Abstract
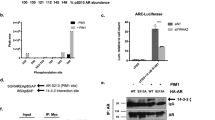
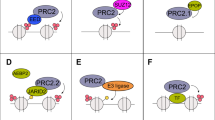
The androgen receptor (AR) is a transcription factor that employs many diverse interactions with coregulatory proteins in normal physiology and in prostate cancer (PCa). The AR mediates cellular responses in association with chromatin complexes and kinase cascades. Here we report that the nuclear matrix protein, scaffold attachment factor B1 (SAFB1), regulates AR activity and AR levels in a manner that suggests its involvement in PCa. SAFB1 mRNA expression was lower in PCa in comparison with normal prostate tissue in a majority of publicly available RNA expression data sets. SAFB1 protein levels were also reduced with disease progression in a cohort of human PCa that included metastatic tumors. SAFB1 bound to AR and was phosphorylated by the MST1 (Hippo homolog) serine-threonine kinase, previously shown to be an AR repressor, and MST1 localization to AR-dependent promoters was inhibited by SAFB1 depletion. Knockdown of SAFB1 in androgen-dependent LNCaP PCa cells increased AR and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, stimulated growth of cultured cells and subcutaneous xenografts and promoted a more aggressive phenotype, consistent with a repressive AR regulatory function. SAFB1 formed a complex with the histone methyltransferase EZH2 at AR-interacting chromatin sites in association with other polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) proteins. We conclude that SAFB1 acts as a novel AR co-regulator at gene loci where signals from the MST1/Hippo and EZH2 pathways converge.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, Vessella R et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med 2004; 10: 33–39.
Debes JD, Tindall DJ . Mechanisms of androgen-refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1488–1490.
Grossmann ME, Huang H, Tindall DJ . Androgen receptor signaling in androgen-refractory prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93: 1687–1697.
Hara T, Nakamura K, Araki H, Kusaka M, Yamaoka M . Enhanced androgen receptor signaling correlates with the androgen-refractory growth in a newly established MDA PCa 2b-hr human prostate cancer cell subline. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5622–5628.
Scher HI, Sawyers CL . Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 8253–8261.
Taplin ME, Balk SP . Androgen receptor: a key molecule in the progression of prostate cancer to hormone independence. J Cell Biochem 2004; 91: 483–490.
Hara T, Miyazaki H, Lee A, Tran CP, Reiter RE . Androgen receptor and invasion in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 1128–1135.
Hermanson O, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG . Nuclear receptor coregulators: multiple modes of modification. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002; 13: 55–60.
Robyr D, Wolffe AP, Wahli W . Nuclear hormone receptor coregulators in action: diversity for shared tasks. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 329–347.
Knudsen KE, Penning TM . Partners in crime: deregulation of AR activity and androgen synthesis in prostate cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2010; 21: 315–324.
Burd CJ, Morey LM, Knudsen KE . Androgen receptor corepressors and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 2006; 13: 979–994.
Baek SH . When signaling kinases meet histones and histone modifiers in the nucleus. Mol Cell 2011; 42: 274–284.
Vicent GP, Nacht AS, Font-Mateu J, Castellano G, Gaveglia L, Ballare C et al. Four enzymes cooperate to displace histone H1 during the first minute of hormonal gene activation. Genes Dev 2011; 25: 845–862.
Creasy CL, Chernoff J . Cloning and characterization of a member of the MST subfamily of Ste20-like kinases. Gene 1995; 167: 303–306.
Cinar B, Collak FK, Lopez D, Akgul S, Mukhopadhyay NK, Kilicarslan M et al. MST1 is a multifunctional caspase-independent inhibitor of androgenic signaling. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4303–4313.
Cinar B, Fang PK, Lutchman M, Di Vizio D, Adam RM, Pavlova N et al. The pro-apoptotic kinase Mst1 and its caspase cleavage products are direct inhibitors of Akt1. EMBO J 2007; 26: 4523–4534.
Cinar B, Mukhopadhyay NK, Meng G, Freeman MR . Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-independent non-genomic signals transit from the androgen receptor to Akt1 in membrane raft microdomains. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 29584–29593.
Li LC, Carroll PR, Dahiya R . Epigenetic changes in prostate cancer: implication for diagnosis and treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005; 97: 103–115.
