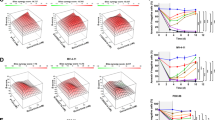
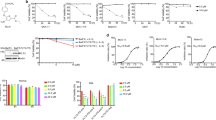
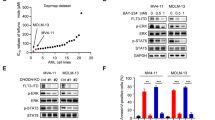
Abstract
FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) is an activating mutation found in 20–30% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which makes FLT3 an attractive target for the treatment of AML. Although FLT3-mutant patients respond to current FLT3 inhibitors, relapse usually happens because of the acquisition of resistant secondary mutations at the FLT3 catalytic domain, which is mainly on D835. In the search for compounds with broad FLT3 inhibition activities, we screened a kinase inhibitor library by using our unique FLT3 substrate and identified JAK3 inhibitor VI (designated JI6 hereafter) as a novel FLT3 inhibitor, which selectively targets FLT3 D835 mutants as well as FLT3-ITD. JI6 effectively inhibited FLT3-ITD-containing MV4-11 cells and HCD-57 cells transformed with FLT3-ITD and D835 mutants. Furthermore, administration of JI6 effectively targeted FLT3 signaling in vivo and suppressed the myeloproliferative phenotypes in FLT3-ITD knock-in mice, and significantly prolonged the survival of immunodeficient mice implanted with the transformed HCD-57 cells. Therefore, JI6 is a promising candidate for the development of next-generation anti-AML drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estey E, Döhner H . Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2006; 368: 1894–1907.
Estey E . Acute myeloid leukemia: 2014 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 2014; 89: 1063–1081.
Takahashi S . Current findings for recurring mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 2011; 4: 36.
Swords R, Freeman C, Giles F . Targeting the FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2176–2185.
Leung AY, Man CH, Kwong YL . FLT3 inhibition—a moving and evolving target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2012; 27: 260–268.
Annesley CE, Brown P . The biology and targeting of FLT3 in pediatric leukemia. Front Oncol 2014; 4: 263.
Stirewalt DL, Radich JP . The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 650–665.
Gregory TK, Wald D, Chen Y, Vermaat JM, Xiong Y, Tse W . Molecular prognostic markers for adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics. J Hematol Oncol 2009; 2: 23.
Schlenk RF, Kayser S, Bullinger L, Kobbe G, Casper J, Ringhoffer M et al. Differential impact of allelic ratio and insertion site in FLT3-ITD-positive AML with respect to allogeneic transplantation. Blood 2014; 124: 3441–3449.
Zarrinkar PP, Gunawardane RN, Cramer MD, Gardner MF, Brigham D, Belli B et al. AC220 is a uniquely potent and selective inhibitor of FLT3 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia(AML). Blood 2009; 114: 2984–2992.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Shi YX, McQueen T, Harris D, Ling X et al. Mutant FLT3: a direct target of sorafenib in acute myelogenous leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 184–198.
Hofmann M, Große-Hovest L, Nübling T, Pyż E, Bamberg ML, Aulwurm S et al. Generation, selection and preclinical characterization of an Fc-optimized FLT3 antibody for the treatment of myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1228–1237.
Weisberg E, Boulton C, Kelly LM, Manley P, Fabbro D, Meyer T et al. Inhibition of mutant FLT3 receptors in leukemia cells by the small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor PKC412. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 433–443.
Levis M . Quizartinib for the treatment of FLT3/ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Fut Oncol 2014; 10: 1571–1579.
Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ, Klimek V, Galinsky I, Estey E, Nimer SD et al. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia and an activating mutation in FLT3 respond to a small-molecule FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PKC412. Blood 2005; 105: 54–60.
Cools J, Mentens N, Furet P, Fabbro D, Clark JJ, Griffin JD et al. Prediction of resistance to small molecule FLT3 inhibitors: implications for molecularly targeted therapy of acute leukemia. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 6385–6389.
Williams AB, Nguyen B, Li L, Brown P, Levis M, Leahy D et al. Mutations of FLT3/ITD confer resistance to multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Leukemia 2013; 27: 48–55.
Smith CC, Wang Q, Chin CS, Salerno S, Damon LE, Levis MJ et al. Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target inhuman acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2012; 485: 260–263.
Chen Y, Guo Y, Han J, Ho WT, Li S, Fu X et al. Generation and characterization of a highly effective protein substrate for analysis of FLT3 activity. J Hematol Oncol 2012; 5: 39.
Guo Y, Chen Y, Xu X, Fu X, Zhao ZJ . SU11652 inhibits tyrosine kinase activity of FLT3 and growth of MV-4-11 cells. J Hematol Oncol 2012; 5: 72.
Hsu FY, Johnston PB, Burke KA, Zhao Y . The expression of CD30 in anaplastic large cell lymphoma is regulated by nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase-mediated JunB Level in a cell type-specific manner. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9002–9008.
Zhao W, Du Y, Ho WT, Fu X, Zhao ZJ . JAK2V617F and p53 mutations coexist in erythroleukemia and megakaryoblastic leukemic cell lines. Exp Hematol Oncol 2012; 1: 15.
Lee BH, Tothova Z, Levine RL, Anderson K, Buza-Vidas N, Cullen DE et al. FLT3 mutations confer enhanced proliferation and survival properties to multipotent progenitors in a murine model of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 367–380.
Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blastcrisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 117–125.
