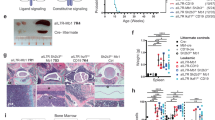
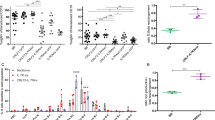
Abstract
ZFP521 was previously identified as a putative gene involved in induction of B-cell lymphomagenesis. However, the contribution of ZFP521 to lymphomagenesis has not been confirmed. In this study, we sought to elucidate the role of ZFP521 in B-cell lymphomagenesis. To this end, we used a retroviral insertion method to show that ZFP521 was a target of mutagenesis in pre-B-lymphoblastic lymphoma cells. The pre-B-cell receptor (pre-BCR) signaling molecules BLNK, BTK and BANK1 were positively regulated by the ZFP521 gene, leading to enhancement of the pre-BCR signaling pathway. In addition, c-myc and c-jun were upregulated following activation of ZFP521. Stimulation of pre-BCR signaling using anti-Vpreb antibodies caused aberrant upregulation of c-myc and c-jun and of Ccnd3, which encodes cyclin D3, thereby inducing the growth of pre-B cells. Stimulation with Vpreb affected the growth of pre-B cells, and addition of interleukin (IL)-7 receptor exerted competitive effects on pre-B-cell growth. Knockdown of BTK and BANK1, targets of ZFP521, suppressed the effects of Vpreb stimulation on cell growth. Furthermore, in human lymphoblastic lymphoma, analogous to pre-B-cell lymphoma in mice, the expression of ZNF521, the homolog of ZFP521 in humans, was upregulated. In conclusion, our data showed that the ZFP521 gene comprehensively induced pre-B-cell lymphomagenesis by modulating the pre-B-cell receptor signaling pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imai C, Ross ME, Reid G, Coustan-Smith E, Schultz KR, Pui CH et al. Expression of the adaptor protein BLNK/SLP-65 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 922–925.
Wollscheid B, Wienands J, Reth M . The adaptor protein SLP-65/BLNK controls the calcium response in activated B cells. CurrTopics Microbiol Immunol 1999; 246: 283–288.
Melchers F . The pre-B-cell receptor: selector of fitting immunoglobulin heavy chains for the B-cell repertoire. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 578–584.
Minegishi Y, Conley ME . Negative selection at the pre-BCR checkpoint elicited by human mu heavy chains with unusual CDR3 regions. Immunity 2001; 14: 631–641.
Stadhouders R, de Bruijn MJ, Rother MB, Yuvaraj S, Ribeiro de Almeida C, Kolovos P et al. Pre-B cell receptor signaling induces immunoglobulin kappa locus accessibility by functional redistribution of enhancer-mediated chromatin interactions. PLoS Biol 2014; 12: e1001791.
Flemming A, Brummer T, Reth M, Jumaa H . The adaptor protein SLP-65 acts as a tumor suppressor that limits pre-B cell expansion. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 38–43.
Akinleye A, Chen Y, Mukhi N, Song Y, Liu D . Ibrutinib and novel BTK inhibitors in clinical development. J Hematol Oncol 2013; 6: 59.
Murray MY, Zaitseva L, Auger MJ, Craig JI, MacEwan DJ, Rushworth SA et al. Ibrutinib inhibits BTK-driven NF-kappaB p65 activity to overcome bortezomib-resistance in multiple myeloma. Cell Cycle 2015: ;14: 2367–2375.
Rushworth SA, Bowles KM, Barrera LN, Murray MY, Zaitseva L, MacEwan DJ . BTK inhibitor ibrutinib is cytotoxic to myeloma and potently enhances bortezomib and lenalidomide activities through NF-kappaB. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 106–112.
Yasuda T, Tezuka T, Maeda A, Inazu T, Yamanashi Y, Gu H et al. Cbl-b positively regulates Btk-mediated activation of phospholipase C-gamma2 in B cells. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 51–63.
Bernal-Quiros M, Wu YY, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Castillejo-Lopez C . BANK1 and BLK act through phospholipase C gamma 2 in B-cell signaling. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e59842.
Warming S, Liu P, Suzuki T, Akagi K, Lindtner S, Pavlakis GN et al. Evi3, a common retroviral integration site in murine B-cell lymphoma, encodes an EBFAZ-related Kruppel-like zinc finger protein. Blood 2003; 101: 1934–1940.
