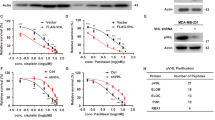
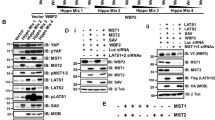
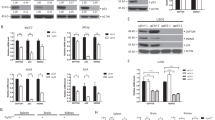
Abstract
Emerging evidence from The Cancer Genome Atlas has revealed that nuclear factor κB2 (nfκb2) gene encoding p100 is genetically deleted or mutated in human cancers, implicating NFκB2 as a potential tumor suppressor. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the antitumorigenic action of p100 remains poorly understood. Here we report that p100 inhibits cancer cell anchorage-independent growth, a hallmark of cellular malignancy, by stabilizing the tumor-suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) mRNA via a mechanism that is independent of p100’s inhibitory role in NFκB activation. We further demonstrate that the regulatory effect of p100 on PTEN expression is mediated by its downregulation of miR-494 as a result of the inactivation of extracellular signal–regulated kinase 2 (ERK2), in turn leading to inhibition of c-Jun/activator protein-1-dependent transcriptional activity. Furthermore, we identify that p100 specifically interacts with non-phosphorylated ERK2 and prevents ERK2 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Moreover, the death domain at C-terminal of p100 is identified as being crucial and sufficient for its interaction with ERK2. Taken together, our findings provide novel mechanistic insights into the understanding of the tumor-suppressive role for NFκB2 p100.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008; 132: 344–362.
Basak S, Kim H, Kearns JD, Tergaonkar V, O'Dea E, Werner SL et al. A fourth IkappaB protein within the NF-kappaB signaling module. Cell 2007; 128: 369–381.
Courtois G, Gilmore TD . Mutations in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: implications for human disease. Oncogene 2006; 25: 6831–6843.
Chen K, Coonrod EM, Kumanovics A, Franks ZF, Durtschi JD, Margraf RL et al. Germline mutations in NFKB2 implicate the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway in the pathogenesis of common variable immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 93: 812–824.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 2013; 6: pl1.
Busino L, Millman SE, Scotto L, Kyratsous CA, Basrur V, O'Connor O et al. Fbxw7alpha- and GSK3-mediated degradation of p100 is a pro-survival mechanism in multiple myeloma. Nat Cell Biol 2012; 14: 375–385.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP . The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 283–296.
Maehama T, Dixon JE . The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 13375–13378.
Shi Y, Paluch BE, Wang X, Jiang X . PTEN at a glance. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 4687–4692.
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, Birle D, Mercola D, Mustelin T et al. The Egr-1 transcription factor directly activates PTEN during irradiation-induced signalling. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 1124–1128.
Hettinger K, Vikhanskaya F, Poh MK, Lee MK, de Belle I, Zhang JT et al. c-Jun promotes cellular survival by suppression of PTEN. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 218–229.
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B, Haveman WJ, Pandolfi PP . A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 2010; 465: 1033–1038.
Vasudevan KM, Gurumurthy S, Rangnekar VM . Suppression of PTEN expression by NF-kappa B prevents apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 1007–1021.
Xia D, Srinivas H, Ahn YH, Sethi G, Sheng X, Yung WK et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-4 promotes cell survival by decreasing PTEN expression through an NF kappa B-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 3507–3519.
Arabi A, Ullah K, Branca RM, Johansson J, Bandarra D, Haneklaus M et al. Proteomic screen reveals Fbw7 as a modulator of the NF-kappaB pathway. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 976.
Fukushima H, Matsumoto A, Inuzuka H, Zhai B, Lau AW, Wan L et al. SCF(Fbw7) modulates the NFkB signaling pathway by targeting NFkB2 for ubiquitination and destruction. Cell Rep 2012; 1: 434–443.
Li J, Simpson L, Takahashi M, Miliaresis C, Myers MP, Tonks N et al. The PTEN/MMAC1 tumor suppressor induces cell death that is rescued by the AKT/protein kinase B oncogene. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5667–5672.
Wang Y, Cui H, Schroering A, Ding JL, Lane WS, McGill G et al. NF-kappa B2 p100 is a pro-apoptotic protein with anti-oncogenic function. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 888–893.
Wang Z, Zhang B, Yang L, Ding J, Ding HF . Constitutive production of NF-kappaB2 p52 is not tumorigenic but predisposes mice to inflammatory autoimmune disease by repressing Bim expression. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 10698–10706.
Fusco AJ, Savinova OV, Talwar R, Kearns JD, Hoffmann A, Ghosh G . Stabilization of RelB requires multidomain interactions with p100/p52. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 12324–12332.
Alimonti A, Carracedo A, Clohessy JG, Trotman LC, Nardella C, Egia A et al. Subtle variations in Pten dose determine cancer susceptibility. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 454–458.
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP . Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010; 466: 835–840.
Liu L, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Greenlee AR, Han Z . Overexpressed miR-494 down-regulates PTEN gene expression in cells transformed by anti-benzo(a)pyrene-trans-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide. Life Sci 2010; 86: 192–198.
Romano G, Acunzo M, Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Cascione L, Zanca C et al. MiR-494 is regulated by ERK1/2 and modulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer through BIM down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 16570–16575.
Li J, Chen H, Tang MS, Shi X, Amin S, Desai D et al. PI-3 K and Akt are mediators of AP-1 induction by 5-MCDE in mouse epidermal Cl41 cells. J Cell Biol 2004; 165: 77–86.
Li J, Tang MS, Liu B, Shi X, Huang C . A critical role of PI-3 K/Akt/JNKs pathway in benzo[a]pyrene diol-epoxide (B[a]PDE)-induced AP-1 transactivation in mouse epidermal Cl41 cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 3932–3944.