Burgess MR, Skaggs BJ, Shah NP, Lee FY, Sawyers CL . Comparative analysis of two clinically active BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors reveals the role of conformation-specific binding in resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 3395–3400.
Wodicka LM, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Hunt JP, Floyd M, Salerno S et al. Activation state-dependent binding of small molecule kinase inhibitors: structural insights from biochemistry. Chem Biol 2010; 17: 1241–1249.
Li Z, Wang X, Eksterowicz J, Gribble Jr MW, Alba GQ, Ayres M et al. Discovery of AMG 925, a FLT3 and CDK4 dual kinase inhibitor with preferential affinity for the activated state of FLT3. J Med Chem 2014; 57: 3430–3449.
Lee HK, Kim HW, Lee IY, Lee J, Lee J, Jung DS et al. G-749, a novel FLT3 kinase inhibitor, can overcome drug resistance for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2014; 123: 2209–2219.
Smith CC, Lasater EA, Lin KC, Wang Q, McCreery MQ, Stewart WK et al. Crenolanib is a selective type I pan-FLT3 inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 5319–5324.
Zimmerman EI, Turner DC, Buaboonnam J, Hu S, Orwick S, Roberts MS et al. Crenolanib is active against models of drug-resistant FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 3607–3615.
Ma HS, Nguyen B, Duffield AS, Li L, Galanis A, Williams AB et al. FLT3 kinase inhibitor TTT-3002 overcomes both activating and drug resistance mutations in FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 5206–5217.
Li C, Liu L, Liang L, Xia Z, Li Z, Wang X et al. AMG 925 is a dual FLT3/CDK4 inhibitor with the potential to overcome FLT3 inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 2015; 14: 375–383.
Adams C, Aldous DJ, Amendola S, Bamborough P, Bright C, Crowe S et al. Mapping the kinase domain of janus kinase 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2003; 13: 3105–3110.
Farkas T, Daugaard M, Jäättelä M . Identification of small molecule inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and autophagy. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 38904–38912.
Mackarehtschian K, Hardin JD, Moore KA, Boast S, Goff SP, Lemischka IR . Targeted disruption of the flk2/flt3 gene leads to deficiencies in primitive hematopoietic progenitors. Immunity 1995; 3: 147–161.
Bramson HN, Corona J, Davis ST, Dickerson SH, Edelstein M, Frye SV et al. Oxindole-based inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2): design, synthesis, enzymatic activities, and X-ray crystallographic analysis. J Med Chem 2001; 44: 4339–4358.
Wood ER, Kuyper L, Petrov KG, Hunter RN 3rd, Harris PA, Lackey K . Discovery and in vitro evaluation of potent TrkA kinase inhibitors: oxindole and aza-oxindoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 953–957.
Lockman JW, Reeder MD, Robinson R, Ormonde PA, Cimbora DM, Williams BL et al. Oxindole derivatives as inhibitors of TAK1 kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011; 21: 1724–1727.
Papaetis GS, Syrigos KN . Sunitinib: a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the era of molecular cancer therapies. BioDrugs 2009; 23: 377–389.
Wen D, Boissel JP, Showers M, Ruch BC, Bunn HF . Erythropoietin structure–function relationships. Identification of functionally important domains. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 22839–22846.
Zhao W, Zou K, Farasyn T, Ho WT, Zhao ZJ . Generation and characterization of a JAK2V617F-containing erythroleukemia cell line. PLoS One 2014; 9: e99017.
Li Z, Xu M, Xing S, Ho WT, Ishii T, Li Q et al. Erlotinib effectively inhibits JAK2V617F activity and polycythemia vera cell growth. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 3428–3432.
Li Z, Xing S, Wang S, Ho WT, Zhao ZJ . Characterization of a highly effective protein substrate for analysis of JAK2(V617F) Activity. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1624–1632.
Xu MJ, Sui X, Zhao R, Dai C, Krantz SB, Zhao ZJ . PTP-MEG2 is activated in polycythemia vera erythroid progenitor cells and is essential for growth and expansion of erythroid cells. Blood 2003; 102: 4354–4360.
Moreno-Miralles I, Pan L, Keates-Baleeiro J, Durst-Goodwin K, Yang C, Kim HG et al. The inv(16) cooperates with ARF haploinsufficiency to induce acute myeloid leukemia. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 40097–40103.
Xing S, Wanting TH, Zhao W, Ma J, Wang S, Xu X et al. Transgenic expression of JAK2V617F causes myeloproliferative disorders in mice. Blood 2008; 111: 5109–5117.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant HL079441 from the National Institutes of Health and a grant from Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Guo, Y., Zhao, W. et al. Identification of an orally available compound with potent and broad FLT3 inhibition activity. Oncogene 35, 2971–2978 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.362
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.362
This article is cited by
-
Leukemogenic SHP2 mutations lead to erythropoietin independency of HCD-57 cells: a novel model for preclinical research of SHP2-mutant JMML
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Indole-based FLT3 inhibitors and related scaffolds as potential therapeutic agents for acute myeloid leukemia
BMC Chemistry (2023)
-
miR-221/222 induce instability of p53 By downregulating deubiquitinase YOD1 in acute myeloid leukemia
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Efficacy of SCF drug conjugate targeting c-KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumor
BMC Medicine (2022)
-
Aberrantly expressed Wnt5a in nurse-like cells drives resistance to Venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Cell Death Discovery (2022)