Abstract
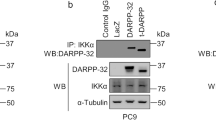
Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is linked to tumor progression, metastasis and poor survival rates. Here we report the role of Cdc42-interacting protein 4 (CIP4) in the regulation of NSCLC cell invasiveness and tumor metastasis. CIP4 was highly expressed in a panel of NSCLC cell lines and normal lung epithelial cell lines. Stable knockdown (KD) of CIP4 in lung adenocarcinoma H1299 cells, expressing wild-type EGFR, led to increased EGFR levels on the cell surface and defects in sustained activation of Erk kinase in H1299 cells treated with EGF. CIP4 localized to leading edge projections in NSCLC cells, and CIP4 KD cells displayed defects in EGF-induced cell motility and invasion through extracellular matrix. This correlated with reduced expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in CIP4 KD cells compared with control. In xenograft assays, CIP4 silencing had no effect on tumor growth but resulted in significant defects in spontaneous metastases to the lungs from these subcutaneous tumors. This correlated with reduced expression of the Erk target gene Zeb1 and the Zeb1 target gene MMP-2 in CIP4 KD tumors compared with control. CIP4 also enhanced rates of metastasis to the liver and lungs in an intrasplenic experimental metastasis model. In human NSCLC tumor sections, CIP4 expression was elevated greater than or equal to twofold in 43% of adenocarcinomas and 32% of squamous carcinomas compared with adjacent normal lung tissues. Analysis of microarray data for NSCLC patients also revealed that high CIP4 transcript levels correlated with reduced overall survival. Together, these results identify CIP4 as a positive regulator of NSCLC metastasis and a potential poor prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rusch V, Klimstra D, Venkatraman E, Pisters PW, Langenfeld J, Dmitrovsky E . Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand transforming growth factor alpha is frequent in resectable non-small cell lung cancer but does not predict tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 1997; 3: 515–522.
Hirsch FR, Herbst RS, Olsen C, Chansky K, Crowley J, Kelly K et al. Increased EGFR gene copy number detected by fluorescent in situ hybridization predicts outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with cetuximab and chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 3351–3357.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2129–2139.
Zhao M, Pu J, Forrester JV, McCaig CD . Membrane lipids, EGF receptors, and intracellular signals colocalize and are polarized in epithelial cells moving directionally in a physiological electric field. FASEB J 2002; 16: 857–859.
Rosell R, Moran T, Carcereny E, Quiroga V, Molina MA, Costa C et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations in the EGFR kinase domain. Clin Transl Oncol 2010; 12: 75–80.
Yang M, Shan B, Li Q, Song X, Cai J, Deng J et al. Overcoming erlotinib resistance with tailored treatment regimen in patient-derived xenografts from naive Asian NSCLC patients. Intl J Cancer 2013; 132: E74–E84.
Downward J . Targeting RAS and PI3K in lung cancer. Nat Med 2008; 14: 1315–1316.
Ishikawa D, Takeuchi S, Nakagawa T, Sano T, Nakade J, Nanjo S et al. mTOR inhibitors control the growth of EGFR mutant lung cancer even after acquiring resistance by HGF. PLoS One 2013; 8: e62104.
Kim LC, Song L, Haura EB . Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009; 6: 587–595.
Hu J, Mukhopadhyay A, Truesdell P, Chander H, Mukhopadhyay UK, Mak AS et al. Cdc42-interacting protein 4 is a Src substrate that regulates invadopodia and invasiveness of breast tumors by promoting MT1-MMP endocytosis. J Cell Sci 2011; 124: 1739–1751.
Hu J, Troglio F, Mukhopadhyay A, Everingham S, Kwok E, Scita G et al. F-BAR-containing adaptor CIP4 localizes to early endosomes and regulates Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor trafficking and downregulation. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 1686–1697.
Pichot CS, Arvanitis C, Hartig SM, Jensen SA, Bechill J, Marzouk S et al. Cdc42-interacting protein 4 promotes breast cancer cell invasion and formation of invadopodia through activation of N-WASp. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 8347–8356.
Aspenstrom P . A Cdc42 target protein with homology to the non-kinase domain of FER has a potential role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 479–487.
Aspenstrom P, Fransson A, Richnau N . Pombe Cdc15 homology proteins: regulators of membrane dynamics and the actin cytoskeleton. Trends Biochem Sci 2006; 31: 670–679.
Frost A, Perera R, Roux A, Spasov K, Destaing O, Egelman EH et al. Structural basis of membrane invagination by F-BAR domains. Cell 2008; 132: 807–817.
Shimada A, Niwa H, Tsujita K, Suetsugu S, Nitta K, Hanawa-Suetsugu K et al. Curved EFC/F-BAR-domain dimers are joined end to end into a filament for membrane invagination in endocytosis. Cell 2007; 129: 761–772.
Itoh T, Erdmann KS, Roux A, Habermann B, Werner H, De Camilli P . Dynamin and the actin cytoskeleton cooperatively regulate plasma membrane invagination by BAR and F-BAR proteins. Dev Cell 2005; 9: 791–804.
Saengsawang W, Taylor KL, Lumbard DC, Mitok K, Price A, Pietila L et al. CIP4 coordinates with phospholipids and actin-associated proteins to localize to the protruding edge and produce actin ribs and veils. J Cell Sci 2013; 126: 2411–2423.
Tsujita K, Suetsugu S, Sasaki N, Furutani M, Oikawa T, Takenawa T . Coordination between the actin cytoskeleton and membrane deformation by a novel membrane tubulation domain of PCH proteins is involved in endocytosis. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 269–279.
