Abstract
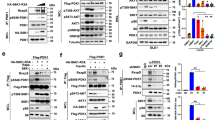
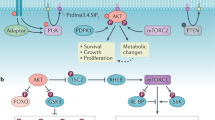
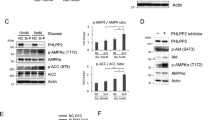
The PI3K/PDK1/Akt signaling axis is centrally involved in cellular homeostasis and controls cell growth and proliferation. Due to its key function as regulator of cell survival and metabolism, the dysregulation of this pathway is manifested in several human pathologies including cancers and immunological diseases. Thus, current therapeutic strategies target the components of this signaling cascade. In recent years, numerous feedback loops have been identified that attenuate PI3K/PDK1/Akt-dependent signaling. Here, we report the identification of an additional level of feedback regulation that depends on the negative transcriptional control of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) class IA subunits. Genetic deletion of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) or the pharmacological inhibition of its downstream effectors, that is, Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), relieves this suppression and leads to the upregulation of PI3K subunits, resulting in enhanced generation of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). Apparently, this transcriptional induction is mediated by the concerted action of different transcription factor families, including the transcription factors cAMP-responsive element-binding protein and forkhead box O. Collectively, we propose that PDK1 functions as a cellular sensor that balances basal PIP3 generation at levels sufficient for survival but below a threshold being harmful to the cell. Our study suggests that the efficiency of therapies targeting the aberrantly activated PI3K/PDK1/Akt pathway might be increased by the parallel blockade of feedback circuits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunney TD, Katan M . Phosphoinositide signalling in cancer: beyond PI3K and PTEN. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 342–352.
Carnero A . The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer. Curr Pharm Des 2010; 16: 34–44.
Chalhoub N, Baker SJ . PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2009; 4: 127–150.
Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW . Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 184–192.
Engelman JA . Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 550–562.
Hers I, Vincent EE, Tavare JM . Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal 2011; 23: 1515–1527.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL . The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 489–501.
So L, Fruman DA . PI3K signalling in B- and T-lymphocytes: new developments and therapeutic advances. Biochem J 2012; 442: 465–481.
Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC . The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 2006; 7: 606–619.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B . The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 329–341.
Liu Y, Bankaitis VA . Phosphoinositide phosphatases in cell biology and disease. Prog Lipid Res 2010; 49: 201–217.
Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM, Alessi DR . PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2004; 15: 161–170.
Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR . The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 9–22.
Alessi DR, Deak M, Casamayor A, Caudwell FB, Morrice N, Norman DG et al. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 776–789.
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 261–269.
Alessi DR, Kozlowski MT, Weng QP, Morrice N, Avruch J . 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) phosphorylates and activates the p70 S6 kinase in vivo and in vitro. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 69–81.
Kobayashi T, Cohen P . Activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase by agonists that activate phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase is mediated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and PDK2. Biochem J 1999; 339: 319–328.
Kobayashi T, Deak M, Morrice N, Cohen P . Characterization of the structure and regulation of two novel isoforms of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase. Biochem J 1999; 344: 189–197.
Dong LQ, Zhang RB, Langlais P, He H, Clark M, Zhu L et al. Primary structure, tissue distribution, and expression of mouse phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, a protein kinase that phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Czeta. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8117–8122.
Jensen CJ, Buch MB, Krag TO, Hemmings BA, Gammeltoft S, Frodin M . 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase is phosphorylated and activated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 27168–27176.
Le Good JA, Ziegler WH, Parekh DB, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Parker PJ . Protein kinase C isotypes controlled by phosphoinositide 3-kinase through the protein kinase PDK1. Science 1998; 281: 2042–2045.
Park J, Leong ML, Buse P, Maiyar AC, Firestone GL, Hemmings BA . Serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) is a target of the PI 3-kinase-stimulated signaling pathway. EMBO J 1999; 18: 3024–3033.
Pullen N, Dennis PB, Andjelkovic M, Dufner A, Kozma SC, Hemmings BA et al. Phosphorylation and activation of p70s6k by PDK1. Science 1998; 279: 707–710.
Bayascas JR . PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2010; 346: 9–29.
Currie RA, Walker KS, Gray A, Deak M, Casamayor A, Downes CP et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in regulating the activity and localization of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. Biochem J 1999; 337: 575–583.
