Abstract
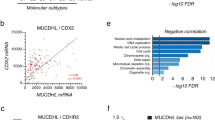
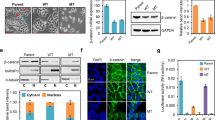
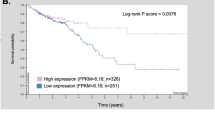
In normal colon, claudin-7 is one of the highly expressed claudin proteins and its knockdown in mice results in altered epithelial cell homeostasis and neonatal death. Notably, dysregulation of the epithelial homeostasis potentiates oncogenic transformation and growth. However, the role of claudin-7 in the regulation of colon tumorigenesis remains poorly understood. Using a large colorectal cancer (CRC) patient database and mouse models of colon cancer, we found claudin-7 expression to be significantly downregulated in cancer samples. Most notably, forced claudin-7 expression in poorly differentiated and highly metastatic SW620 colon cancer cells induced epithelial characteristics and inhibited their growth in soft agar and tumor growth in vivo. By contrast, knockdown of claudin-7 in HT-29 or DLD-1 cells induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), colony formation, xenograft-tumor growth in athymic mice and invasion. Importantly, a claudin-7 signature gene profile generated by overlapping the DEGs (differentially expressed genes in a high-throughput transcriptome analysis using claudin-7-manipulated cells) with human claudin-7 signature genes identified high-risk CRC patients. Furthermore, Rab25, a colon cancer suppressor and regulator of the polarized cell trafficking constituted one of the highly upregulated DEGs in claudin-7 overexpressing cells. Notably, silencing of Rab25 expression counteracted the effects of claudin-7 expression and not only increased proliferation and cell invasion but also increased the expression of p-Src and mitogen-activated protein kinase–extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2 that were suppressed upon claudin-7 overexpression. Of interest, CRC cell lines, which exhibited decreased claudin-7 expression, also exhibited promoter DNA hypermethylation, a modification associated with transcriptional silencing. Taken together, our data demonstrate a previously undescribed role of claudin-7 as a colon cancer suppressor and suggest that loss of claudin-7 potentiates EMT to promote colon cancer, in a manner dependent on Rab25.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M . Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 285–293.
Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD . The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C1213–C1228.
Soler AP, Miller RD, Laughlin KV, Carp NZ, Klurfeld DM, Mullin JM . Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1999; 20: 1425–1431.
Turksen K, Troy TC . Barriers built on claudins. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 2435–2447.
Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Ross JS . Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol 2007; 38: 564–569 2007.
De Oliveira SS, De Oliveira IM, De Souza W, Morgado-Diaz JA . Claudins upregulation in human colorectal cancer. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 6179–6185.
Swisshelm K, Macek R, Kubbies M . Role of claudins in tumorigenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2005; 57: 919–928.
Ding L, Lu Z, Foreman O, Tatum R, Lu Q, Renegar R, Cao J, Chen YH . Inflammation and disruption of the mucosal architecture in claudin-7-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 305–315.
Nam KT, Lee HJ, Smith JJ, Lapierre LA, Kamath VP, Chen X et al. Loss of Rab25 promotes the development of intestinal neoplasia in mice and is associated with human colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 840–849.
Cheng JM, Ding M, Aribi A, Shah P, Rao K . Loss of RAB25 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 2957–2964.
Cheng JM, Volk L, Janaki DK, Vyakaranam S, Ran S, Rao KA . Tumor suppressor function of Rab25 in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 2799–2812.
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, Merchant NB, Zhang B, Jiang A et al. Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 958–968.
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou SR, Schmidt C et al. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1765–1776.
Casanova JE, Wang X, Kumar R, Bhartur SG, Navarre J, Woodrum JE et al. Rab11a and Rab25 association with the apical recycling system of polarized MDCK cells. Mol Biol Cell 1999; 10: 47–61.
Caswell PT, Norman JC . Integrin trafficking and the control of cell migration. Traffic 2006; 7: 14–21.
Esteller M, Corn PG, Baylin SB, Herman JG . A gene hypermethylation profile of human cancer. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 225–3229.
Evron E, Umbricht CB, Korz D, Raman V, Loeb DM, Niranjan B et al. Loss of cyclin D2 expression in the majority of breast cancers is associated with promoter hypermethylation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2782–2787.
Ferguson AT, Evron E, Umbricht CB, Pandita TK, Chan TA, Hermeking H et al. High frequency of hypermethylation at the 14-3-3 sigma locus leads to gene silencing in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 6049–6054.
Jones PA, Baylin SB . The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 415–428.
Boireau S, Buchert M, Samuel MS, Pannequin J, Ryan JL, Choquet A et al. DNA-methylation-dependent alterations of claudin-4 expression in human bladder carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2007; 28: 246–258.
Kalluri R . EMT: when epithelial cells decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 1417–1419.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009; 139: 871–890.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC . Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 563–572.
Nakayama F, Semba S, Usami Y, Chiba H, Sawada N, Yokozaki H . Hypermethylation-modulated downregulation of claudin-7 expression promotes the progression of colorectal carcinoma. Pathobiology 2008; 75: 177–185.