Yu HS, Lin TH, Tang CH . Involvement of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 up-regulation in bradykinin promotes cell motility in human prostate cancers. Int J Mol Sci 2013; 14: 13329–13345.
Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ . Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med (Berl) 1996; 74: 589–607.
Waterfield MR, Zhang M, Norman LP, Sun SC . NF-kappaB1/p105 regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated MAP kinase signaling by governing the stability and function of the Tpl2 kinase. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 685–694.
Owens DM, Keyse SM . Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3203–3213.
Arroyo JD, Hahn WC . Involvement of PP2A in viral and cellular transformation. Oncogene 2005; 24: 7746–7755.
Mace PD, Wallez Y, Egger MF, Dobaczewska MK, Robinson H, Pasquale EB et al. Structure of ERK2 bound to PEA-15 reveals a mechanism for rapid release of activated MAPK. Nat Commun 2013; 4: 1681.
Hill JM, Vaidyanathan H, Ramos JW, Ginsberg MH, Werner MH . Recognition of ERK MAP kinase by PEA-15 reveals a common docking site within the death domain and death effector domain. EMBO J 2002; 21: 6494–6504.
Dioletis E, Dingley AJ, Driscoll PC . Structural and functional characterization of the recombinant death domain from death-associated protein kinase. PLoS One 2013; 8: e70095.
Sun SC . The noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway. Immunol Rev 2012; 246: 125–140.
Caamano JH, Rizzo CA, Durham SK, Barton DS, Raventos-Suarez C, Snapper CM et al. Nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B2 (p100/p52) is required for normal splenic microarchitecture and B cell-mediated immune responses. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 185–196.
Ishikawa H, Carrasco D, Claudio E, Ryseck RP, Bravo R . Gastric hyperplasia and increased proliferative responses of lymphocytes in mice lacking the COOH-terminal ankyrin domain of NF-kappaB2. J Exp Med 1997; 186: 999–1014.
Fang JY, Richardson BC . The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2005; 6: 322–327.
Montagut C, Settleman J . Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 2009; 283: 125–134.
Yilmaz ZB, Kofahl B, Beaudette P, Baum K, Ipenberg I, Weih F et al. Quantitative dissection and modeling of the NF-kappaB p100-p105 module reveals interdependent precursor proteolysis. Cell Rep 2014; 9: 1756–1769.
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ, Greenberg ME . Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 1995; 270: 1326–1331.
Skeen JE, Bhaskar PT, Chen CC, Chen WS, Peng XD, Nogueira V et al. Akt deficiency impairs normal cell proliferation and suppresses oncogenesis in a p53-independent and mTORC1-dependent manner. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 269–280.
Kim WK, Park M, Kim YK, Tae YK, Yang HK, Lee JM et al. MicroRNA-494 downregulates KIT and inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell proliferation. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 7584–7594.
Wang X, Zhang X, Ren XP, Chen J, Liu H, Yang J et al. MicroRNA-494 targeting both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Circulation 2010; 122: 1308–1318.
Romagnoli M, Belguise K, Yu Z, Wang X, Landesman-Bollag E, Seldin DC et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-beta1 is mediated by Blimp-1-dependent repression of BMP-5. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 6268–6278.
Shaulian E . AP-1—the Jun proteins: oncogenes or tumor suppressors in disguise? Cell Signal 2010; 22: 894–899.
Zhang R, Wang Y, Li J, Jin H, Song S, Huang C . The Chinese herb isolate yuanhuacine (YHL-14) induces G2/M arrest in human cancer cells by up-regulating p21 protein expression through an p53 protein-independent cascade. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 6394–6403.
Song L, Li J, Ye J, Yu G, Ding J, Zhang D et al. p85alpha acts as a novel signal transducer for mediation of cellular apoptotic response to UV radiation. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 2713–2731.
Yu Y, Zhang D, Huang H, Li J, Zhang M, Wan Y et al. NF-kappaB1 p50 promotes p53 protein translation through miR-190 downregulation of PHLPP1. Oncogene 2014; 33: 996–1005.
Zhang D, Wang Y, Liang Y, Zhang M, Wei J, Zheng X et al. Loss of p27 upregulates MnSOD in a STAT3-dependent manner, disrupts intracellular redox activity and enhances cell migration. J Cell Sci 2014; 127: 2920–2933.
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate Dr Han-Fei Ding for his generous gifts about constructs expressing p100 and various deletion mutants of p100. We also appreciate Dr Shao-Cong Sun from the Department of Immunology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center for the gift of constructs expressing p100Ser866/870Ala or p100ΔDD. This work was supported partially by grants from NIH/NCI CA165980, CA177665 and CA112557, as well as NIH/NIEHS ES000260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Xu, J., Gao, G. et al. Tumor-suppressor NFκB2 p100 interacts with ERK2 and stabilizes PTEN mRNA via inhibition of miR-494. Oncogene 35, 4080–4090 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.470
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.470
This article is cited by
-
Tumorigenesis of basal muscle invasive bladder cancer was mediated by PTEN protein degradation resulting from SNHG1 upregulation
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2024)
-
Differential functions of RhoGDIβ in malignant transformation and progression of urothelial cell following N-butyl-N-(4-hydmoxybutyl) nitrosamine exposure
BMC Biology (2023)
-
Cooperative miRNA-dependent PTEN regulation drives resistance to BTK inhibition in B-cell lymphoid malignancies
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Macrophage-derived EDA-A2 inhibits intestinal stem cells by targeting miR-494/EDA2R/β-catenin signaling in mice
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Selenium-binding protein 1 transcriptionally activates p21 expression via p53-independent mechanism and its frequent reduction associates with poor prognosis in bladder cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2020)