Abstract
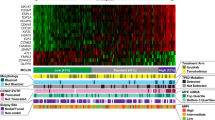
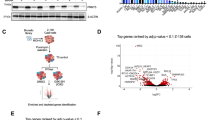
Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) by ibrutinib is an effective treatment for patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). However, both primary and acquired resistance to ibrutinib have developed in a significant number of these patients. A combinatory strategy targeting multiple oncogenic pathways is critical to enhance the efficacy of ibrutinib. Here, we focus on the BCL2 anti-apoptotic pathway. In a tissue microarray of 62 MCL samples, BCL2 expression positively correlated with BTK expression. Increased levels of BCL2 were shown to be due to a defect in protein degradation because of no or little expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXO10, as well as transcriptional upregulation through BTK-mediated canonical nuclear factor-κB activation. RNA-seq analysis confirmed that a set of anti-apoptotic genes (for example, BCL2, BCL-XL and DAD1) was downregulated by BTK short hairpin RNA. The downregulated genes also included those that are critical for B-cell growth and proliferation, such as BCL6, MYC, PIK3CA and BAFF-R. Targeting BCL2 by the specific inhibitor ABT-199 synergized with ibrutinib in inhibiting growth of both ibrutinib-sensitive and -resistant cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest co-targeting of BTK and BCL2 as a new therapeutic strategy in MCL, especially for patients with primary resistance to ibrutinib.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E . Molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 3416–3423.
Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, Goy A, Auer R, Kahl BS et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 507–516.
Chiorazzi N, Hatzi K, Albesiano E . B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, a clonal disease of B lymphocytes with receptors that vary in specificity for (auto)antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005; 1062: 1–12.
Kuppers R . Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 251–262.
Kenkre VP, Kahl BS . The future of B-cell lymphoma therapy: the B-cell receptor and its downstream pathways. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2012; 7: 216–220.
Young RM, Staudt LM . Targeting pathological B cell receptor signalling in lymphoid malignancies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2013; 12: 229–243.
Hadzidimitriou A, Agathangelidis A, Darzentas N, Murray F, Delfau-Larue MH, Pedersen LB et al. Is there a role for antigen selection in mantle cell lymphoma? Immunogenetic support from a series of 807 cases. Blood 2011; 118: 3088–3095.
Rinaldi A, Kwee I, Taborelli M, Largo C, Uccella S, Martin V et al. Genomic and expression profiling identifies the B-cell associated tyrosine kinase Syk as a possible therapeutic target in mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2006; 132: 303–316.
Cinar M, Hamedani F, Mo Z, Cinar B, Amin HM, Alkan S . Bruton tyrosine kinase is commonly overexpressed in mantle cell lymphoma and its attenuation by Ibrutinib induces apoptosis. Leuk Res 2013; 37: 1271–1277.
Rahal R, Frick M, Romero R, Korn JM, Kridel R, Chan FC et al. Pharmacological and genomic profiling identifies NF-kappaB-targeted treatment strategies for mantle cell lymphoma. Nat Med 2014; 20: 87–92.
Chiron D, Di Liberto M, Martin P, Huang X, Sharman J, Blecua P et al. Cell-cycle reprogramming for PI3K inhibition overrides a relapse-specific C481S BTK mutation revealed by longitudinal functional genomics in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov 2014; 4: 1022–1035.
Ma J, Lu P, Guo A, Cheng S, Zong H, Martin P et al. Characterization of ibrutinib-sensitive and -resistant mantle lymphoma cells. Br J Haematol 2014; 166: 849–861.
O'Brien S, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Sharman JP, Burger JA, Blum KA et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b/2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 48–58.
Hendriks RW, Yuvaraj S, Kil LP . Targeting Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2014; 14: 219–232.
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010; 463: 88–92.
Lee MH, Mabb AM, Gill GB, Yeh ET, Miyamoto S . NF-kappaB induction of the SUMO protease SENP2: a negative feedback loop to attenuate cell survival response to genotoxic stress. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 180–191.
Eferl R, Wagner EF . AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 859–868.
Lam LT, Wright G, Davis RE, Lenz G, Farinha P, Dang L et al. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008; 111: 3701–3713.
