Abstract
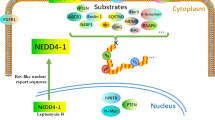
HER3/ErbB3, a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family, has a pivotal role in cancer and is emerging as a therapeutic antibody target. In this study, we identified NEDD4 (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 4) as a novel interaction partner and ubiquitin E3 ligase of human HER3. Using molecular and biochemical approaches, we demonstrated that the C-terminal tail of HER3 interacted with the WW domains of NEDD4 and the interaction was independent of neuregulin-1. Short hairpin RNA knockdown of NEDD4 elevated HER3 levels and resulted in increased HER3 signaling and cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. A similar inverse relationship between HER3 and NEDD4 levels was observed in prostate cancer tumor tissues. More importantly, the upregulated HER3 expression by NEDD4 knockdown sensitized cancer cells for growth inhibition by an anti-HER3 antibody. Taken together, our results suggest that low NEDD4 levels may predict activation of HER3 signaling and efficacies of anti-HER3 antibody therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hynes NE, Lane HA . ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 341–354.
Baselga J, Swain SM . Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 463–475.
Menendez JA, Lupu R . Transphosphorylation of kinase-dead HER3 and breast cancer progression: a new standpoint or an old concept revisited? Breast Cancer Res 2007; 9: 111.
Shi F, Telesco SE, Liu Y, Radhakrishnan R, Lemmon MA . ErbB3/HER3 intracellular domain is competent to bind ATP and catalyze autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 7692–7697.
Carraway KL, Cantley LC . A neu acquaintance for erbB3 and erbB4: a role for receptor heterodimerization in growth signaling. Cell 1994; 78: 5–8.
Vijapurkar U, Cheng K, Koland JG . Mutation of a Shc binding site tyrosine residue in ErbB3/HER3 blocks heregulin-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 20996–21002.
Prigent SA, Gullick WJ . Identification of c-erbB-3 binding sites for phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase and SHC using an EGF receptor/c-erbB-3 chimera. EMBO J 1994; 13: 2831–2841.
Soltoff SP, Carraway KL, Prigent SA, Gullick WG, Cantley LC . ErbB3 is involved in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 3550–3558.
Hellyer NJ, Cheng K, Koland JG . ErbB3 (HER3) interaction with the p85 regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Biochem J 1998; 333: 757–763.
Sithanandam G, Anderson LM . The ERBB3 receptor in cancer and cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2008; 15: 413–448.
Witton CJ, Reeves JR, Going JJ, Cooke TG, Bartlett JMS . Expression of the HER1-4 family of receptor tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. J Pathol 2003; 200: 290–297.
Holbro T, Beerli RR, Maurer F, Koziczak M, Barbas CF, Hynes NE . The ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimer functions as an oncogenic unit: ErbB2 requires ErbB3 to drive breast tumor cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8933–8938.
Holbro T, Civenni G, Hynes NE . The ErbB receptors and their role in cancer progression. Exp Cell Res 2003; 284: 99–110.
Jaiswal BS, Kljavin NM, Stawiski EW, Chan E, Parikh C, Durinck S et al. Oncogenic ERBB3 Mutations in Human Cancers. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 603–617.
Nahta R, Yu D, Hung M-C, Hortobagyi GN, Esteva FJ . Mechanisms of disease: understanding resistance to HER2-targeted therapy in human breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2006; 3: 269–280.
Baselga J . Treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2010; 21 (Suppl 7): vii36–vii40.
Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK, Perez EA, Puglisi F, Gianni L . Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2012; 9: 16–32.
Hsieh a C, Moasser MM . Targeting HER proteins in cancer therapy and the role of the non-target HER3. Br J Cancer 2007; 97: 453–457.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007; 316: 1039–1043.
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM et al. Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 2007; 445: 437–441.
Schoeberl B, Pace EA, Fitzgerald JB, Harms BD, Xu L, Nie L et al. Therapeutically targeting ErbB3: a key node in ligand-induced activation of the ErbB receptor-PI3K axis. Sci Signal 2009; 2: ra31.
