Abstract
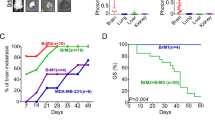
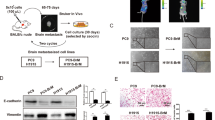
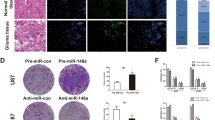
The median survival time of breast cancer patients with brain metastasis is less than 6 months, and even a small metastatic lesion often causes severe neurological disabilities. Because of the location of metastatic lesions, a surgical approach is limited and most chemotherapeutic drugs are ineffective owing to the blood brain barrier (BBB). Despite this clinical importance, the molecular basis of the brain metastasis is poorly understood. In this study, we have isolated RNA from samples obtained from primary breast tumors and also from brain metastatic lesions followed by microRNA profiling analysis. Our results revealed that the miR-509 is highly expressed in the primary tumors, whereas the expression of this microRNA is significantly decreased in the brain metastatic lesions. MicroRNA target prediction and the analysis of cytokine array for the cells ectopically expressed with miR-509 demonstrated that this microRNA was capable of modulating the two genes essential for brain invasion, RhoC and TNF-α that affect the invasion of cancer cells and permeability of BBB, respectively. Importantly, high levels of TNF-α and RhoC-induced MMP9 were significantly correlated with brain metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients. Furthermore, the results of our in vivo experiments indicate that miR-509 significantly suppressed the ability of cancer cells to metastasize to the brain. These findings suggest that miR-509 has a critical role in brain metastasis of breast cancer by modulating the RhoC-TNF-α network and that this miR-509 axis may represent a potential therapeutic target or serve as a prognostic tool for brain metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62: 10–29.
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van 't Veer LJ . Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 591–602.
Eichler AF, Kuter I, Ryan P, Schapira L, Younger J, Henson JW . Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer: the importance of HER-2 status. Cancer 2008; 112: 2359–2367.
Bindal RK, Sawaya R, Leavens ME, Lee JJ . Surgical treatment of multiple brain metastases. J Neurosurg 1993; 79: 210–216.
Bindal AK, Bindal RK, Hess KR, Shiu A, Hassenbusch SJ, Shi WM et al. Surgery versus radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 1996; 84: 748–754.
Steeg PS, Camphausen KA, Smith QR . Brain metastases as preventive and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 352–363.
Arslan C, Dizdar O, Altundag K . Systemic treatment in breast-cancer patients with brain metastasis. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2010; 11: 1089–1100.
He L, Hannon GJ . miRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 522–531.
Tie J, Fan D . Big roles of miRNAs in tumorigenesis and tumor development. Histol Histopathol 2011; 26: 1353–1361.
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE, Peter ME . The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 2010; 17: F19–F36.
Bussing I, Slack FJ, Grosshans H . let-7 miRNAs in development, stem cells and cancer. Trends Mol Med 2008; 14: 400–409.
Nagpal N, Ahmad HM, Molparia B, Kulshreshtha R . miRNA-191, an estrogen-responsive miRNA, functions as an oncogenic regulator in human breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013; 34: 1889–1899.
Bockhorn J, Dalton R, Nwachukwu C, Huang S, Prat A, Yee K et al. miRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11. Nat Commun 2013; 4: 1393.
Nie W, Jin L, Wang Y, Wang Z, Guan X . The bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs signatures differentially expressed in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2013; 28: 71–76.
Volinia S, Croce CM . Prognostic miRNA/mRNA signature from the integrated analysis of patients with invasive breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 7413–7417.
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, Rosenwald S, Spector Y, Zepeniuk M et al. miRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 462–469.
Zhou W, Fong MY, Min Y, Somlo G, Liu L, Palomares MR et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 501–515.
van Golen KL, Wu ZF, Qiao XT, Bao LW, Merajver SD . RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5832–5838.
Wheeler AP, Ridley AJ . Why three Rho proteins? RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and cell motility. Exp Cell Res 2004; 301: 43–49.