Hailfinger S, Lenz G, Ngo V, Posvitz-Fejfar A, Rebeaud F, Guzzardi M et al. Essential role of MALT1 protease activity in activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 19946–19951.
Staudt LM . Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a000109.
Bea S, Valdes-Mas R, Navarro A, Salaverria I, Martin-Garcia D, Jares P et al. Landscape of somatic mutations and clonal evolution in mantle cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 18250–18255.
Zhang J, Jima D, Moffitt AB, Liu Q, Czader M, Hsi ED et al. The genomic landscape of mantle cell lymphoma is related to the epigenetically determined chromatin state of normal B cells. Blood 2014; 123: 2988–2996.
Sun SC . Non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Res 2011; 21: 71–85.
Briones J, Timmerman JM, Hilbert DM, Levy R . BLyS and BLyS receptor expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 135–141.
Novak AJ, Grote DM, Stenson M, Ziesmer SC, Witzig TE, Habermann TM et al. Expression of BLyS and its receptors in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: correlation with disease activity and patient outcome. Blood 2004; 104: 2247–2253.
Abe M, Kido S, Hiasa M, Nakano A, Oda A, Amou H et al. BAFF and APRIL as osteoclast-derived survival factors for myeloma cells: a rationale for TACI-Fc treatment in patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1313–1315.
Wada K, Maeda K, Tajima K, Kato T, Kobata T, Yamakawa M . Expression of BAFF-R and TACI in reactive lymphoid tissues and B-cell lymphomas. Histopathology 2009; 54: 221–232.
Takahata H, Ohara N, Ichimura K, Tanaka T, Sato Y, Morito T et al. BAFF-R is expressed on B-cell lymphomas depending on their origin, and is related to proliferation index of nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J Clin Exp Hematop 2010; 50: 121–127.
Paterson JC, Tedoldi S, Craxton A, Jones M, Hansmann ML, Collins G et al. The differential expression of LCK and BAFF-receptor and their role in apoptosis in human lymphomas. Haematologica 2006; 91: 772–780.
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM . Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 2011; 30: 3667–3683.
Tracey L, Perez-Rosado A, Artiga MJ, Camacho FI, Rodriguez A, Martinez N et al. Expression of the NF-kappaB targets BCL2 and BIRC5/survivin characterizes small B-cell and aggressive B-cell lymphomas, respectively. J Pathol 2005; 206: 123–134.
Perkins ND . The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 121–132.
Bakhshi A, Jensen JP, Goldman P, Wright JJ, McBride OW, Epstein AL et al. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell 1985; 41: 899–906.
de Leeuw RJ, Davies JJ, Rosenwald A, Bebb G, Gascoyne RD, Dyer MJ et al. Comprehensive whole genome array CGH profiling of mantle cell lymphoma model genomes. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 1827–1837.
Schuetz JM, Johnson NA, Morin RD, Scott DW, Tan K, Ben-Nierah S et al. BCL2 mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1383–1390.
Chiorazzi M, Rui L, Yang Y, Ceribelli M, Tishbi N, Maurer CW et al. Related F-box proteins control cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans and human lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 3943–3948.
Oberley MJ, Rajguru SA, Zhang C, Kim K, Shaw GR, Grindle KM et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of MYC expression in mantle cell lymphoma. Histopathology 2013; 63: 499–508.
Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER, Ackler SL, Catron ND, Chen J et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med 2013; 19: 202–208.
Chiron D, Dousset C, Brosseau C, Touzeau C, Maiga S, Moreau P et al. Biological rational for sequential targeting of Bruton tyrosine kinase and Bcl-2 to overcome CD40-induced ABT-199 resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 8750–8759.
Zhao X, Bodo J, Sun D, Durkin L, Lin J, Smith MR et al. Combination of ibrutinib with ABT-199: synergistic effects on proliferation inhibition and apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma cells through perturbation of BTK, AKT and BCL2 pathways. Br J Haematol 2015; 168: 765–768.
Yang Y, Shaffer AL 3rd, Emre NC, Ceribelli M, Zhang M, Wright G et al. Exploiting synthetic lethality for the therapy of ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 723–737.
