdiz D et al. Tubulin acetylation favors Hsp90 recruitment to microtubules and stimulates the signaling function of the Hsp90 clients Akt/PKB and p53. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 529–539.
Wang B, Rao YH, Inoue M, Hao R, Lai CH, Chen D et al. Microtubule acetylation amplifies p38 kinase signalling and anti-inflammatory IL-10 production. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 3479.
Miyake Y, Keusch JJ, Wang L, Saito M, Hess D, Wang X et al. Structural insights into HDAC6 tubulin deacetylation and its selective inhibition. Nat Chem Biol 2016; 12: 748–754.
Kreis NN, Sanhaji M, Rieger MA, Louwen F, Yuan J . p21Waf1/Cip1 deficiency causes multiple mitotic defects in tumor cells. Oncogene 2014; 33: 5716–5728.
Vassilev LT, Tovar C, Chen S, Knezevic D, Zhao X, Sun H et al. Selective small-molecule inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 10660–10665.
Muschol-Steinmetz C, Friemel A, Kreis NN, Reinhard J, Yuan J, Louwen F . Function of survivin in trophoblastic cells of the placenta. PLoS One 2013; 8: e73337.
Sanhaji M, Friel CT, Kreis NN, Kramer A, Martin C, Howard J et al. Functional and spatial regulation of mitotic centromere-associated kinesin by cyclin-dependent kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 2594–2607.
Sanhaji M, Louwen F, Zimmer B, Kreis NN, Roth S, Yuan J . Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors, mitotic stress and the tumor suppressor p53. Cell Cycle 2013; 12: 1340–1351.
Sanhaji M, Kreis NN, Zimmer B, Berg T, Louwen F, Yuan J . p53 is not directly relevant to the response of Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 543–553.
Muschol-Steinmetz C, Jasmer B, Kreis NN, Steinhauser K, Ritter A, Rolle U et al. B-cell lymphoma 6 promotes proliferation and survival of trophoblastic cells. Cell Cycle 2016; 15: 827–839.
Nguyen HL, Gruber D, Bulinski JC . Microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4) regulates assembly, protomer-polymer partitioning and synthesis of tubulin in cultured cells. J Cell Sci 1999; 112 (Pt 12): 1813–1824.
Sharma N, Kosan ZA, Stallworth JE, Berbari NF, Yoder BK . Soluble levels of cytosolic tubulin regulate ciliary length control. Mol Biol Cell 2011; 22: 806–816.
Eckerdt F, Yuan J, Saxena K, Martin B, Kappel S, Lindenau C et al. Polo-like kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation stabilizes Pin1 by inhibiting its ubiquitination in human cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 36575–36583.
Kreis NN, Louwen F, Zimmer B, Yuan J . Loss of p21Cip1/CDKN1A renders cancer cells susceptible to Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 6611–6626.
Kreis NN, Sanhaji M, Kramer A, Sommer K, Rodel F, Strebhardt K et al. Restoration of the tumor suppressor p53 by downregulating cyclin B1 in human papillomavirus 16/18-infected cancer cells. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5591–5603.
Magiera MM, Janke C . Investigating tubulin posttranslational modifications with specific antibodies. Methods Cell Biol 2013; 115: 247–267.
Ritter A, Sanhaji M, Friemel A, Roth S, Rolle U, Louwen F et al. Functional analysis of phosphorylation of the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin by Aurora B kinase in human tumor cells. Cell Cycle 2015; 14: 3755–3767.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr L Wordeman, University of Washington, and Dr A Bird, MPI, Dortmund, Germany, for their critical manuscript reading and valuable comments. The work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB1074/A3 to FO), the BMBF (research nucleus SyStAR to FO). PK was supported by the International Graduate School in Molecular Medicine, Ulm, Germany (GSC270).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinhäuser, K., Klöble, P., Kreis, NN. et al. Deficiency of RITA results in multiple mitotic defects by affecting microtubule dynamics. Oncogene 36, 2146–2159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.372
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.372
This article is cited by
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of murine RBPJ by Hairless protein matches that of Su(H) protein in the model system Drosophila melanogaster
Hereditas (2021)
-
Restoration of primary cilia in obese adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting Aurora A or extracellular signal-regulated kinase
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2019)
-
Potential involvement of RITA in the activation of Aurora A at spindle poles during mitosis
Oncogene (2019)