Schoeberl B, Faber AC, Li D, Liang M-C, Crosby K, Onsum M et al. An ErbB3 antibody, MM-121, is active in cancers with ligand-dependent activation. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2485–2494.
Schaefer G, Haber L, Crocker LM, Shia S, Shao L, Dowbenko D et al. A Two-in-One Antibody against HER3 and EGFR Has Superior Inhibitory Activity Compared with Monospecific Antibodies. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 472–486.
Lipkowitz S . The role of the ubiquitination-proteasome pathway in breast cancer: ubiquitin mediated degradation of growth factor receptors in the pathogenesis and treatment of cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2003; 5: 8–15.
Hershko A, Ciechanover A . The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 425–479.
Ardley HC, Robinson PA . E3 ubiquitin ligases. Essays Biochem 2005; 41: 15–30.
Carraway KL . E3 ubiquitin ligases in ErbB receptor quantity control. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2010; 21: 936–943.
Thien CB, Langdon WY . Cbl: many adaptations to regulate protein tyrosine kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 294–307.
Xu W, Marcu M, Yuan X, Mimnaugh E, Patterson C, Neckers L . Chaperone-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP mediates a degradative pathway for c-ErbB2/Neu. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 12847–12852.
Omerovic J, Santangelo L, Puggioni EM-R, Marrocco J, Dall’Armi C, Palumbo C et al. The E3 ligase Aip4/Itch ubiquitinates and targets ErbB-4 for degradation. FASEB J 2007; 21: 2849–2862.
Zeng F, Xu J, Harris RC . Nedd4 mediates ErbB4 JM-a/CYT-1 ICD ubiquitination and degradation in MDCK II cells. FASEB J 2009; 23: 1935–1945.
Diamonti AJ, Guy PM, Ivanof C, Wong K, Sweeney C, Carraway KL . An RBCC protein implicated in maintenance of steady-state neuregulin receptor levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 2866–2871.
Qiu X-B, Goldberg AL . Nrdp1/FLRF is a ubiquitin ligase promoting ubiquitination and degradation of the epidermal growth factor receptor family member, ErbB3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 14843–14848.
Maspero E, Mari S, Valentini E, Musacchio A, Fish A, Pasqualato S et al. Structure of the HECT:ubiquitin complex and its role in ubiquitin chain elongation. EMBO Rep 2011; 12: 342–349.
Rotin D, Kumar S . Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 398–409.
Persaud A, Alberts P, Hayes M, Guettler S, Clarke I, Sicheri F et al. Nedd4-1 binds and ubiquitylates activated FGFR1 to control its endocytosis and function. EMBO J 2011; 30: 3259–3273.
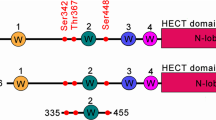
Ingham RJ, Gish G, Pawson T . The Nedd4 family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: functional diversity within a common modular architecture. Oncogene 2004; 23: 1972–1984.
Huang X, Poy F, Zhang R, Joachimiak A, Sudol M, Eck MJ . letters Structure of a WW domain containing fragment of dystrophin in complex with β-dystroglycan. Nature 2000. 7634–8.
Choi B-K, Cai X, Yuan B, Huang Z, Fan X, Deng H et al. HER3 intracellular domains play a crucial role in HER3/HER2 dimerization and activation of downstream signaling pathways. Protein Cell 2012; 3: 781–789.
Choi B-K, Fan X, Deng H, Zhang N, An Z . ERBB3 (HER3) is a key sensor in the regulation of ERBB-mediated signaling in both low and high ERBB2 (HER2) expressing cancer cells. Cancer Med 2012; 1: 28–38.
Söderberg O, Gullberg M, Jarvius M, Ridderstråle K, Leuchowius K-J, Jarvius J et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nat Methods 2006; 3: 995–1000.
Persaud A, Alberts P, Amsen EM, Xiong X, Wasmuth J, Saadon Z et al. Comparison of substrate specificity of the ubiquitin ligases Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 using proteome arrays. Mol Syst Biol 2009; 5: 333.
