Abstract
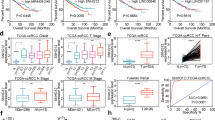
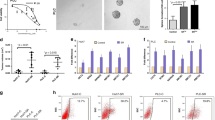
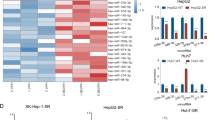
Although the use of sorafenib appears to increase the survival rate of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients, there is also a proportion of patients who exhibit a poor primary response to sorafenib therapy. It is therefore critical to elucidate the mechanisms underlying sorafenib resistance and find representative biomarkers for sorafenib treatment in RCC patients. Herein, we identified a long non-coding RNA referred to as lncRNA-SRLR (sorafenib resistance-associated lncRNA in RCC) that is upregulated in intrinsically sorafenib-resistant RCCs. lncRNA-SRLR knockdown sensitized nonresponsive RCC cells to sorafenib treatment, whereas the overexpression of lncRNA-SRLR conferred sorafenib resistance to responsive RCC cells. Mechanistically, lncRNA-SRLR directly binds to NF-κB and promotes IL-6 transcription, leading to the activation of STAT3 and the development of sorafenib tolerance. A STAT3 inhibitor and IL-6-receptor antagonist both restored the response to sorafenib treatment. Moreover, a clinical investigation demonstrated that high levels of lncRNA-SRLR correlated with poor responses to sorafenib therapy in RCC patients. Collectively, lncRNA-SRLR may serve as not only a predictive biomarker for inherent sorafenib resistance but also as a therapeutic target to enhance responses to sorafenib in RCC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- RCC:
-
renal cell carcinoma
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- KIT:
-
stem-cell growth factor receptor
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2
References
Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY, Jacqmin D, Lee JE, Weikert S et al. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 2011; 60: 615–621.
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM . Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 865–875.
Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S, Dabestani S, Hofmann F, Hora M et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol 2015; 67: 913–924.
Patil S, Manola J, Elson P, Negrier S, Escudier B, Eisen T et al. Improvement in overall survival of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: prognostic factor trend analysis from an international data set of clinical trials. J Urol 2012; 188: 2095–2100.
Abe H, Kamai T . Recent advances in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol 2013; 20: 944–955.
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 125–134.
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7099–7109.
Ye DW, Zhang HL . Critical appraisal of sorafenib in the treatment of Chinese patients with renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 2014; 7: 925–935.
Heng DY, Mackenzie MJ, Vaishampayan UN, Bjarnason GA, Knox JJ, Tan MH et al. Primary anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical characteristics, risk factors, and subsequent therapy. Ann Oncol 2012; 23: 1549–1555.
Powles T, Staehler M, Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield SE, Dabestani S et al. Updated EAU Guidelines for clear cell renal cancer patients who fail VEGF targeted therapy. Eur Urol 2016; 69: 4–6.
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS . Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 155–159.
Geisler S, Coller J . RNA in unexpected places: long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2013; 14: 699–712.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL . Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 1494–1504.
Pang KC, Frith MC, Mattick JS . Rapid evolution of noncoding RNAs: lack of conservation does not mean lack of function. Trends Genet 2006; 22: 1–5.
Martens-Uzunova ES, Bottcher R, Croce CM, Jenster G, Visakorpi T, Calin GA . Long noncoding RNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. Eur Urol 2014; 65: 1140–1151.
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Shahryari V, Deng G, Nakajima K, Tabatabai ZL et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes aggressive renal cell carcinoma through Ezh2 and interacts with miR-205. Cancer Res 2015; 75: 1322–1331.
Sotillo E, Thomas-Tikhonenko A . The long reach of noncoding RNAs. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 616–617.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM . The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 391–407.
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Yu B, Li YH, Jin Y, Bai XZ . LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and invasion-metastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 11652–11663.
Liu J, Wan L, Lu K, Sun M, Pan X, Zhang P et al. The long noncoding RNA MEG3 contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma. PloS One 2015; 10: e0114586.
Kong J, Kong F, Gao J, Zhang Q, Dong S, Gu F et al. YC-1 enhances the anti-tumor activity of sorafenib through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 7.
Liang Y, Zheng T, Song R, Wang J, Yin D, Wang L et al. Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1alpha inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 2013; 57: 1847–1857.
Banfai B, Jia H, Khatun J, Wood E, Risk B, Gundling WE Jr et al. Long noncoding RNAs are rarely translated in two human cell lines. Genome Res 2012; 22: 1646–1657.
Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Balbin OA, Dhanasekaran SM, Cao Q, Brenner JC et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol 2011; 29: 742–749.
Lin MF, Jungreis I, Kellis M . PhyloCSF: a comparative genomics method to distinguish protein coding and non-coding regions. Bioinformatics 2011; 27: i275–i282.
Chandarlapaty S . Negative feedback and adaptive resistance to the targeted therapy of cancer. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 311–319.
Guttman M, Donaghey J, Carey BW, Garber M, Grenier JK, Munson G et al. lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 2011; 477: 295–300.
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010; 329: 689–693.
Karin M, Greten FR . NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 749–759.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008; 132: 344–362.
Ozturk G, Ginis Z, Akyol S, Erden G, Gurel A, Akyol O . The anticancer mechanism of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE): review of melanomas, lung and prostate cancers. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2012; 16: 2064–2068.
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K . An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009; 139: 693–706.
Grivennikov S, Karin M . Autocrine IL-6 signaling: a key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 7–9.
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R . Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer 2014; 14: 736–746.
Kharaziha P, Rodriguez P, Li Q, Rundqvist H, Bjorklund AC, Augsten M et al. Targeting of distinct signaling cascades and cancer-associated fibroblasts define the efficacy of sorafenib against prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2012; 3: e262.
Liu B, Sun L, Liu Q, Gong C, Yao Y, Lv X et al. A cytoplasmic NF-kappaB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IkappaB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015; 27: 370–381.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 228–247.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Feng Liu and Qifei Tao for editing this manuscript. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272817, 81472691 and 81572521), the Leading Talent Project of Shanghai (2013046) and Youth Talent Sailing Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (16YF1403600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Yang, F., Wei, D. et al. Long noncoding RNA-SRLR elicits intrinsic sorafenib resistance via evoking IL-6/STAT3 axis in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 36, 1965–1977 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.356
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.356
This article is cited by
-
The regulatory relationship between transcription factor STAT3 and noncoding RNA
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2024)
-
circPTPN12 promotes the progression and sunitinib resistance of renal cancer via hnRNPM/IL-6/STAT3 pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
TOPK/PBK is phosphorylated by ERK2 at serine 32, promotes tumorigenesis and is involved in sorafenib resistance in RCC
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
PGK1 contributes to tumorigenesis and sorafenib resistance of renal clear cell carcinoma via activating CXCR4/ERK signaling pathway and accelerating glycolysis
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
LINC00958 promotes the proliferation of TSCC via miR-211-5p/CENPK axis and activating the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway
Cancer Cell International (2021)