Chen Z, Wang L, Wang Q, Li W . Histone modifications and chromatin organization in prostate cancer. Epigenomics 2010; 2: 551–560.
Crea F, Hurt EM, Mathews LA, Cabarcas SM, Sun L, Marquez VE et al. Pharmacologic disruption of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 inhibits tumorigenicity and tumor progression in prostate cancer. Molecular cancer 2011; 10: 40.
Garee JP, Oesterreich S . SAFB1's multiple functions in biological control-lots still to be done!. J Cell Biochem 2010; 109: 312–319.
Townson SM, Kang K, Lee AV, Oesterreich S . Structure-function analysis of the estrogen receptor alpha corepressor scaffold attachment factor-B1: identification of a potent transcriptional repression domain. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 26074–26081.
Debril MB, Dubuquoy L, Feige JN, Wahli W, Desvergne B, Auwerx J et al. Scaffold attachment factor B1 directly interacts with nuclear receptors in living cells and represses transcriptional activity. J Mol Endocrinol 2005; 35: 503–517.
Mukhopadhyay NK, Kim J, Cinar B, Ramachandran A, Hager MH, Di Vizio D et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a novel regulator of androgen receptor translation. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 2210–2218.
Di Vizio D, Morello M, Sotgia F, Pestell RG, Freeman MR, Lisanti MP . An absence of stromal caveolin-1 is associated with advanced prostate cancer, metastatic disease and epithelial Akt activation. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 2420–2424.
Wang X, Yeh S, Wu G, Hsu CL, Wang L, Chiang T et al. Identification and characterization of a novel androgen receptor coregulator ARA267-alpha in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 40417–40423.
Xu LL, Shanmugam N, Segawa T, Sesterhenn IA, McLeod DG, Moul JW et al. A novel androgen-regulated gene, PMEPA1, located on chromosome 20q13 exhibits high level expression in prostate. Genomics 2000; 66: 257–263.
Magee JA, Chang LW, Stormo GD, Milbrandt J . Direct, androgen receptor-mediated regulation of the FKBP5 gene via a distal enhancer element. Endocrinology 2006; 147: 590–598.
Li SS, Sharief FS . The prostatic acid phosphatase (ACPP) gene is localized to human chromosome 3q21-q23. Genomics 1993; 17: 765–766.
Mukhopadhyay NK, Cinar B, Mukhopadhyay L, Lutchman M, Ferdinand AS, Kim J et al. The zinc finger protein ras-responsive element binding protein-1 is a coregulator of the androgen receptor: implications for the role of the Ras pathway in enhancing androgenic signaling in prostate cancer. Mol Endocrinol 2007; 21: 2056–2070.
Lawrence MG, Lai J, Clements JA . Kallikreins on steroids: structure, function, and hormonal regulation of prostate-specific antigen and the extended kallikrein locus. Endocr Rev 2010; 31: 407–446.
Hammerich-Hille S, Kaipparettu BA, Tsimelzon A, Creighton CJ, Jiang S, Polo JM et al. SAFB1 mediates repression of immune regulators and apoptotic genes in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 3608–3616.
Yamamoto S, Yang G, Zablocki D, Liu J, Hong C, Kim SJ et al. Activation of Mst1 causes dilated cardiomyopathy by stimulating apoptosis without compensatory ventricular myocyte hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 1463–1474.
Collak FK, Yagiz K, Luthringer DJ, Erkaya B, Cinar B . Threonine-120 phosphorylation regulated by phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin pathway signaling limits the antitumor activity of mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 23698–23709.
Cheung WL, Ajiro K, Samejima K, Kloc M, Cheung P, Mizzen CA et al. Apoptotic phosphorylation of histone H2B is mediated by mammalian sterile twenty kinase. Cell 2003; 113: 507–517.
Hu Y, Liu Z, Yang SJ, Ye K . Acinus-provoked protein kinase C delta isoform activation is essential for apoptotic chromatin condensation. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 2035–2046.
Hu Y, Yao J, Liu Z, Liu X, Fu H, Ye K . Akt phosphorylates acinus and inhibits its proteolytic cleavage, preventing chromatin condensation. EMBO J 2005; 24: 3543–3554.