Iiizumi M, Bandyopadhyay S, Pai SK, Watabe M, Hirota S, Hosobe S et al. RhoC promotes metastasis via activation of the Pyk2 pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 7613–7620.
Benveniste EN . Inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system: sources, function, and mechanism of action. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: C1–16.
Lucas SM, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM . The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 147: S232–S240.
Tsao N, Hsu HP, Wu CM, Liu CC, Lei HY . Tumour necrosis factor-alpha causes an increase in blood-brain barrier permeability during sepsis. J Med Microbiol 2001; 50: 812–821.
Ramakrishna R, Rostomily R . Seed, soil, and beyond: The basic biology of brain metastasis. Surg Neurol Int 2013; 4: S256–S264.
Korpal M, Ell BJ, Buffa FM, Ibrahim T, Blanco MA, Celia-Terrassa T et al. Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1101–1108.
Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Sharma S, Watabe M, Pai SK et al. miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 1434–1444.
Arora S, Ranade AR, Tran NL, Nasser S, Sridhar S, Korn RL et al. miRNA-328 is associated with (non-small) cell lung cancer (NSCLC) brain metastasis and mediates NSCLC migration. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 2621–2631.
Rosenthal DT, Zhang J, Bao L, Zhu L, Wu Z, Toy K et al. RhoC impacts the metastatic potential and abundance of breast cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e40979.
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH . Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 448–456.
Wilhelm I, Molnar J, Fazakas C, Hasko J, Krizbai IA . Role of the blood-brain barrier in the formation of brain metastases. Int J Mol Sci 2013; 14: 1383–1411.
Izraely S, Sagi-Assif O, Klein A, Meshel T, Tsarfaty G, Pasmanik-Chor M et al. The metastatic microenvironment: brain-residing melanoma metastasis and dormant micrometastasis. Int J Cancer 2012; 131: 1071–1082.
Wang W, Lv S, Zhou Y, Fu J, Li C, Liu P . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha affects blood-brain barrier permeability in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 23: 552–558.
Yang GY, Gong C, Qin Z, Liu XH, Lorris Betz A . Tumor necrosis factor alpha expression produces increased blood-brain barrier permeability following temporary focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1999; 69: 135–143.
Saija A, Princi P, Lanza M, Scalese M, Aramnejad E, De Sarro A . Systemic cytokine administration can affect blood-brain barrier permeability in the rat. Life Sci 1995; 56: 775–784.
Yang YL, Li JP, Xu XP, Dou KF, Yue SQ, Li KZ . Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody and ulinastatin on liver ischemic reperfusion in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: 3161–3164.
Gerstein MB, Kundaje A, Hariharan M, Landt SG, Yan KK, Cheng C et al. Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data. Nature 2012; 489: 91–100.
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C, Shu W, Gomis RR, Nguyen DX et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 2009; 459: 1005–1009.
Langley RR, Ramirez KM, Tsan RZ, Van Arsdall M, Nilsson MB, Fidler IJ . Tissue-specific microvascular endothelial cell lines from H-2K(b)-tsA58 mice for studies of angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 2971–2976.
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR . Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 1989; 77: 51–59.
Bandyopadhyay S, Wang Y, Zhan R, Pai SK, Watabe M, Iiizumi M et al. The tumor metastasis suppressor gene Drg-1 down-regulates the expression of activating transcription factor 3 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11983–11990.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01CA124650, R01CA129000 and R01CA173499 to K Watabe) and the US Department of Defense (BC096982 to K Watabe).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, F., Sharma, S., Liu, Y. et al. miR-509 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer cells by modulating RhoC and TNF-α. Oncogene 34, 4890–4900 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.412
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.412
This article is cited by
-
The role of microRNAs in brain metastasis
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2024)
-
The origin of brain malignancies at the blood–brain barrier
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Non-coding RNAs in the regulation of blood–brain barrier functions in central nervous system disorders
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2022)
-
Evaluating the Role of IL-1β in Transmigration of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells Across the Brain Endothelium
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2022)
-
ChrXq27.3 miRNA cluster functions in cancer development
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)