Waterman H, Alroy I, Strano S, Seger R, Yarden Y . The C-terminus of the kinase-defective neuregulin receptor ErbB-3 confers mitogenic superiority and dictates endocytic routing. EMBO J 1999; 18: 3348–3358.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Zamir E, Kam Z, Oved S, Langdon WY et al. c-Cbl/Sli-1 regulates endocytic sorting and ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 3663–3674.
Sweeney C, Carraway KL . Negative regulation of ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases. Br J Cancer 2004; 90: 289–293.
Feng S-M, Muraoka-Cook RS, Hunter D, Sandahl MA, Caskey LS, Miyazawa K et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 selectively targets HER4 and its proteolytically derived signaling isoforms for degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 892–906.
Vecchione A, Marchese A, Henry P, Rotin D, Morrione A . The Grb10/Nedd4 Complex Regulates Ligand-Induced Ubiquitination and Stability of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Receptor The Grb10 / Nedd4 Complex Regulates Ligand-Induced Ubiquitination and Stability of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Receptor. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 3363–3372.
Huang Q, Szebenyi DME . Structural basis for the interaction between the growth factor-binding protein GRB10 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 42130–42139.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M . Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 1997; 387: 296–299.
Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S et al. Pirh2, a p53-Induced Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase, Promotes p53 Degradation. Cell 2003; 112: 779–791.
Dornan D, Bheddah S, Newton K, Ince W, Frantz GD, Dowd P et al. COP1, the negative regulator of p53, is overexpressed in breast and ovarian adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7226–7230.
Bouyain S, Leahy D . Structure-based mutagenesis of the substrate recognition domain of Nrdp1/FLRF identifies the binding site for the receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB3. Protein Sci 2007; 16: 654–661.
Tsang RY, Finn RS . Beyond trastuzumab: novel therapeutic strategies in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 2012; 106: 6–13.
Garrett JT, Olivares MG, Rinehart C, Granja-Ingram ND, Sánchez V, Chakrabarty A et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational up-regulation of HER3 (ErbB3) compensates for inhibition of the HER2 tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 5021–5026.
Chaib H, Cockrell EK, Rubin MA, Macoska JA . Profiling and verification of gene expression patterns in normal and malignant human prostate tissues by cDNA microarray analysis. Neoplasia 2001.;3: 43–52.
Koumakpayi IH, Diallo J-S, Le Page C, Lessard L, Gleave M, Bégin LR et al. Expression and nuclear localization of ErbB3 in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 2730–2737.
Li Z, Szabolcs M, Terwilliger JD, Efstratiadis A . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma in mice expressing a probasin-Neu oncogenic transgene. Carcinogenesis 2006; 27: 1054–1067.
Lyne JC, Melhem MF, Finley GG, Wen D, Liu N, Deng DH et al. Tissue expression of neu differentiation factor/heregulin and its receptor complex in prostate cancer and its biologic effects on prostate cancer cells in vitro. Cancer J Sci Am 1997.;3: 21–30.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Hui Deng for help on cell cultures; Professor Renping Zhou and Dr Kendra Carmon for critical comments on the manuscript; Dr Stephen Hewitt of NIH/NCI for providing the prostate cancer clinical samples; and Dr Rabih Said for interpretation of immunohistochemistry experiments. The work was partially funded by grants from the Texas Emerging Technology Fund, Johnson and Johnson, and the Welch Foundation grant no. AU00024 to ZA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Choi, BK., Mujoo, K. et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 negatively regulates HER3/ErbB3 level and signaling. Oncogene 34, 1105–1115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.56
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.56
This article is cited by
-
The role of NEDD4 related HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligases in defective autophagy in cancer cells: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives
Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Systematic identification of NF90 target RNAs by iCLIP analysis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Insufficient ablation induces E3-ligase Nedd4 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression by tuning TGF-β signaling
Oncogene (2022)
-
NEDD4L represses prostate cancer cell proliferation via modulating PHF8 through the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)
-
Nedd4l downregulation of NRG1 in the mPFC induces depression-like behaviour in CSDS mice
Translational Psychiatry (2020)