Abstract
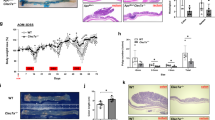
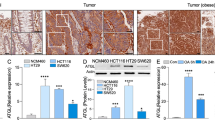
In both humans with long-standing ulcerative colitis and mouse models of colitis-associated carcinogenesis (CAC), tumors develop predominantly in the distal part of the large intestine but the biological basis of this intriguing pathology remains unknown. Herein we report intrinsic differences in gene expression between proximal and distal colon in the mouse, which are augmented during dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)/azoxymethane (AOM)-induced CAC. Functional enrichment of differentially expressed genes identified discrete biological pathways operating in proximal vs distal intestine and revealed a cluster of genes involved in lipid metabolism to be associated with the disease-resistant proximal colon. Guided by this finding, we have further interrogated the expression and function of one of these genes, apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), a major component of high-density lipoprotein. We show that ApoA-I is expressed at higher levels in the proximal compared with the distal part of the colon and its ablation in mice results in exaggerated DSS-induced colitis and disruption of epithelial architecture in larger areas of the large intestine. Conversely, treatment with an ApoA-I mimetic peptide ameliorated the phenotypic, histopathological and inflammatory manifestations of the disease. Genetic interference with ApoA-I levels in vivo impacted on the number, size and distribution of AOM/DSS-induced colon tumors. Mechanistically, ApoA-I was found to modulate signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor-κB activation in response to the bacterial product lipopolysaccharide with concomitant impairment in the production of the pathogenic cytokine interleukin-6. Collectively, these data demonstrate a novel protective role for ApoA-I in colitis and CAC and unravel an unprecedented link between lipid metabolic processes and intestinal pathologies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaden JA, Abrams KR, Mayberry JF . The risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Gut 2001; 48: 526–535.
Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, Wajda A . Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Cancer 2001; 91: 854–862.
Maloy KJ, Powrie F . Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2011; 474: 298–306.
Gkouskou KK, Deligianni C, Tsatsanis C, Eliopoulos AG . The gut microbiota in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014; 4: 28.
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R . A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 1990; 98: 694–702.
Laroui H, Ingersoll SA, Liu HC, Baker MT, Ayyadurai S, Charania MA et al. Dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induces colitis in mice by forming nano-lipocomplexes with medium-chain-length fatty acids in the colon. PloS one 2012; 7: e32084.
Bersudsky M, Luski L, Fishman D, White RM, Ziv-Sokolovskaya N, Dotan S et al. Non-redundant properties of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta during acute colon inflammation in mice. Gut 2014; 63: 598–609.
Mudter J, Neurath MF . Il-6 signaling in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiological role and clinical relevance. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007; 13: 1016–1023.
Yan Y, Kolachala V, Dalmasso G, Nguyen H, Laroui H, Sitaraman SV et al. Temporal and spatial analysis of clinical and molecular parameters in dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis. PloS One 2009; 4: e6073.
Okayasu I, Ohkusa T, Kajiura K, Kanno J, Sakamoto S . Promotion of colorectal neoplasia in experimental murine ulcerative colitis. Gut 1996; 39: 87–92.
Mahler M, Bristol IJ, Leiter EH, Workman AE, Birkenmeier EH, Elson CO et al. Differential susceptibility of inbred mouse strains to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Am J Physiol 1998; 274: G544–G551.
Choi PM . Predominance of rectosigmoid neoplasia in ulcerative colitis and its implication on cancer surveillance. Gastroenterology 1993; 104: 666–667.
Goldstone R, Itzkowitz S, Harpaz N, Ullman T . Dysplasia is more common in the distal than proximal colon in ulcerative colitis surveillance. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2012; 18: 832–837.
Goldstone R, Itzkowitz S, Harpaz N, Ullman T . Progression of low-grade dysplasia in ulcerative colitis: effect of colonic location. Gastrointest Endosc 2011; 74: 1087–1093.
Wu AL, Windmueller HG . Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem 1979; 254: 7316–7322.
Ramasamy I . Recent advances in physiological lipoprotein metabolism. Clin Chem Lab Med 2014; 52: 1695–1727.
Bollrath J, Greten FR . IKK/NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis. EMBO Rep 2009; 10: 1314–1319.
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 103–113.
Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA, Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T et al. gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 91–102.
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 2004; 21: 491–501.
Miller JC, Barth RK, Shaw PH, Elliott RW, Hastie ND . Identification of a cDNA clone for mouse apoprotein A-1 (apo A-1) and its use in characterization of apo A-1 mRNA expression in liver and small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1983; 80: 1511–1515.
