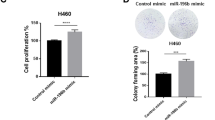
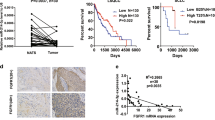
Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and thus new molecular targets need to be identified to improve treatment efficacy. Although epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/KRAS mutation-driven lung tumorigenesis is well understood, the mechanism of EGFR/KRAS-independent signal activation remains elusive. Enhanced TFAP2C (transcription factor activating enhancer-binding protein 2C) expression is associated with poor prognosis in some types of cancer patients, but little is known of its relation with the pathogenesis of lung cancer. In the present study, we found that TFAP2C overexpression was associated with cell cycle activation and NSCLC cell tumorigenesis. Interestingly, TFAP2C blocked AKAP12-mediated cyclin D1 inhibition by inducing the overexpression of oncogenic microRNA (miRNA)-183 and simultaneously activated cyclin-dependent kinase 6-mediated cell cycle progression by downregulating tumor-suppressive miRNA-33a. In a mouse xenograft model, TFAP2C promoted lung tumorigenesis and disease aggressiveness via the miR-183 and miR-33a pathways. The study provides a mechanism of mitogenic and oncogenic signaling via two functionally opposed miRNAs and suggests that TFAP2C-induced cell cycle hyperactivation contributes to lung tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Shai A, Dankort D, Juan J, Green S, McMahon M . TP53 silencing bypasses growth arrest of BRAFV600E-induced lung tumor cells in a two-switch model of lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2015; 75: 3167–3180.
Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Bepler G, Blum MG, Chang A, Cheney RT et al. Non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2010; 8: 740–801.
Janku F, Stewart DJ, Kurzrock R . Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer–is it becoming a reality? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2010; 7: 401–414.
Imielinski M, Greulich H, Kaplan B, Araujo L, Amann J, Horn L et al. Oncogenic and sorafenib-sensitive ARAF mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 1582–1586.
Hynes NE, Lane HA . ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 341–354.
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM . Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1367–1380.
Guin S, Theodorescu D . The RAS-RAL axis in cancer: evidence for mutation-specific selectivity in non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2015; 36: 291–297.
Mansi L, Viel E, Curtit E, Medioni J, Le Tourneau C . [Targeting the RAS signalling pathway in cancer]. Bull Cancer 2011; 98: 1019–1028.
Baines AT, Xu D, Der CJ . Inhibition of Ras for cancer treatment: the search continues. Future Med Chem 2011; 3: 1787–1808.
Eckert D, Buhl S, Weber S, Jager R, Schorle H . The AP-2 family of transcription factors. Genome Biol 2005; 6: 246.
Hilger-Eversheim K, Moser M, Schorle H, Buettner R . Regulatory roles of AP-2 transcription factors in vertebrate development, apoptosis and cell-cycle control. Gene 2000; 260: 1–12.
Aqeilan RI, Palamarchuk A, Weigel RJ, Herrero JJ, Pekarsky Y, Croce CM . Physical and functional interactions between the Wwox tumor suppressor protein and the AP-2gamma transcription factor. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 8256–8261.
Ailan H, Xiangwen X, Daolong R, Lu G, Xiaofeng D, Xi Q et al. Identification of target genes of transcription factor activator protein 2 gamma in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2009; 9: 279.
Woodfield GW, Chen Y, Bair TB, Domann FE, Weigel RJ . Identification of primary gene targets of TFAP2C in hormone responsive breast carcinoma cells. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2010; 49: 948–962.
Williamson JA, Bosher JM, Skinner A, Sheer D, Williams T, Hurst HC . Chromosomal mapping of the human and mouse homologues of two new members of the AP-2 family of transcription factors. Genomics 1996; 35: 262–264.
Cho WC . OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer 2007; 6: 60.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005; 120: 15–20.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008; 455: 64–71.
Croce CM . Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 704–714.
Lazar V, Suo C, Orear C, van den Oord J, Balogh Z, Guegan J et al. Integrated molecular portrait of non-small cell lung cancers. BMC Med Genomics 2013; 6: 53.
Calin GA, Croce CM . MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 857–866.
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, Shimada Y, Shiraishi K, Iwakawa R et al. Identification of genes upregulated in ALK-positive and EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 100–111.
Hou J, Aerts J, den Hamer B, van Ijcken W, den Bakker M, Riegman P et al. Gene expression-based classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas and survival prediction. PLoS One 2010; 5: e10312.
Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT, Wong N . Wnt/beta-Catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett 2015; 362: 97–105.
Zhang L, Quan H, Wang S, Li X, Che X . MiR-183 promotes growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells through FoxO1 inhibition. Tumour Biol 2015; 36: 8121–8126.
Zhou J, Xu D, Xie H, Tang J, Liu R, Li J et al. miR-33a functions as a tumor suppressor in melanoma by targeting HIF-1alpha. Cancer Biol Ther 2015; 16: 846–855.
Cirera-Salinas D, Pauta M, Allen RM, Salerno AG, Ramirez CM, Chamorro-Jorganes A et al. Mir-33 regulates cell proliferation and cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 922–933.
Yoon DK, Jeong CH, Jun HO, Chun KH, Cha JH, Seo JH et al. AKAP12 induces apoptotic cell death in human fibrosarcoma cells by regulating CDKI-cyclin D1 and caspase-3 activity. Cancer Lett 2007; 254: 111–118.
Landis MW, Pawlyk BS, Li T, Sicinski P, Hinds PW . Cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity in murine development and mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 13–22.
Grossel MJ, Hinds PW . From cell cycle to differentiation: an expanding role for cdk6. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 266–270.
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J, Stone A, Sutherland RL . Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 558–572.