Ura S, Nishina H, Gotoh Y, Katada T . Activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway by MST1 is essential and sufficient for the induction of chromatin condensation during apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 5514–5522.
Beisel C, Paro R . Silencing chromatin: comparing modes and mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12: 123–135.
Ross PJ, Ragina NP, Rodriguez RM, Iager AE, Siripattarapravat K, Lopez-Corrales N et al. Polycomb gene expression and histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation changes during bovine preimplantation development. Reproduction 2008; 136: 777–785.
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M, Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature 2002; 419: 624–629.
Chng KR, Chang CW, Tan SK, Yang C, Hong SZ, Sng NY et al. A transcriptional repressor co-regulatory network governing androgen response in prostate cancers. EMBO J 2012; 31: 2810–2823.
Aldiri I, Vetter ML . Characterization of the expression pattern of the PRC2 core subunit Suz12 during embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. Developmental dynamics: an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 2009; 238: 3185–3192.
Pinskaya M, Morillon A . Histone H3 lysine 4 di-methylation: a novel mark for transcriptional fidelity? Epigenetics 2009; 4: 302–306.
Oesterreich S, Lee AV, Sullivan TM, Samuel SK, Davie JR, Fuqua SA . Novel nuclear matrix protein HET binds to and influences activity of the HSP27 promoter in human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 1997; 67: 275–286.
Renz A, Fackelmayer FO . Purification and molecular cloning of the scaffold attachment factor B (SAF-B), a novel human nuclear protein that specifically binds to S/MAR-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 1996; 24: 843–849.
Waltering KK, Helenius MA, Sahu B, Manni V, Linja MJ, Janne OA et al. Increased expression of androgen receptor sensitizes prostate cancer cells to low levels of androgens. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8141–8149.
Oesterreich S . Scaffold attachment factors SAFB1 and SAFB2: Innocent bystanders or critical players in breast tumorigenesis? J Cell Biochem 2003; 90: 653–661.
Townson SM, Dobrzycka KM, Lee AV, Air M, Deng W, Kang K et al. SAFB2, a new scaffold attachment factor homolog and estrogen receptor corepressor. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 20059–20068.
Gao AC, Lou W, Ichikawa T, Denmeade SR, Barrett JC, Isaacs JT . Suppression of the tumorigenicity of prostatic cancer cells by gene(s) located on human chromosome 19p13.1-13.2. The Prostate 1999; 38: 46–54.
Wiklund F, Gillanders EM, Albertus JA, Bergh A, Damber JE, Emanuelsson M et al. Genome-wide scan of Swedish families with hereditary prostate cancer: suggestive evidence of linkage at 5q11.2 and 19p13.3. The Prostate 2003; 57: 290–297.
Mukhopadhyay NK, Ferdinand AS, Mukhopadhyay L, Cinar B, Lutchman M, Richie JP et al. Unraveling androgen receptor interactomes by an array-based method: discovery of proto-oncoprotein c-Rel as a negative regulator of androgen receptor. Exp Cell Res 2006; 312: 3782–3795.
Kim J, Ji M, DiDonato JA, Rackley RR, Kuang M, Sadhukhan PC et al. An hTERT-immortalized human urothelial cell line that responds to anti-proliferative factor. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2011; 47: 2–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Thomas Roberts (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute) for critical comments and Delia Lopez, Kristine Pelton and Paul Guthrie for technical assistance. This study was supported by NIH 1R01CA143777, 1R01CA112303, and US Department of Defense PC093459 (to MRF), NIH 5R00CA131472 (to DDV) and NIH R01 CA097213 (to SO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, N., Kim, J., You, S. et al. Scaffold attachment factor B1 regulates the androgen receptor in concert with the growth inhibitory kinase MST1 and the methyltransferase EZH2. Oncogene 33, 3235–3245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.294
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.294
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Going beyond Polycomb: EZH2 functions in prostate cancer
Oncogene (2021)
-
SAIL: a new conserved anti-fibrotic lncRNA in the heart
Basic Research in Cardiology (2021)
-
FUS interacts with nuclear matrix-associated protein SAFB1 as well as Matrin3 to regulate splicing and ligand-mediated transcription
Scientific Reports (2016)