Hiai H, Tsuruyama T, Yamada Y . Pre-B lymphomas in SL/Kh mice: a multifactorial disease model. Cancer Sci 2003; 94: 847–850.
Bond HM, Mesuraca M, Carbone E, Bonelli P, Agosti V, Amodio N et al. Early hematopoietic zinc finger protein (EHZF), the human homolog to mouse Evi3, is highly expressed in primitive human hematopoietic cells. Blood 2004; 103: 2062–2070.
Honda H, Yamasaki N, Miyazaki K, Nagamachi A, Koller R, Oda H et al. Identification of Zfp521/ZNF521 as a cooperative gene for E2A-HLF to develop acute B-lineage leukemia. Oncogene 2010; 29: 1963–1975.
Kiviranta R, Yamana K, Saito H, Ho DK, Laine J, Tarkkonen K et al. Coordinated transcriptional regulation of bone homeostasis by Ebf1 and Zfp521 in both mesenchymal and hematopoietic lineages. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 969–985.
Mega T, Lupia M, Amodio N, Horton SJ, Mesuraca M, Pelaggi D et al. Zinc finger protein 521 antagonizes early B-cell factor 1 and modulates the B-lymphoid differentiation of primary hematopoietic progenitors. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 2129–2139.
Hardy RR, Carmack CE, Shinton SA, Kemp JD, Hayakawa K . Resolution and characterization of pro-B and pre-pro-B cell stages in normal mouse bone marrow. J Exp Med 1991; 173: 1213–1225.
Bond HM, Mesuraca M, Amodio N, Mega T, Agosti V, Fanello D et al. Early hematopoietic zinc finger protein-zinc finger protein 521: a candidate regulator of diverse immature cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2008; 40: 848–854.
Sasai Y, Kamiya D, Banno S, Sasai N, Ohgushi M, Inomata H et al. Intrinsic transition of embryonic stem-cell differentiation into neural progenitors. Nature 2011; 470: 503–U592.
Malin S, McManus S, Cobaleda C, Novatchkova M, Delogu A, Bouillet P et al. Role of STAT5 in controlling cell survival and immunoglobulin gene recombination during pro-B cell development. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 171–179.
Hiratsuka T, Tsuruyama T, Kaszynski R, Kometani K, Minato N, Nakamura T et al. Bone marrow pre-B expansion by SL/Kh-Bomb1 locus: not sufficient for lymphomagenesis. Leuk Res 2008; 32: 309–314.
Tsuruyama T, Hiratsuka T, Jin G, Imai Y, Takeuchi H, Maruyama Y et al. Murine leukemia retrovirus integration induces the formation of transcription factor complexes on palindromic sequences in the signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 5a gene during the development of pre-B lymphomagenesis. Am J Pathol 2011; 178: 1374–1386.
Tsuruyama T, Imai Y, Takeuchi H, Hiratsuka T, Maruyama Y, Kanaya K et al. Dual retrovirus integration tagging: identification of new signaling molecules Fiz1 and Hipk2 that are involved in the IL-7 signaling pathway in B lymphoblastic lymphomas. J Leukoc Biol 2010; 88: 107–116.
Tsuruyama T, Nakamura T, Jin G, Ozeki M, Yamada Y, Hiai H . Constitutive activation of Stat5a by retrovirus integration in early pre-B lymphomas of SL/Kh strain mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 8253–8258.
Kaszynski RH, Akatsuka S, Hiratsuka T, Jin G, Ozeki M, Okuno T et al. A quantitative trait locus responsible for inducing B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma is a hotspot for microsatellite instability. Cancer Sci 2010; 101: 800–805.
Yokoyama K, Su Ih IH, Tezuka T, Yasuda T, Mikoshiba K, Tarakhovsky A et al. BANK regulates BCR-induced calcium mobilization by promoting tyrosine phosphorylation of IP(3) receptor. EMBO J 2002; 21: 83–92.
Mandal M, Powers SE, Ochiai K, Georgopoulos K, Kee BL, Singh H et al. Ras orchestrates exit from the cell cycle and light-chain recombination during early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 1110–U1191.
Li LX, Goetz CA, Katerndahl CD, Sakaguchi N, Farrar MA . A Flt3- and Ras-dependent pathway primes B cell development by inducing a state of IL-7 responsiveness. J Immunol 2010; 184: 1728–1736.
