Abstract
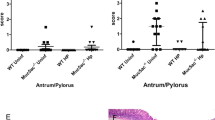
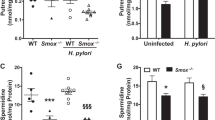
Helicobacter pylori is the strongest risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. Although the specific mechanisms by which this pathogen induces carcinogenesis have not been fully elucidated, high-expression interleukin (IL)-1β alleles are associated with increased gastric cancer risk among H. pylori-infected persons. In addition, loss of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) increases mucosal inflammation in mouse models of epithelial injury, and we have shown that gastric inflammation is increased in H. pylori-infected MMP7−/− C57BL/6 mice. In this report, we define mechanisms that underpin such responses and extend these results into a genetic model of MMP7 deficiency and gastric cancer. Wild-type (WT) or MMP7−/− C57BL/6 mice were challenged with broth alone as an uninfected control or the H. pylori strain PMSS1. All H. pylori-challenged mice were successfully colonized. As expected, H. pylori-infected MMP7−/− C57BL/6 mice exhibited a significant increase in gastric inflammation compared with uninfected or infected WT C57BL/6 animals. Loss of MMP7 resulted in M1 macrophage polarization within H. pylori-infected stomachs, as assessed by Luminex technology and immunohistochemistry, and macrophages isolated from infected MMP7-deficient mice expressed significantly higher levels of the M1 macrophage marker IL-1β compared with macrophages isolated from WT mice. To extend these findings into a model of gastric cancer, hypergastrinemic WT INS-GAS or MMP7−/− INS-GAS mice were challenged with H. pylori strain PMSS1. Consistent with findings in the C57BL/6 model, H. pylori-infected MMP7-deficient INS-GAS mice exhibited a significant increase in gastric inflammation compared with either uninfected or infected WT INS-GAS mice. In addition, the incidence of gastric hyperplasia and dysplasia was significantly increased in H. pylori-infected MMP7−/− INS-GAS mice compared with infected WT INS-GAS mice, and loss of MMP7 promoted M1 macrophage polarization. These results suggest that MMP7 exerts a restrictive role on H. pylori-induced gastric injury and the development of premalignant lesions by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E, Ferlay J . Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. Int J Cancer 2013; 132: 1133–1145.
Polk DB, Peek RM Jr . Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 403–414.
El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow WH, McColl KE, Bream JH, Young HA et al. Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature 2000; 404: 398–402.
Ogden SR, Noto JM, Allen SS, Patel DA, Romero-Gallo J, Washington MK et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 and premalignant host responses in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 30–35.
McDonnell S, Navre M, Coffey RJ Jr, Matrisian LM . Expression and localization of the matrix metalloproteinase pump-1 (MMP-7) in human gastric and colon carcinomas. Mol Carcinog 1991; 4: 527–533.
Chung WC, Jung SH, Lee KM, Paik CN, Kawk JW, Jung JH et al. The detection of Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity islands (PAIs) and expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) in gastric epithelial dysplasia and intramucosal cancer. Gastric Cancer 2010; 13: 162–169.
Senota A, Itoh F, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Hinoda Y, Imai K . Relation of matrilysin messenger RNA expression with invasive activity in human gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 1998; 16: 313–321.
Sierra JC, Hobbs S, Chaturvedi R, Yan F, Wilson KT, Peek RM Jr et al. Induction of COX-2 expression by Helicobacter pylori is mediated by activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in gastric epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2013; 305: G196–G203.
Noto JM, Gaddy JA, Lee JY, Piazuelo MB, Friedman DB, Colvin DC et al. Iron deficiency accelerates Helicobacter pylori-induced carcinogenesis in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 479–492.
Schumacher MA, Donnelly JM, Engevik AC, Xiao C, Yang L, Kenny S et al. Gastric sonic hedgehog acts as a macrophage chemoattractant during the immune response to Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 1150–1159 e1156.
Cassetta L, Cassol E, Poli G . Macrophage polarization in health and disease. ScientificWorldJournal 2011; 11: 2391–2402.
Mosser DM, Edwards JP . Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 958–969.
Quante M, Varga J, Wang TC, Greten FR . The gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2013; 145: 63–78.
Wilson CL, Matrisian LM . Matrilysin: an epithelial matrix metalloproteinase with potentially novel functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1996; 28: 123–136.
Egeblad M, Werb Z . New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 161–174.
Barry DP, Asim M, Scull BP, Piazuelo MB, de Sablet T, Lewis ND et al. Cationic amino acid transporter 2 enhances innate immunity during Helicobacter pylori infection. PloS ONE 2011; 6: e29046.
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M . The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 677–686.
Kassim SY, Gharib SA, Mecham BH, Birkland TP, Parks WC, McGuire JK . Individual matrix metalloproteinases control distinct transcriptional responses in airway epithelial cells infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 2007; 75: 5640–5650.
Lifsted T, Le Voyer T, Williams M, Muller W, Klein-Szanto A, Buetow KH et al. Identification of inbred mouse strains harboring genetic modifiers of mammary tumor age of onset and metastatic progression. Int J Cancer 1998; 77: 640–644.
Fox JG, Wang TC, Rogers AB, Poutahidis T, Ge Z, Taylor N et al. Host and microbial constituents influence Helicobacter pylori-induced cancer in a murine model of hypergastrinemia. Gastroenterology 2003; 124: 1879–1890.
Weischenfeldt J, Porse B . Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM): isolation and applications. CSH Protoc 2008; 2008: pdb.prot5080.
Zhang X, Goncalves R, Mosser DM . The isolation and characterization of murine macrophages. Curr Protoc Immunol 2008; Chapter 14: Unit 14.1.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by T32CA009592 (MSK), F32CA153539 (JMN), T32GM008554 (DMH), K01AT007324 (RC), P01CA028842 (KTW and PC), R01DK053620 and 1I01BX001453 from the Department of Veterans Affairs (KTW), R01DK058587, R01CA077955, P30DK058404 and P01CA116087 (RMP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krakowiak, M., Noto, J., Piazuelo, M. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 7 restrains Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation and premalignant lesions in the stomach by altering macrophage polarization. Oncogene 34, 1865–1871 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.135
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.135