Basque JR, Levy E, Beaulieu JF, Menard D . Apolipoproteins in human fetal colon: immunolocalization, biogenesis, and hormonal regulation. J Cell Biochem 1998; 70: 354–365.
Toft NJ, Winton DJ, Kelly J, Howard LA, Dekker M, te Riele H et al. Msh2 status modulates both apoptosis and mutation frequency in the murine small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 3911–3915.
Gupta J, del Barco Barrantes I, Igea A, Sakellariou S, Pateras IS, Gorgoulis VG et al. Dual function of p38alpha MAPK in colon cancer: suppression of colitis-associated tumor initiation but requirement for cancer cell survival. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 484–500.
Neufert C, Becker C, Neurath MF . An inducible mouse model of colon carcinogenesis for the analysis of sporadic and inflammation-driven tumor progression. Nat Protoc 2007; 2: 1998–2004.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST, Fogelman AM . Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides and their role in atherosclerosis prevention. Nat Clin Pract Card 2006; 3: 540–547.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Hama S, Garber DW, Chaddha M, Hough G et al. Oral administration of an Apo A-I mimetic peptide synthesized from D-amino acids dramatically reduces atherosclerosis in mice independent of plasma cholesterol. Circulation 2002; 105: 290–292.
Do RQ, Nicholls SJ, Schwartz GG . Evolving targets for lipid-modifying therapy. EMBO Mol Med 2014; 6: 1215–1230.
Ou J, Wang J, Xu H, Ou Z, Sorci-Thomas MG, Jones DW et al. Effects of D-4F on vasodilation and vessel wall thickness in hypercholesterolemic LDL receptor-null and LDL receptor/apolipoprotein A-I double-knockout mice on western diet. Circ Res 2005; 97: 1190–1197.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Fogelman AM . An apolipoprotein A-I mimetic works best in the presence of apolipoprotein A-I. Circ Res 2005; 97: 1085–1086.
Fukata M, Hernandez Y, Conduah D, Cohen J, Chen A, Breglio K et al. Innate immune signaling by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) shapes the inflammatory microenvironment in colitis-associated tumors. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009; 15: 997–1006.
Gribar SC, Anand RJ, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ . The role of epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 2008; 83: 493–498.
Ma J, Liao XL, Lou B, Wu MP . Role of apolipoprotein A-I in protecting against endotoxin toxicity. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2004; 36: 419–424.
Gupta H, Dai L, Datta G, Garber DW, Grenett H, Li Y et al. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by an apolipoprotein AI mimetic peptide. Circ Res 2005; 97: 236–243.
Cooper HS, Murthy S, Kido K, Yoshitake H, Flanigan A . Dysplasia and cancer in the dextran sulfate sodium mouse colitis model. Relevance to colitis-associated neoplasia in the human: a study of histopathology B-catenin and p53 expression and the role of inflammation. Carcinogenesis 2000; 21: 757–768.
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ . Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 1993; 69: 238–249.
Danese S, Mantovani A . Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: a paradigm of the Yin-Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 3313–3323.
Rubin DC, Shaker A, Levin MS . Chronic intestinal inflammation: inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer. Front Immunol 2012; 3: 107.
Li Y, de Haar C, Chen 1M, Deuring J, Gerrits MM, Smits R et al. Disease-related expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 signalling pathway in ulcerative colitis and ulcerative colitis-related carcinogenesis. Gut 2010; 59: 227–235.
Haghpassand M, Bourassa PA, Francone OL, Aiello RJ . Monocyte/macrophage expression of ABCA1 has minimal contribution to plasma HDL levels. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1315–1320.
Brunham LR, Kruit JK, Iqbal J, Fievet C, Timmins JM, Pape TD et al. Intestinal ABCA1 directly contributes to HDL biogenesis in vivo. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1052–1062.
Davidson NO, Glickman RM . Apolipoprotein A-I synthesis in rat small intestine: regulation by dietary triglyceride and biliary lipid. J Lipid Res 1985; 26: 368–379.
Rong R, Ramachandran S, Penumetcha M, Khan N, Parthasarathy S . Dietary oxidized fatty acids may enhance intestinal apolipoprotein A-I production. J Lipid Res 2002; 43: 557–564.
Haberman Y, Tickle TL, Dexheimer PJ, Kim MO, Tang D, Karns R et al. Pediatric Crohn disease patients exhibit specific ileal transcriptome and microbiome signature. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 3617–3633.
