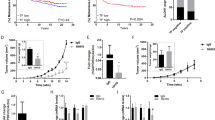
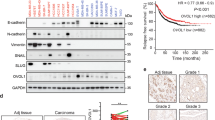
Abstract
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is an important regulator of breast cancer progression. However, how the breast cancer microenvironment regulates TGF-β signaling during breast cancer progression remains largely unknown. Here, we identified fibulin-3 as a secreted protein in the breast cancer microenvironment, which efficiently inhibits TGF-β signaling in both breast cancer cells and endothelial cells. Mechanistically, fibulin-3 interacts with the type I TGF-β receptor (TβRI) to block TGF-β induced complex formation of TβRI with the type II TGF-β receptor (TβRII) and subsequent downstream TGF-β signaling. Fibulin-3 expression decreases during breast cancer progression, with low fibulin-3 levels correlating with a poorer prognosis. Functionally, high fibulin-3 levels inhibited TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration, invasion and endothelial permeability, while loss of fibulin-3 expression/function promoted these TGF-β-mediated effects. Further, restoring fibulin-3 expression in breast cancer cells inhibited TGF-β signaling, breast cancer cell EMT, invasion and metastasis in vivo. These studies provide a novel mechanism for how TGF-β signaling is regulated by the tumor microenvironment, and provide insight into targeting the TGF-β signaling pathway in human breast cancer patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korkaya H, Liu S, Wicha MS . Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 3804–3809.
Culig Z . Cytokine disbalance in common human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1813: 308–314.
Hynes NE, Watson CJ . Mammary gland growth factors: roles in normal development and in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a003186.
Nicolini A, Carpi A, Rossi G . Cytokines in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2006; 17: 325–337.
Muraoka-Cook RS, Dumont N, Arteaga CL . Dual role of transforming growth factor beta in mammary tumorigenesis and metastatic progression. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 937s–943s.
Moses H, Barcellos-Hoff MH . TGF-beta biology in mammary development and breast cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3: a003277.
Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF . Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1350–1358.
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M et al. TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 1992; 71: 1003–1014.
Andres JL, DeFalcis D, Noda M, Massague J . Binding of two growth factor families to separate domains of the proteoglycan betaglycan. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 5927–5930.
Massague J . TGFbeta signaling: receptors, transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell 1996; 85: 947–950.
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P . TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997; 390: 465–471.
ten Dijke P, Miyazono K, Heldin CH . Signaling inputs converge on nuclear effectors in TGF-beta signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 2000; 25: 64–70.
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH . Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 1998; 95: 737–740.
Derynck R, Zhang YE . Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 2003; 425: 577–584.
Imamura T, Hikita A, Inoue Y . The roles of TGF-beta signaling in carcinogenesis and breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer 2012; 19: 118–124.
Zu X, Zhang Q, Cao R, Liu J, Zhong J, Wen G et al. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in tumor initiation, progression and therapy in breast cancer: an update. Cell Tissue Res 2012; 347: 73–84.
Drabsch Y, ten Dijke P . TGF-beta signaling in breast cancer cell invasion and bone metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2011; 16: 97–108.
Bierie B, Moses HL . Gain or loss of TGFbeta signaling in mammary carcinoma cells can promote metastasis. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 3319–3327.
Place AE, Jin Huh S, Polyak K . The microenvironment in breast cancer progression: biology and implications for treatment. Breast Cancer Res 2011; 13: 227.
Mao Y, Keller ET, Garfield DH, Shen K, Wang J . Stromal cells in tumor microenvironment and breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2013; 32: 303–315.
Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C, Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H et al. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 17–32.
Whiteside TL . The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5904–5912.
Buck MB, Knabbe C . TGF-beta signaling in breast cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci 2006; 1089: 119–126.
Gold LI . The role for transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in human cancer. Crit Rev Oncog 1999; 10: 303–360.
Chang CF, Westbrook R, Ma J, Cao D . Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in breast cancer. Front Biosci 2007; 12: 4393–4401.
Hanks BA, Holtzhausen A, Evans KS, Jamieson R, Gimpel P, Campbell OM et al. Type III TGF-beta receptor downregulation generates an immunotolerant tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 3925–3940.
Dong M, How T, Kirkbride KC, Gordon KJ, Lee JD, Hempel N et al. The type III TGF-beta receptor suppresses breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 206–217.
Lee JK, Park SR, Jung BK, Jeon YK, Lee YS, Kim MK et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e84256.
O'Brien K, Rani S, Corcoran C, Wallace R, Hughes L, Friel AM et al. Exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer cells can transfer phenotypic traits representing their cells of origin to secondary cells. Eur J Cancer 2013; 49: 1845–1859.
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Lee KW . Exosomes from breast cancer cells can convert adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblast-like cells. Int J Oncol 2012; 40: 130–138.