Mathews Griner LA, Guha R, Shinn P, Young RM, Keller JM, Liu D et al. High-throughput combinatorial screening identifies drugs that cooperate with ibrutinib to kill activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 2349–2354.
Ponader S, Chen SS, Buggy JJ, Balakrishnan K, Gandhi V, Wierda WG et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2012; 119: 1182–1189.
Herman SE, Sun X, McAuley EM, Hsieh MM, Pittaluga S, Raffeld M et al. Modeling tumor-host interactions of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in xenografted mice to study tumor biology and evaluate targeted therapy. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2311–2321.
Shinners NP, Carlesso G, Castro I, Hoek KL, Corn RA, Woodland RT et al. Bruton's tyrosine kinase mediates NF-kappa B activation and B cell survival by B cell-activating factor receptor of the TNF-R family. J Immunol 2007; 179: 3872–3880.
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012; 7: 562–578.
Tsujimoto Y, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM . Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science 1985; 228: 1440–1443.
Iqbal J, Neppalli VT, Wright G, Dave BJ, Horsman DE, Rosenwald A et al. BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 961–968.
Knezevich S, Ludkovski O, Salski C, Lestou V, Chhanabhai M, Lam W et al. Concurrent translocation of BCL2 and MYC with a single immunoglobulin locus in high-grade B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2005; 19: 659–663.
Nagy B, Lundan T, Larramendy ML, Aalto Y, Zhu Y, Niini T et al. Abnormal expression of apoptosis-related genes in haematological malignancies: overexpression of MYC is poor prognostic sign in mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 434–441.
Rawlings DJ, Saffran DC, Tsukada S, Largaespada DA, Grimaldi JC, Cohen L et al. Mutation of unique region of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science 1993; 261: 358–361.
Tucker CA, Kapanen AI, Chikh G, Hoffman BG, Kyle AH, Wilson IM et al. Silencing Bcl-2 in models of mantle cell lymphoma is associated with decreases in cyclin D1, nuclear factor-kappaB, p53, bax, and p27 levels. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 749–758.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
Freedman A . Follicular lymphoma: 2014 update on diagnosis and management. Am J Hematol 2014; 89: 429–436.
Hiddemann W, Cheson BD . How we manage follicular lymphoma. Leukemia 2014; 28: 1388–1395.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Louis Staudt for providing the reagents, Dr Sameer Mathur for providing peripheral blood mononuclear cells, Dr Wei Huang for helping with analysis of immunohistochemical data, Drs Debra Bloom and Peiman Hematti for providing CD40, BAFF and BAFF receptor antibody, and Kirsti Walker for monitoring xenografted mice. This work was supported by the UW-Madison Start-up funds, KL2 Scholar Award (UL1TR0000427 and KL2TR000428), and NIH R01 CA187299 to LR, the MACC fund and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute (K08 CA174750) to CMC, the UW-Madison Start-up funds and USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture (Hatch 1002874) to XZ, and the UW Forward Lymphoma Fund. We thank the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center (UWCCC) for the funds to complete this project. This work was also supported in part by NIH/NCI P30 CA014520- UW Comprehensive Cancer Center Support.
Accession Codes
All sequencing data were deposited into GEO with the accession number GSE80563.
Author contributions
LR designed research; LR, CMC, DTY, SM and BSK conceived and supervised the project; YL, MNB, LR, JW, KMG, LL, SQ, NP and SM. W-D performed research. LL, XZ and JCE analyzed data; CJT contributed reagents and intellectual input; LR, YL and MNB wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Bouchlaka, M., Wolff, J. et al. FBXO10 deficiency and BTK activation upregulate BCL2 expression in mantle cell lymphoma. Oncogene 35, 6223–6234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.155
This article is cited by
-
Beyond Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in mantle cell lymphoma: bispecific antibodies, antibody–drug conjugates, CAR T-cells, and novel agents
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Combining BTK inhibitors with BCL2 inhibitors for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma
Biomarker Research (2022)
-
Clinical experiences with venetoclax and other pro-apoptotic agents in lymphoid malignancies: lessons from monotherapy and chemotherapy combination
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Tipping the balance: toward rational combination therapies to overcome venetoclax resistance in mantle cell lymphoma
Leukemia (2022)
-
BH3-mimetics: recent developments in cancer therapy
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)