Greenhill CJ, Rose-John S, Lissilaa R, Ferlin W, Ernst M, Hertzog PJ et al. IL-6 trans-signaling modulates TLR4-dependent inflammatory responses via STAT3. J Immunol 2011; 186: 1199–1208.
Eyking A, Ey B, Runzi M, Roig AI, Reis H, Schmid KW et al. Toll-like receptor 4 variant D299G induces features of neoplastic progression in Caco-2 intestinal cells and is associated with advanced human colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2011; 141: 2154–2165.
Fukata M, Chen A, Vamadevan AS, Cohen J, Breglio K, Krishnareddy S et al. Toll-like receptor-4 promotes the development of colitis-associated colorectal tumors. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 1869–1881.
van Duijnhoven FJ, Bueno-De-Mesquita HB, Calligaro M, Jenab M, Pischon T, Jansen EH et al. Blood lipid and lipoprotein concentrations and colorectal cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Gut 2011; 60: 1094–1102.
Smythies LE, White CR, Maheshwari A, Palgunachari MN, Anantharamaiah GM, Chaddha M et al. Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic 4F alters the function of human monocyte-derived macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2010; 298: C1538–C1548.
Su F, Grijalva V, Navab K, Ganapathy E, Meriwether D, Imaizumi S et al. HDL mimetics inhibit tumor development in both induced and spontaneous mouse models of colon cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 1311–1319.
Bonn V, Cheung RC, Chen B, Taghibiglou C, Van Iderstine SC, Adeli K . Simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, induces the synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein AI in HepG2 cells and primary hamster hepatocytes. Atherosclerosis 2002; 163: 59–68.
Kanagarajan N, Nam JH, Noah ZA, Murthy S . Disease modifying effect of statins in dextran sulfate sodium model of mouse colitis. Inflamm Res 2008; 57: 34–38.
Poynter JN, Gruber SB, Higgins PD, Almog R, Bonner JD, Rennert HS et al. Statins and the risk of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2184–2192.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Hama S, Hough G, Reddy ST, Frank JS et al. D-4F and statins synergize to render HDL antiinflammatory in mice and monkeys and cause lesion regression in old apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 1426–1432.
Gkirtzimanaki K, Gkouskou KK, Oleksiewicz U, Nikolaidis G, Vyrla D, Liontos M et al. TPL2 kinase is a suppressor of lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E1470–E1479.
Su F, Kozak KR, Imaizumi S, Gao F, Amneus MW, Grijalva V et al. Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and apoA-I mimetic peptides inhibit tumor development in a mouse model of ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 19997–20002.
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, Bloemena E, Pena AS, Meuwissen SG et al. Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol 1998; 114: 385–391.
Williams KL, Fuller CR, Dieleman LA, DaCosta CM, Haldeman KM, Sartor RB et al. Enhanced survival and mucosal repair after dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in transgenic mice that overexpress growth hormone. Gastroenterology 2001; 120: 925–937.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dimitra Vyrla (University of Crete Medical School), Triantafyllos Liloglou (University of Liverpool) and Maria Denis (Biomedcode Hellas SA) for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the European Commission (EC) research program Inflammation and Cancer Research in Europe (INFLA-CARE; EC contract number 223151) to AGE and Almac Diagnostics and the EC REGPOT support program Translational Potential (TransPOT; EC contract number 285948) to AGE, KP, II and DK.
Author contributions
KKG and MI contributed equally to this work. KKG, MI, AS, KG, GN, DCK, DK and ED contributed to acquisition, analysis and interpretation of experimental data and critical reading of the manuscript; SM and FAM performed the gene expression profiling and contributed to in silico analysis of results; GAP and II contributed to bioinformatic analyses and critically reviewed the manuscript; KAP, DK and ED contributed to interpretation of experimental data and critically reviewed the manuscript; AGE contributed to conception, design, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gkouskou, K., Ioannou, M., Pavlopoulos, G. et al. Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesis. Oncogene 35, 2496–2505 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.307
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.307
This article is cited by
-
HDL, ApoA-I and ApoE-Mimetic Peptides: Potential Broad Spectrum Agent for Clinical Use?
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2022)
-
APOA1: a Protein with Multiple Therapeutic Functions
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2021)
-
AIBP and APOA-I synergistically inhibit intestinal tumor growth and metastasis by promoting cholesterol efflux
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
Caspase-11 regulates the tumour suppressor function of STAT1 in a murine model of colitis-associated carcinogenesis
Oncogene (2019)
-
Investigating the Proteomic Profile of HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells After Lactobacillus kefiri SGL 13 Exposure Using the SWATH Method
Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry (2019)