Abstract
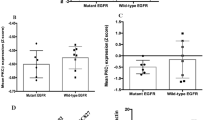
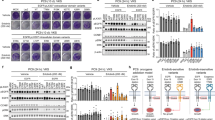
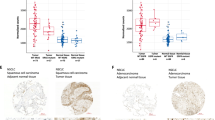
Recent efforts to comprehensively characterize the mutational landscape of non-small cell lung cancer have identified frequent mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinase ERBB4. However, the significance of mutated ERBB4 in non-small cell lung cancer remains elusive. Here, we have functionally characterized nine ERBB4 mutations previously identified in lung adenocarcinoma. Four out of the nine mutations, Y285C, D595V, D931Y and K935I, were found to be activating, increasing both basal and ligand-induced ErbB4 phosphorylation. According to structural analysis, the four activating mutations were located at critical positions at the dimerization interfaces of the ErbB4 extracellular (Y285C and D595V) and kinase (D931Y and K935I) domains. Consistently, the mutations enhanced ErbB4 dimerization and increased the trans activation in ErbB4 homodimers and ErbB4-ErbB2 heterodimers. The expression of the activating ERBB4 mutants promoted survival of NIH 3T3 cells in the absence of serum. Interestingly, serum starvation of NIH 3T3 cells expressing the ERBB4 mutants only moderately increased the phosphorylation of canonical ErbB signaling pathway effectors Erk1/2 and Akt as compared with wild-type ERBB4. In contrast, the mutations clearly enhanced the proteolytic release of signaling-competent ErbB4 intracellular domain. These results suggest the presence of activating driver mutations of ERBB4 in non-small cell lung cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center M, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Herbst RS, Heymach J V, Lippman SM . Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1367–1380.
Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria J-C, Rabe KF . Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: recent developments. Lancet 2013; 382: 709–719.
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER, McLellan MD, Cibulskis K et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008; 455: 1069–1075.
Imielinski M, Berger AH, Hammerman PS, Hernandez B, Pugh TJ, Hodis E et al. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell 2012; 150: 1107–1120.
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012; 489: 519–525.
The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cancergenome/projects/cosmic/.
Prickett TD, Agrawal NS, Wei X, Yates KE, Lin JC, Wunderlich JR et al. Analysis of the tyrosine kinome in melanoma reveals recurrent mutations in ERBB4. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1127–1132.
Hodis E, Watson IR, Kryukov G V, Arold ST, Imielinski M, Theurillat J-P et al. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell 2012; 150: 251–263.
Krauthammer M, Kong Y, Ha BH, Evans P, Bacchiocchi A, McCusker JP et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic RAC1 mutations in melanoma. Nat Genet 2012; 44: 1006–1014.
Kurppa K, Elenius K . Mutated ERBB4: a novel drug target in metastatic melanoma? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2009; 22: 708–710.
Settleman J . Therapeutic opportunity in melanoma: ErbB4 makes a mark on skin. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 278–279.
Tvorogov D, Sundvall M, Kurppa K, Hollmén M, Repo S, Johnson MS et al. Somatic mutations of ErbB4: selective loss-of-function phenotype affecting signal transduction pathways in cancer. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 5582–5591.
Pao W, Chmielecki J . Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 760–774.
Bouyain S, Longo P a, Li S, Ferguson KM, Leahy DJ . The extracellular region of ErbB4 adopts a tethered conformation in the absence of ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 15024–15029.
Liu P, Cleveland TE, Bouyain S, Byrne PO, Longo PA, Leahy DJ . A single ligand is sufficient to activate EGFR dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 10861–10866.
Graus-Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE . ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J 1997; 16: 1647–1655.
Tzahar E, Waterman H, Chen X, Levkowitz G, Karunagaran D, Lavi S et al. A hierarchical network of interreceptor interactions determines signal transduction by Neu differentiation factor/neuregulin and epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 5276–5287.
Alvarado D, Klein DE, Lemmon MA . Structural basis for negative cooperativity in growth factor binding to an EGF receptor. Cell 2010; 142: 568–579.
Toivanen PI, Nieminen T, Viitanen L, Alitalo A, Roschier M, Jauhiainen S et al. Novel vascular endothelial growth factor D variants with increased biological activity. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 16037–16048.
Qiu C, Tarrant MK, Choi SH, Sathyamurthy A, Bose R, Banjade S et al. Mechanism of activation and inhibition of the HER4/ErbB4 kinase. Structure 2008; 16: 460–467.
Zhang X, Gureasko J, Shen K, Cole PA, Kuriyan J . An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 2006; 125: 1137–1149.
Monsey J, Shen W, Schlesinger P, Bose R . Her4 and Her2/neu tyrosine kinase domains dimerize and activate in a reconstituted in vitro system. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 7035–7044.