Fayard E, Xue G, Parcellier A, Bozulic L, Hemmings BA . Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a key mediator of the PI3K signaling pathway. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2010; 346: 31–56.
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM . Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor–mTOR complex. Science 2005; 307: 1098–1101.
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH, Sabatini DM . RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 1432–1437.
Garcia-Martinez JM, Alessi DR . mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) controls hydrophobic motif phosphorylation and activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 (SGK1). Biochem J 2008; 416: 375–385.
Balendran A, Biondi RM, Cheung PC, Casamayor A, Deak M, Alessi DR . A 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) docking site is required for the phosphorylation of protein kinase Czeta (PKCzeta) and PKC-related kinase 2 by PDK1. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 20806–20813.
Biondi RM, Kieloch A, Currie RA, Deak M, Alessi DR . The PIF-binding pocket in PDK1 is essential for activation of S6K and SGK, but not PKB. EMBO J 2001; 20: 4380–4390.
Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP . The PTEN-PI3K pathway: of feedbacks and cross-talks. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5527–5541.
Shinohara H, Maeda S, Watarai H, Kurosaki T . IkappaB kinase beta-induced phosphorylation of CARMA1 contributes to CARMA1 Bcl10 MALT1 complex formation in B cells. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 3285–3293.
Lawlor MA, Mora A, Ashby PR, Williams MR, Murray-Tait V, Malone L et al. Essential role of PDK1 in regulating cell size and development in mice. EMBO J 2002; 21: 3728–3738.
Takata M, Homma Y, Kurosaki T . Requirement of phospholipase C-gamma 2 activation in surface immunoglobulin M-induced B cell apoptosis. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 907–914.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999; 96: 857–868.
Kops GJ, Medema RH, Glassford J, Essers MA, Dijkers PF, Coffer PJ et al. Control of cell cycle exit and entry by protein kinase B-regulated forkhead transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 2025–2036.
Kurosaki T . Regulation of BCR signaling. Mol Immunol 2011; 48: 1287–1291.
Feldman RI, Wu JM, Polokoff MA, Kochanny MJ, Dinter H, Zhu D et al. Novel small molecule inhibitors of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 19867–19874.
Los M, Maddika S, Erb B, Schulze-Osthoff K . Switching Akt: from survival signaling to deadly response. Bioessays 2009; 31: 492–495.
Nogueira V, Park Y, Chen CC, Xu PZ, Chen ML, Tonic I et al. Akt determines replicative senescence and oxidative or oncogenic premature senescence and sensitizes cells to oxidative apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 458–470.
Yamazoe M, Sonoda E, Hochegger H, Takeda S . Reverse genetic studies of the DNA damage response in the chicken B lymphocyte line DT40. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004; 3: 1175–1185.
Nagashima T, Shigematsu N, Maruki R, Urano Y, Tanaka H, Shimaya A et al. Discovery of novel forkhead box O1 inhibitors for treating type 2 diabetes: improvement of fasting glycemia in diabetic db/db mice. Mol Pharmacol 2010; 78: 961–970.
Gray A, Olsson H, Batty IH, Priganica L, Peter Downes C . Nonradioactive methods for the assay of phosphoinositide 3-kinases and phosphoinositide phosphatases and selective detection of signaling lipids in cell and tissue extracts. Anal Biochem 2003; 313: 234–245.
Bayascas JR, Wullschleger S, Sakamoto K, Garcia-Martinez JM, Clacher C, Komander D et al. Mutation of the PDK1 PH domain inhibits protein kinase B/Akt, leading to small size and insulin resistance. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 3258–3272.
Hirai H, Sootome H, Nakatsuru Y, Miyama K, Taguchi S, Tsujioka K et al. MK-2206, an allosteric Akt inhibitor, enhances antitumor efficacy by standard chemotherapeutic agents or molecular targeted drugs in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2010; 9: 1956–1967.
Lindsley CW . The Akt/PKB family of protein kinases: a review of small molecule inhibitors and progress towards target validation: a 2009 update. Curr Top Med Chem 2010; 10: 458–477.
Denley A, Gymnopoulos M, Kang S, Mitchell C, Vogt PK . Requirement of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)trisphosphate in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-induced oncogenic transformation. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1132–1138.
Kang S, Denley A, Vanhaesebroeck B, Vogt PK . Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 1289–1294.