Aspenstrom P, Richnau N, Johansson AS . The diaphanous-related formin DAAM1 collaborates with the Rho GTPases RhoA and Cdc42, CIP4 and Src in regulating cell morphogenesis and actin dynamics. Exp Cell Res 2006; 312: 2180–2194.
Richnau N, Aspenstrom P . Rich, a rho GTPase-activating protein domain-containing protein involved in signaling by Cdc42 and Rac1. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 35060–35070.
Takano K, Toyooka K, Suetsugu S . EFC/F-BAR proteins and the N-WASP-WIP complex induce membrane curvature-dependent actin polymerization. EMBO J 2008; 27: 2817–2828.
Tian L, Nelson DL, Stewart DM . Cdc42-interacting protein 4 mediates binding of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein to microtubules. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 7854–7861.
Feng Y, Hartig SM, Bechill JE, Blanchard EG, Caudell E, Corey SJ . The Cdc42-interacting protein-4 (CIP4) gene knock-out mouse reveals delayed and decreased endocytosis. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 4348–4354.
Koduru S, Kumar L, Massaad MJ, Ramesh N, Le Bras S, Ozcan E et al. Cdc42 interacting protein 4 (CIP4) is essential for integrin-dependent T-cell trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 16252–16256.
Saengsawang W, Mitok K, Viesselmann C, Pietila L, Lumbard DC, Corey SJ et al. The F-BAR protein CIP4 inhibits neurite formation by producing lamellipodial protrusions. Curr Biol 2012; 22: 494–501.
Malet-Engra G, Viaud J, Ysebaert L, Farcé M, Lafouresse F, Laurent G et al. CIP4 controls CCL19-driven cell steering and chemotaxis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3412–3424.
Koshkina NV, Yang G, Kleinerman ES . Inhibition of Cdc42-interacting protein 4 (CIP4) impairs osteosarcoma tumor progression. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2013; 13: 48–56.
Tsuji E, Tsuji Y, Fujiwara T, Ogata S, Tsukamoto K, Saku K . Splicing variant of Cdc42 interacting protein-4 disrupts beta-catenin-mediated cell-cell adhesion: expression and function in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 339: 1083–1088.
Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y . Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J 2010; 277: 301–308.
Ahn J, Truesdell P, Meens J, Kadish C, Yang X, Boag AH et al. Fer protein-tyrosine kinase promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and tumor metastasis. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 952–963.
Huang MS, Wang TJ, Liang CL, Huang HM, Yang IC, Yi-Jan H et al. Establishment of fluorescent lung carcinoma metastasis model and its real-time microscopic detection in SCID mice. Clin Exp Metastatis 2002; 19: 359–368.
Bae GY, Choi SJ, Lee JS, Jo J, Lee J, Kim J et al. Loss of E-cadherin activates EGFR-MEK/ERK signaling, which promotes invasion via the ZEB1/MMP2 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2013; 4: 2512–2522.
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lanczky A . Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 2013; 8: e82241.
Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q et al. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010; 123: 725–731.
Dong QZ, Wang Y, Tang ZP, Fu L, Li QC, Wang ED et al. Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion via EGFR-ERK-mediated up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Am J Pathol 2013; 182: 954–964.
Taylor MJ, Perrais D, Merrifield CJ . A high precision survey of the molecular dynamics of mammalian clathrin-mediated endocytosis. PLoS Biol 2011; 9: e1000604.
Kao SJ, Su JL, Chen CK, Yu MC, Bai KJ, Chang JH et al. Osthole inhibits the invasive ability of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via suppression of NF-kappaB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2012; 261: 105–115.
Li Z, Dong Q, Wang Y, Qu L, Qiu X, Wang E . Downregulation of Mig-6 in nonsmall-cell lung cancer is associated with EGFR signaling. Mol Carcinog 2012; 51: 522–534.
Bai S, Zeng R, Zhou Q, Liao W, Zhang Y, Xu C et al. Cdc42-interacting protein-4 promotes TGF-Beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Intl J Biol Sci 2012; 8: 859–869.
Zhang J, Bi M, Zhong F, Jiao X, Zhang D, Dong Q . Role of CIP4 in high glucose induced epithelial—mesenchymal transition of rat peritoneal mesothelial cells. Ren Fail 2013; 35: 989–995.
Leibfried A, Fricke R, Morgan MJ, Bogdan S, Bellaiche Y . Drosophila Cip4 and WASp define a branch of the Cdc42-Par6-aPKC pathway regulating E-cadherin endocytosis. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 1639–1648.
Hsu CC, Leu YW, Tseng MJ, Lee KD, Kuo TY, Yen JY et al. Functional characterization of Trip10 in cancer cell growth and survival. J Biomed Sci 2011; 18: 12.
Zhou Z, Hao Y, Liu N, Raptis L, Tsao MS, Yang X . TAZ is a novel oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2181–2186.
Acknowledgements
We thank Stephanie Everingham for technical assistance, Jeff Mewburn for help with time-lapse confocal microscopy and Lee Boudreau (Queen’s Laboratory for Molecular Pathology) for help in optimizing IHC staining. Thanks also to Lois Mulligan, Peter Greer and Chris Nicol for sharing reagents and equipment. This research was supported by operating grants from Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and Canadian Institutes for Health Research to AWBC (MOP119562).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truesdell, P., Ahn, J., Chander, H. et al. CIP4 promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis. Oncogene 34, 3527–3535 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.280
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.280