Hendriks RW, Middendorp S . The pre-BCR checkpoint as a cell-autonomous proliferation switch. Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 249–256.
Nakayama J, Yamamoto M, Hayashi K, Satoh H, Bundo K, Kubo M et al. BLNK suppresses pre-B-cell leukemogenesis through inhibition of JAK3. Blood 2009; 113: 1483–1492.
Imamura Y, Oda A, Katahira T, Bundo K, Pike KA, Ratcliffe MJ et al. BLNK binds active H-Ras to promote B cell receptor-mediated capping and ERK activation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 9804–9813.
Fernandez-Vega I, Quiros LM, Santos-Juanes J, Pane-Foix M, Marafioti T . Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) is a useful marker for Hodgkin and B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Virchows Arch 2015; 466: 229–235.
Muschen M . Rationale for targeting the pre-B cell receptor signaling pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2015; 125: 3688–3693.
Rickert RC . New insights into pre-BCR and BCR signalling with relevance to B cell malignancies. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 578–591.
Geier JK, Schlissel MS . Pre-BCR signals and the control of Ig gene rearrangements. Semin Immunol 2006; 18: 31–39.
Clark MR, Mandal M, Ochiai K, Singh H . Orchestrating B cell lymphopoiesis through interplay of IL-7 receptor and pre-B cell receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14: 69–80.
Corcoran AE, Riddell A, Krooshoop D, Venkitaraman AR . Impaired immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in mice lacking the IL-7 receptor. Nature 1998; 391: 904–907.
Wei CJ, Zeff R, Goldschneider I . Murine pro-B cells require IL-7 and its receptor complex to up-regulate IL-7 R alpha, terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase, and c-mu expression. J Immunol 2000; 164: 1961–1970.
Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, Miller CB, Coustan-Smith E, Dalton JD et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2007; 446: 758–764.
Davidson WF, Fredrickson TN, Rudikoff EK, Coffman RL, Hartley JW, Morse HC 3rd . A unique series of lymphomas related to the Ly-1+ lineage of B lymphocyte differentiation. J Immunol 1984; 133: 744–753.
Dai X, Chen Y, Di L, Podd A, Li G, Bunting KD et al. Stat5 is essential for early B cell development but not for B cell maturation and function. J Immunol 2007; 179: 1068–1079.
Nutt SL, Urbanek P, Rolink A, Busslinger M . Essential functions of Pax5 (BSAP) in pro-B cell development: difference between fetal and adult B lymphopoiesis and reduced V-to-DJ recombination at the IgH locus. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 476–491.
Lu LM, Shimada R, Higashi S, Zeng Z, Hiai H . Bone marrow pre-B-1 (Bomb1): a quantitative trait locus inducing bone marrow pre-B-cell expansion in lymphoma-prone SL/Kh mice. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2593–2595.
Addison WN, Fu MM, Yang HX, Lin Z, Nagano K, Gori F et al. Direct transcriptional repression of Zfp423 by Zfp521 mediates a bone morphogenic protein-dependent osteoblast versus adipocyte lineage commitment switch. Mol Cell Biol 2014; 34: 3076–3085.
Jin G, Tsuruyama T, Yamada Y, Hiai H . Svi3: A provirus common integration site in c-myc in SL/Kh pre-B lymphomas. Cancer Sci 2003; 94: 791–795.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas, MEXT, Japan. Project name is ‘Synergy of fluctuation and Structure’. Significance statement: ZFP521 regulates pre-B-cell receptor-related genes and enhances pre-B-cell growth through the pre-B-cell receptor.
Author contributions
YT, RO, YI, TH and TT performed experiments. KT and TN provided materials. TT, YT and RO wrote the manuscript.
Disclaimer
This funding agency had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with, or financial interest in, any commercial companies pertaining to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiratsuka, T., Takei, Y., Ohmori, R. et al. ZFP521 contributes to pre-B-cell lymphomagenesis through modulation of the pre-B-cell receptor signaling pathway. Oncogene 35, 3227–3238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.385
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.385
This article is cited by
-
Proteome analysis of CD5-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma FFPE tissue reveals downregulation of DDX3X, DNAJB1, and B cell receptor signaling pathway proteins including BTK and Immunoglobulins
Clinical Proteomics (2023)
-
ZNF521 Has an Inhibitory Effect on the Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2018)
-
Hotspots of MLV integration in the hematopoietic tumor genome
Oncogene (2017)