Gao H, Chakraborty G, Lee-Lim AP, Mo Q, Decker M, Vonica A et al. The BMP inhibitor Coco reactivates breast cancer cells at lung metastatic sites. Cell 2012; 150: 764–779.
Gallagher WM, Currid CA, Whelan LC . Fibulins and cancer: friend or foe? Trends Mol Med 2005; 11: 336–340.
Argraves WS, Greene LM, Cooley MA, Gallagher WM . Fibulins: physiological and disease perspectives. EMBO Rep 2003; 4: 1127–1131.
Kobayashi N, Kostka G, Garbe JH, Keene DR, Bachinger HP, Hanisch FG et al. A comparative analysis of the fibulin protein family. Biochemical characterization, binding interactions, and tissue localization. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 11805–11816.
Luo R, Zhang M, Liu L, Lu S, Zhang CZ, Yun J . Decrease of fibulin-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma indicates poor prognosis. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e70511.
Sadr-Nabavi A, Ramser J, Volkmann J, Naehrig J, Wiesmann F, Betz B et al. Decreased expression of angiogenesis antagonist EFEMP1 in sporadic breast cancer is caused by aberrant promoter methylation and points to an impact of EFEMP1 as molecular biomarker. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 1727–1735.
Tong JD, Jiao NL, Wang YX, Zhang YW, Han F . Downregulation of fibulin-3 gene by promoter methylation in colorectal cancer predicts adverse prognosis. Neoplasma 2011; 58: 441–448.
Kim YJ, Yoon HY, Kim SK, Kim YW, Kim EJ, Kim IY et al. EFEMP1 as a novel DNA methylation marker for prostate cancer: array-based DNA methylation and expression profiling. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 4523–4530.
Camaj P, Seeliger H, Ischenko I, Krebs S, Blum H, De Toni EN et al. EFEMP1 binds the EGF receptor and activates MAPK and Akt pathways in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Biol Chem 2009; 390: 1293–1302.
Hwang CF, Chien CY, Huang SC, Yin YF, Huang CC, Fang FM et al. Fibulin-3 is associated with tumour progression and a poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinomas and inhibits cell migration and invasion via suppressed AKT activity. J Pathol 2010; 222: 367–379.
Hu B, Nandhu MS, Sim H, Agudelo-Garcia PA, Saldivar JC, Dolan CE et al. Fibulin-3 promotes glioma growth and resistance through a novel paracrine regulation of Notch signaling. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 3873–3885.
Chen X, Meng J, Yue W, Yu J, Yang J, Yao Z et al. Fibulin-3 suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and lung cancer invasion. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 1707–1716.
Massague J . TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 753–791.
ten Dijke P, Miyazono K, Heldin CH . Signaling via hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996; 8: 139–145.
Tang B, Vu M, Booker T, Santner SJ, Miller FR, Anver MR et al. TGF-beta switches from tumor suppressor to prometastatic factor in a model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1116–1124.
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005; 436: 518–524.
Aslakson CJ, Miller FR . Selective events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the sequential diss.e.m.ination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 1399–1405.
Kim EJ, Lee SY, Woo MK, Choi SI, Kim TR, Kim MJ et al. Fibulin-3 promoter methylation alters the invasive behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines via MMP-7 and MMP-2 regulation. Int J Oncol 2012; 40: 402–408.
Wang Z, Yuan X, Jiao N, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Tong J . CDH13 and FLBN3 gene methylation are associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 2012; 18: 263–270.
Laib AM, Bartol A, Alajati A, Korff T, Weber H, Augustin HG . Spheroid-based human endothelial cell microvessel formation in vivo. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 1202–1215.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Komen for the Cure Grants KG111383 (HT) and SAC100002 (GCB), NIH/NCI Grants R01-135006 (GCB), and R01-136786 (GCB). We thank Yi-Hong Zhou at University of California Irvine for the fibulin-3 pcDNA3.1 overexpression plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Liu, J., Chen, J. et al. Fibulin-3 is a novel TGF-β pathway inhibitor in the breast cancer microenvironment. Oncogene 34, 5635–5647 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.13
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.13
This article is cited by
-
A simulacrum of proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR): development and proteomics-based validation of an in vitro model
Journal of Proteins and Proteomics (2024)
-
Fibulin-3 knockout mice demonstrate corneal dysfunction but maintain normal retinal integrity
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Overexpression of mircoRNA-137 inhibits cervical cancer cell invasion, migration and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by suppressing the TGF-β/smad pathway via binding to GREM1
Cancer Cell International (2019)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Fibulin-3 knockdown inhibits cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Fibulin-6 regulates pro-fibrotic TGF-β responses in neonatal mouse ventricular cardiac fibroblasts
Scientific Reports (2017)