Kominsky SL, Argani P, Korz D, Evron E, Raman V, Garrett E et al. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene 2003; 22: 2021–2033.
Usami Y, Chiba H, Nakayama F, Ueda J, Matsuda Y, Sawada N et al. Reduced expression of claudin-7 correlates with invasion and metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Hum Pathol 2006; 37: 569–577.
Lourenço SV, Coutinho-Camillo CM, Buim ME, de Carvalho AC, Lessa RC, Pereira CM et al. Claudin-7 down-regulation is an important feature in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2010; 57: 689–698.
Melchers LJ, Bruine de Bruin L, Schnell U, Slagter-Menkema L, Mastik MF, de Bock GH et al. Lack of claudin-7 is a strong predictor of regional recurrence in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2013; 49: 998–1005.
Yoshizawa K, Nozaki S, Kato A, Hirai M, Yanase M, Yoshimoto T et al. Loss of claudin-7 is a negative prognostic factor for invasion and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2013; 29: 445–450.
Robertson K . DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2005; 6: 597–610.
Laird PW, Jaenisch R . The role of DNA methylation in cancer genetic and epigenetics. Annu Rev Genet 1996; 30: 441–464.
Toyota M, Ahuja N, Suzuki H, Ohe-Toyota M, Imai K, Imai K et al. Aberrant methylation in gastric cancer associated with the CpG island methylator phenotype. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5438–5442.
Bird AP . CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature 1986; 321: 209–213.
Issa JP . Cancer prevention: epigenetics steps up to the plate. Cancer Prev Res (Phila Pa) 2008; 1: 219–222.
Bates RC, Mercurio AM . The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Biol Ther 2005; 4: 365–370.
Kang Y, Massagué J . Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell 2004; 118: 277–279.
Lioni M, Brafford P, Andl C, Rustgi A, El-Deiry W, Herlyn M et al. Dysregulation of claudin-7 leads to loss of E-cadherin expression and the increased invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 709–721.
Fujita H, Chiba H, Yokozaki H, Sakai N, Sugimoto K, Wada T et al. Differential expression and subcellular localization of claudin-7, -8, -12, -13, and -15 along the mouse intestine. J Histochem Cytochem 2006; 54: 933–944.
Lu Z, Ding L, Hong H, Hoggard J, Lu Q, Chen YH . Claudin-7 inhibits human lung cancer cell migration and invasion through ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 2011; 317: 1935–1946.
Huang RY, Wong MK, Tan TZ, Kuay KT, Ng AH, Chung VY et al. An EMT spectrum defines an anoikis-resistant and spheroidogenic intermediate mesenchymal state that is sensitive to e-cadherin restoration by a src-kinase inhibitor, saracatinib (AZD0530). Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e915.
Park GB, Kim D, Kim YS, Kim S, Lee HK, Yang JW et al. The Epstein-Barr virus causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human corneal epithelial cells via Syk/src and Akt/Erk signaling pathways. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55: 1770–1779.
Pope JL, Bhat AA, Sharma A, Ahmad R, Krishnan M, Washington MK et al. Claudin-1 regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis through the modulation of Notch-signalling. Gut 2014; 63: 622–634.
Singh AB, Sharma A, Smith JJ, Krishnan M, Chen X, Eschrich S et al. Claudin-1 up-regulates the repressor ZEB-1 to inhibit E-cadherin expression in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2011; 141: 2140–2153.
Shiou SR, Singh AB, Moorthy K, Datta PK, Washington MK, Beauchamp RD et al. Smad4 regulates claudin-1 expression in a transforming growth factor-b–independent manner in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 1571–1579.
Miwa N, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Niikawa N, Nakamura Y, Furukawa Y . Involvement of claudin-1 in the βcatenin/ Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in human colorectal cancers. Oncol Res 2001; 12: 469–476.
Caswell PT, Spence HJ, Parsons M, White DP, Clark K, Cheng KW et al. Rab25 associates with alpha5beta1 integrin to promote invasive migration in 3D microenvironments. Dev Cell 2007; 13: 496–510.
Goldenring JR, Nam KT . Rab25 as a tumour suppressor in colon carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer 2011; 104: 33–36.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to John Neff and Jalal Hamaamen for their technical support. This work was supported by VA-merit BX002086 and CA124977 (to PD), DK088902 (to ABS), CA158472 (to XC and RDB), CA069457 (to RDB), GI Cancer SPORE grant CA095103, Vanderbilt DDRC P30DK058404, VICC P30CA68485 and StarBRITE funds (no. VR1258).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhat, A., Pope, J., Smith, J. et al. Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis. Oncogene 34, 4570–4580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.385
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.385
This article is cited by
-
Claudins as biomarkers of differential diagnosis and prognosis of tumors
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2021)
-
The gastrointestinal microbiota in colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2021)
-
CDX2 expression and perioperative patient serum affects the adhesion properties of cultured colon cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Gold/alpha-lactalbumin nanoprobes for the imaging and treatment of breast cancer
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2020)
-
Downregulation of CLDN7 due to promoter hypermethylation is associated with human clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and poor prognosis
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)