Red Brewer M, Yun C, Lai D, Lemmon MA, Eck MJ, Pao W . Mechanism for activation of mutated epidermal growth factor receptors in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E3595–E3604.
Ni CY, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Carpenter G . Gamma-secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 2001; 294: 2179–2181.
Lee H-J, Jung K-M, Huang YZ, Bennett LB, Lee JS, Mei L et al. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 6318–6323.
Komuro A, Nagai M, Navin NE, Sudol M . WW domain-containing protein YAP associates with ErbB-4 and acts as a co-transcriptional activator for the carboxyl-terminal fragment of ErbB-4 that translocates to the nucleus. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 33334–33341.
Williams CC, Allison JG, Vidal GA, Burow ME, Beckman BS, Marrero L et al. The ERBB4/HER4 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates gene expression by functioning as a STAT5A nuclear chaperone. J Cell Biol 2004; 167: 469–478.
Määttä J, Sundvall M, Junttila T . Proteolytic cleavage and phosphorylation of a tumor-associated ErbB4 isoform promote ligand-independent survival and cancer cell growth. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 67–79.
Sardi SP, Murtie J, Koirala S, Patten BA, Corfas G . Presenilin-dependent ErbB4 nuclear signaling regulates the timing of astrogenesis in the developing brain. Cell 2006; 127: 185–197.
Sundvall M, Veikkolainen V, Kurppa K, Salah Z, Tvorogov D, van Zoelen EJ et al. Cell death or survival promoted by alternative isoforms of ErbB4. Mol Biol Cell 2010; 21: 4275–4286.
Jaiswal BS, Kljavin NM, Stawiski EW, Chan E, Parikh C, Durinck S et al. Oncogenic ERBB3 mutations in human cancers. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 603–617.
Greulich H, Kaplan B, Mertins P, Chen T-H, Tanaka K, Yun C-H et al. Functional analysis of receptor tyrosine kinase mutations in lung cancer identifies oncogenic extracellular domain mutations of ERBB2. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2012; 109: 14476–14481.
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004; 304: 1497–1500.
Sharma S V, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA . Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 169–181.
Hegde G V, de la Cruz CC, Chiu C, Alag N, Schaefer G, Crocker L et al. Blocking NRG1 and other ligand-mediated Her4 signaling enhances the magnitude and duration of the chemotherapeutic response of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 2013; 5: 171ra18.
Takahashi Y, Fukuda Y, Yoshimura J, Toyoda A, Kurppa K, Moritoyo H et al. ERBB4 mutations that disrupt the neuregulin-ErbB4 pathway cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 19. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 93: 900–905.
Aertgeerts K, Skene R, Yano J, Sang B-C, Zou H, Snell G et al. Structural analysis of the mechanism of inhibition and allosteric activation of the kinase domain of HER2 protein. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 18756–18765.
Lehtonen J V, Still D-J, Rantanen V-V, Ekholm J, Björklund D, Iftikhar Z et al. BODIL: a molecular modeling environment for structure-function analysis and drug design. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2004; 18: 401–419.
Junttila TT, Laato M, Vahlberg T, Söderström K-O, Visakorpi T, Isola J et al. Identification of patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder overexpressing ErbB2, ErbB3, or specific ErbB4 isoforms : real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis in estimation of ErbB receptor status from cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 5346–5357.
Junttila TT, Sundvall M, Lundin M, Lundin J, Tanner M, Härkönen P et al. Cleavable ErbB4 isoform in estrogen receptor-regulated growth of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1384–1393.
Acknowledgements
We thank Maria Tuominen, Minna Santanen and Mika Savisalo for excellent technical assistance. This work was financially supported by the Academy of Finland, Finnish Cancer Organizations, the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, the Turku University Central Hospital, the Åbo Akademi Center fo Excellence in Cell Stress and Aging and the Joe, Pentti and Tor Borg memorial fund. The use of computational infrastructures of Biocenter Finland (bioinformatics) and CSC IT Center for Science is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurppa, K., Denessiouk, K., Johnson, M. et al. Activating ERBB4 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 35, 1283–1291 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.185
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.185
This article is cited by
-
The role of ERBB4 mutations in the prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Novel RTK VUSs in Breast Cancer with an Emphasis on ROS1, ERBB4, ALK and NTRK3
Pathology & Oncology Research (2020)
-
The role of ErbB4 in cancer
Cellular Oncology (2020)
-
Integrative and comparative genomic analyses identify clinically relevant pulmonary carcinoid groups and unveil the supra-carcinoids
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma displays higher mutation rate and tumor heterogeneity than primary tumors
Nature Communications (2018)