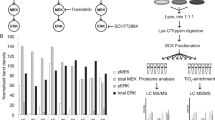
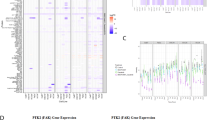
Abstract
The mechanisms by which some melanoma cells adapt to Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf (BRAF) inhibitor therapy are incompletely understood. In the present study, we used mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics to determine how BRAF inhibition remodeled the signaling network of melanoma cell lines that were BRAF mutant and PTEN null. Short-term BRAF inhibition was associated with marked changes in fibronectin-based adhesion signaling that were PTEN dependent. These effects were recapitulated through BRAF siRNA knockdown and following treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. Increased fibronectin expression was also observed in mouse xenograft models as well as specimens from melanoma patients undergoing BRAF inhibitor treatment. Analysis of a melanoma tissue microarray showed loss of PTEN expression to predict for a lower overall survival, with a trend for even lower survival being seen when loss of fibronectin was included in the analysis. Mechanistically, the induction of fibronectin limited the responses of these PTEN-null melanoma cell lines to vemurafenib, with enhanced cytotoxicity observed following the knockdown of either fibronectin or its receptor α5β1 integrin. This in turn abrogated the cytotoxic response to BRAF inhibition via increased AKT signaling, which prevented the induction of cell death by maintaining the expression of the pro-survival protein Mcl-1. The protection conveyed by the induction of FN expression could be overcome through combined treatment with a BRAF and PI3K inhibitor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2507–2516.
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012; 380: 358–365.
McArthur GA, Chapman PB, Robert C, Larkin J, Haanen JB, Dummer R et al. Safety and efficacy of vemurafenib in BRAF(V600E) and BRAF(V600K) mutation-positive melanoma (BRIM-3): extended follow-up of a phase 3, randomised, open-label study. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 323–332.
Long GV, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, Levchenko E, de Braud F, Larkin J et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition versus BRAF inhibition alone in melanoma. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 1877–1888.
Robert C, Karaszewska B, Schachter J, Rutkowski P, Mackiewicz A, Stroiakovski D et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 30–39.
Lito P, Pratilas CA, Joseph EW, Tadi M, Halilovic E, Zubrowski M et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 668–682.
Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya RC, Lee H et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010; 468: 973–977.
Straussman R, Morikawa T, Shee K, Barzily-Rokni M, Qian ZR, Du JY et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012; 487: 500–504.
Abel EV, Basile KJ, Kugel CH 3rd, Witkiewicz AK, Le K, Amaravadi RK et al. Melanoma adapts to RAF/MEK inhibitors through FOXD3-mediated upregulation of ERBB3. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 2155–2168.
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1 R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 683–695.
Sun C, Wang L, Huang S, Heynen GJ, Prahallad A, Robert C et al. Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition in melanoma. Nature 2014; 508: 118–122.
Girotti MR, Pedersen M, Sanchez-Laorden B, Viros A, Turajlic S, Niculescu-Duvaz D et al. Inhibiting EGF receptor or SRC family kinase signaling overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Cancer Discov 2013; 3: 158–167.
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M, Kong XJ, Ng C, Moriceau G et al. RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 2011; 480: 387–U144.
Van Allen EM, Wagle N, Sucker A, Treacy DJ, Johannessen CM, Goetz EM et al. The genetic landscape of clinical resistance to RAF inhibition in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Discov 2014; 4: 94–109.
Paraiso KH, Xiang Y, Rebecca VW, Abel EV, Chen YA, Munko AC et al. PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through the suppression of BIM expression. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 2750–2760.
Xing F, Persaud Y, Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Janakiraman M, She QB et al. Concurrent loss of the PTEN and RB1 tumor suppressors attenuates RAF dependence in melanomas harboring (V600E)BRAF. Oncogene 2011; 31: 446–457.
Nathanson KL, Martin AM, Wubbenhorst B, Greshock J, Letrero R, D'Andrea K et al. Tumor genetic analyses of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436). Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 4868–4878.
Sondergaard JN, Nazarian R, Wang Q, Guo D, Hsueh T, Mok S et al. Differential sensitivity of melanoma cell lines with BRAFV600E mutation to the specific Raf inhibitor PLX4032. J Transl Med 2010; 8: 39.
Gopal YN, Deng W, Woodman SE, Komurov K, Ram P, Smith PD et al. Basal and treatment-induced activation of AKT mediates resistance to cell death by AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in Braf-mutant human cutaneous melanoma cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 8736–8747.
Li J, Rix U, Fang B, Bai Y, Edwards A, Colinge J et al. A chemical and phosphoproteomic characterization of dasatinib action in lung cancer. Nat Chem Biol 2010; 6: 291–299.
Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ et al. Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 94–101.
Cox J, Mann M . MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 1367–1372.
Xiang Y, Remily-Wood ER, Oliveira V, Yarde D, He L, Cheng JQ et al. Monitoring a nuclear factor-kappaB signature of drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011; 10: M110.005520.
Fedorenko IV, Paraiso KH, Smalley KS . Acquired and intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E mutant melanoma. Biochem Pharmacol 2011; 82: 201–209.