Lin H, Huang JF, Qiu JR, Zhang HL, Tang XJ, Li H et al. Significantly upregulated TACSTD2 and Cyclin D1 correlate with poor prognosis of invasive ductal breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 2013; 94: 73–78.
Kim E, Youn H, Kwon T, Son B, Kang J, Yang HJ et al. PAK1 tyrosine phosphorylation is required to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 5520–5531.
Beer DG, Kardia SL, Huang CC, Giordano TJ, Levin AM, Misek DE et al. Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med 2002; 8: 816–824.
Yamagata N, Shyr Y, Yanagisawa K, Edgerton M, Dang TP, Gonzalez A et al. A training-testing approach to the molecular classification of resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 4695–4704.
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M et al. Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 13784–13789.
Bamforth SD, Braganca J, Eloranta JJ, Murdoch JN, Marques FI, Kranc KR et al. Cardiac malformations, adrenal agenesis, neural crest defects and exencephaly in mice lacking Cited2, a new Tfap2 co-activator. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 469–474.
Braganca J, Swingler T, Marques FI, Jones T, Eloranta JJ, Hurst HC et al. Human CREB-binding protein/p300-interacting transactivator with ED-rich tail (CITED) 4, a new member of the CITED family, functions as a co-activator for transcription factor AP-2. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 8559–8565.
Liu H, Tan BC, Tseng KH, Chuang CP, Yeh CW, Chen KD et al. Nucleophosmin acts as a novel AP2alpha-binding transcriptional corepressor during cell differentiation. EMBO Rep 2007; 8: 394–400.
Wong PP, Miranda F, Chan KV, Berlato C, Hurst HC, Scibetta AG . Histone demethylase KDM5B collaborates with TFAP2C and Myc to repress the cell cycle inhibitor p21(cip) (CDKN1A). Mol Cell Biol 2012; 32: 1633–1644.
Williams CM, Scibetta AG, Friedrich JK, Canosa M, Berlato C, Moss CH et al. AP-2gamma promotes proliferation in breast tumour cells by direct repression of the CDKN1A gene. EMBO J 2009; 28: 3591–3601.
Akakura S, Huang C, Nelson PJ, Foster B, Gelman IH . Loss of the SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 gene results in prostatic hyperplasia. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 5096–5103.
Gee JM, Eloranta JJ, Ibbitt JC, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Williams T et al. Overexpression of TFAP2C in invasive breast cancer correlates with a poorer response to anti-hormone therapy and reduced patient survival. J Pathol 2009; 217: 32–41.
Perkins SM, Bales C, Vladislav T, Althouse S, Miller KD, Sandusky G et al. TFAP2C expression in breast cancer: correlation with overall survival beyond 10 years of initial diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2015; 152: 519–531.
Cyr AR, Kulak MV, Park JM, Bogachek MV, Spanheimer PM, Woodfield GW et al. TFAP2C governs the luminal epithelial phenotype in mammary development and carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2015; 34: 436–444.
Bogachek MV, Chen Y, Kulak MV, Woodfield GW, Cyr AR, Park JM et al. Sumoylation pathway is required to maintain the basal breast cancer subtype. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 748–761.
Odegaard E, Staff AC, Kaern J, Florenes VA, Kopolovic J, Trope CG et al. The AP-2gamma transcription factor is upregulated in advanced-stage ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 2006; 100: 462–468.
Su B, Zheng Q, Vaughan MM, Bu Y, Gelman IH . SSeCKS metastasis-suppressing activity in MatLyLu prostate cancer cells correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 5599–5607.
Su B, Bu Y, Engelberg D, Gelman IH . SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 inhibits cancer cell invasiveness and chemotaxis by suppressing a protein kinase C- Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 4578–4586.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 786–792.
Huang MH, Lee JH, Chang YJ, Tsai HH, Lin YL, Lin AM et al. MEK inhibitors reverse resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor mutation lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Mol Oncol 2013; 7: 112–120.
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, Jin YW, Kim J, Youn B . Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S3 and antiapoptotic TRAF2 protein mediates radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 2965–2975.
Kim W, Youn H, Seong KM, Yang HJ, Yun YJ, Kwon T et al. PIM1-activated PRAS40 regulates radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells through interplay with FOXO3a, 14-3-3 and protein phosphatases. Radiat Res 2011; 176: 539–552.
Kim W, Kim E, Yang HJ, Kwon T, Han S, Lee S et al. Inhibition of hedgehog signalling attenuates UVB-induced skin photoageing. Exp Dermatol 2015; 24: 611–617.
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, Yun YJ, Kim W, Kim YH et al. Psoralidin, a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX, regulates ionizing radiation (IR)-induced pulmonary inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 2011; 82: 524–534.
Kwon T, Youn H, Son B, Kim D, Seong KM, Park S et al. DANGER is involved in high glucose-induced radioresistance through inhibiting DAPK-mediated anoikis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 7193–7206.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2014R1A1A1A05002112 and 2013M2A2A7042502), the Ministry of Education (2013R1A1A2059832 to W Kim and 2014R1A1A2004061 to H Youn) and the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning through GCRC-SOP (2011-0030013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J., Kim, W., Lee, S. et al. TFAP2C promotes lung tumorigenesis and aggressiveness through miR-183- and miR-33a-mediated cell cycle regulation. Oncogene 36, 1585–1596 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.328
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.328
This article is cited by
-
Crucial role of the transcription factors family activator protein 2 in cancer: current clue and views
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
MALAT1-regulated gene expression profiling in lung cancer cell lines
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Single-cell multi-omics analysis of human testicular germ cell tumor reveals its molecular features and microenvironment
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Transcription factor AP2 enhances malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer through upregulation of USP22 gene expression
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
APE1 controls DICER1 expression in NSCLC through miR-33a and miR-130b
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)