Jiang X, Chen S, Asara JM, Balk SP . Phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway activation in phosphate and tensin homolog (PTEN)-deficient prostate cancer cells is independent of receptor tyrosine kinases and mediated by the p110beta and p110delta catalytic subunits. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 14980–14989.
Najafov A, Shpiro N, Alessi DR . Akt is efficiently activated by PIF-pocket- and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-dependent mechanisms leading to resistance to PDK1 inhibitors. Biochem J 2012; 448: 285–295.
Shin HW, Hayashi M, Christoforidis S, Lacas-Gervais S, Hoepfner S, Wenk MR et al. An enzymatic cascade of Rab5 effectors regulates phosphoinositide turnover in the endocytic pathway. J Cell Biol 2005; 170: 607–618.
van den Bout I, Divecha N . PIP5K-driven PtdIns(4,5)P2 synthesis: regulation and cellular functions. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 3837–3850.
van Gorp AG, Pomeranz KM, Birkenkamp KU, Hui RC, Lam EW, Coffer PJ . Chronic protein kinase B (PKB/c-akt) activation leads to apoptosis induced by oxidative stress-mediated Foxo3a transcriptional up-regulation. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 10760–10769.
Stocker H, Andjelkovic M, Oldham S, Laffargue M, Wymann MP, Hemmings BA et al. Living with lethal PIP3 levels: viability of flies lacking PTEN restored by a PH domain mutation in Akt/PKB. Science 2002; 295: 2088–2091.
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME . Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K–Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001; 11: 297–305.
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E, Hemmings BA . PKB and the mitochondria: AKTing on apoptosis. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 21–30.
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG . The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 2002; 14: 381–395.
Wang JM, Chao JR, Chen W, Kuo ML, Yen JJ, Yang-Yen HF . The antiapoptotic gene mcl-1 is up-regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway through a transcription factor complex containing CREB. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6195–6206.
Bujor AM, Nakerakanti S, Morris E, Hant FN, Trojanowska M . Akt inhibition up-regulates MMP1 through a CCN2-dependent pathway in human dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol 2010; 19: 347–354.
Figueroa C, Vojtek AB . Akt negatively regulates translation of the ternary complex factor Elk-1. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5554–5561.
Song KS, Lee TJ, Kim K, Chung KC, Yoon JH . cAMP-responding element-binding protein and c-Ets1 interact in the regulation of ATP-dependent MUC5AC gene expression. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 26869–26878.
Kok K, Nock GE, Verrall EA, Mitchell MP, Hommes DW, Peppelenbosch MP et al. Regulation of p110delta PI 3-kinase gene expression. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5145.
Caron E, Ghosh S, Matsuoka Y, Ashton-Beaucage D, Therrien M, Lemieux S et al. A comprehensive map of the mTOR signaling network. Mol Syst Biol 2010; 6: 453.
Guertin DA, Guntur KV, Bell GW, Thoreen CC, Sabatini DM . Functional genomics identifies TOR-regulated genes that control growth and division. Curr Biol 2006; 16: 958–970.
Chandarlapaty S, Sawai A, Scaltriti M, Rodrik-Outmezguine V, Grbovic-Huezo O, Serra V et al. AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression of receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 58–71.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dario Alessi for providing Akti-1/2/3 (MK-2206) and for helpful discussions. This study was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB 773 and GRK 1302 (to SW and BS) and from the Interdisciplinary Center of Clinical Research, Faculty of Medicine, Tübingen (Nachwuchsgruppe 1866-0-0, to BS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dieterle, A., Böhler, P., Keppeler, H. et al. PDK1 controls upstream PI3K expression and PIP3 generation. Oncogene 33, 3043–3053 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting PI3K/Akt in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Alleviation: From Signaling Networks to Targeted Therapy
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Oncogenic potential of BEST4 in colorectal cancer via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling
Oncogene (2022)
-
A systematic molecular and pharmacologic evaluation of AKT inhibitors reveals new insight into their biological activity
British Journal of Cancer (2020)
-
MiR-128b is down-regulated in gastric cancer and negatively regulates tumour cell viability by targeting PDK1/Akt/NF-κB axis
Journal of Biosciences (2016)
-
Signaling mechanisms regulating B-lymphocyte activation and tolerance
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2015)