Solit DB, Rosen N . Resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanomas. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 772–774.
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA . The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 1420–1428.
Old WM, Shabb JB, Houel S, Wang H, Couts KL, Yen CY et al. Functional proteomics identifies targets of phosphorylation by B-Raf signaling in melanoma. Mol Cell 2009; 34: 115–131.
Yu M, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Stott SL, Smas ME, Ting DT et al. Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science 2013; 339: 580–584.
Hsu MY, Meier FE, Nesbit M, Hsu JY, Van Belle P, Elder DE et al. E-cadherin expression in melanoma cells restores keratinocyte-mediated growth control and down-regulates expression of invasion-related adhesion receptors. Am J Pathol 2000; 156: 1515–1525.
Li G, Schaider H, Satyamoorthy K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Herlyn M . Downregulation of E-cadherin and desmoglein 1 by autocrine hepatocyte growth factor during melanoma development. Oncogene 2001; 20: 8125–8135.
Boyd SC, Mijatov B, Pupo GM, Tran SL, Gowrishankar K, Shaw HM et al. Oncogenic B-RAF(V600E) signaling induces the T-Box3 transcriptional repressor to repress E-cadherin and enhance melanoma cell invasion. J Invest Dermatol 2013; 133: 1269–1277.
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang JP, Zeng Q . PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals through PI3K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2922–2926.
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu LJ et al. The polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 3626–3636.
Mulholland DJ, Kobayashi N, Ruscetti M, Zhi A, Tran LM, Huang J et al. Pten loss and RAS/MAPK activation cooperate to promote EMT and metastasis initiated from prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 1878–1889.
Muro AF, Moretti FA, Moore BB, Yan M, Atrasz RG, Wilke CA et al. An essential role for fibronectin extra type III domain A in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 177: 638–645.
White ES, Atrasz RG, Hu B, Phan SH, Stambolic V, Mak TW et al. Negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006; 173: 112–121.
Meads MB, Gatenby RA, Dalton WS . Environment-mediated drug resistance: a major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 665–674.
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C et al. Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5: 662–668.
Sherman-Baust CA, Weeraratna AT, Rangel LBA, Pizer ES, Cho KR, Schwartz DR et al. Remodeling of the extracellular matrix through overexpression of collagen VI contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2003; 3: 377–386.
Muranen T, Selfors LM, Worster DT, Iwanicki MP, Song L, Morales FC et al. Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR leads to adaptive resistance in matrix-attached cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 227–239.
Wang JM, Chao JR, Chen W, Kuo ML, Yen JJ, Yang-Yen HF . The antiapoptotic gene mcl-1 is up-regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway through a transcription factor complex containing CREB. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6195–6206.
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P, Craig RW . MCL1 a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 3516–3520.
Boisvert-Adamo K, Aplin AE . B-RAF and PI-3 kinase signaling protect melanoma cells from anoikis. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4848–4856.
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW . MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 2004; 23: 5301–5315.
Huang Q, Li F, Liu X, Li W, Shi W, Liu FF et al. Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat Med 2011; 17: 860–866.
Quintana E, Shackleton M, Sabel MS, Fullen DR, Johnson TM, Morrison SJ . Efficient tumour formation by single human melanoma cells. Nature 2008; 456: 593–598.
Perkins DN, Pappin DJ, Creasy DM, Cottrell JS . Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999; 20: 3551–3567.
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang W, Bhagabati N et al. TM4: a free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques 2003; 34: 374–378.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Tanabe M . KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res 2012; 40: D109–D114.
Remily-Wood ER, Liu RZ, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Thomas CE, Rajyaguru N et al. A database of reaction monitoring mass spectrometry assays for elucidating therapeutic response in cancer. Proteomics Clin Appl 2011; 5: 383–396.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gideon Bollag (Plexxikon) for providing vemurafenib and the PLX4720 chow; Noel Clark, Ashley Troutman, Kelli Noyd, Jayme O’Neal and Holly Crandell for assistance with IHC staining; Marta Perez and Monica Torres for assistance with xenograft studies; Agnieszka Kasprazak and Joseph Johnson for assistance with microscopy; and Laura Hall for assistance with qRT–PCR. The work in the Smalley laboratory is supported by R01 CA161107 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedorenko, I., Abel, E., Koomen, J. et al. Fibronectin induction abrogates the BRAF inhibitor response of BRAF V600E/PTEN-null melanoma cells. Oncogene 35, 1225–1235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.188
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.188
This article is cited by
-
SOX10 deficiency-mediated LAMB3 upregulation determines the invasiveness of MAPKi-resistant melanoma
Oncogene (2024)
-
The mechanical phenotypic plasticity of melanoma cell: an emerging driver of therapy cross-resistance
Oncogenesis (2023)
-
Matrix stiffening and acquired resistance to chemotherapy: concepts and clinical significance
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
Computational models of melanoma
Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling (2020)
-
Sialidase NEU1 suppresses progression of human bladder cancer cells by inhibiting fibronectin-integrin α5β1 interaction and Akt signaling pathway
Cell Communication and Signaling (2020)