Abstract
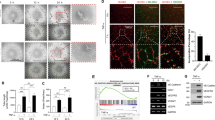
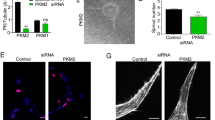
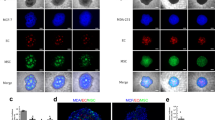
Tumor neo-vasculature is characterized by spatial coordination of endothelial cells with mural cells, which delivers oxygen and nutrients. Here, we explored a key role of the secreted glycoprotein YKL-40, a mesenchymal marker, in the interaction between endothelial cells and mesenchymal mural-like cells for tumor angiogenesis. Xenotransplantation of tumor-derived mural-like cells (GSDCs) expressing YKL-40 in mice developed extensive and stable blood vessels covered with more GSDCs than those in YKL-40 gene knockdown tumors. YKL-40 expressed by GSDCs was associated with increased interaction of neural cadherin/β-catenin/smooth muscle alpha actin; thus, mediating cell-cell adhesion and permeability. YKL-40 also induced the interaction of vascular endothelial cadherin/β-catenin/actin in endothelial cells (HMVECs). In cell co-culture systems, YKL-40 enhanced both GSDC and HMVEC contacts, restricted vascular leakage, and stabilized vascular networks. Collectively, the data inform new mechanistic insights into the cooperation of mural cells with endothelial cells induced by YKL-40 during tumor angiogenesis, and also enhance our understanding of YKL-40 in both mural and endothelial cell biology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- N-cadherin:
-
neural cadherin
- shRNA:
-
short-hairpin RNA gene knockdown
- VE-cadherin:
-
vascular endothelial cadherin
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- YKL-40:
-
human cartilage glycoprotein-39 or Chitinase-3-like-1.
References
Hanahan D . Signaling vascular morphogenesis and maintenance. Science 1997; 277: 48–50.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996; 86: 353–364.
Jain RK . Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat Med 2003; 9: 685–693.
Hellstrom M, Gerhardt H, Kalen M, Li X, Eriksson U, Wolburg H et al. Lack of pericytes leads to endothelial hyperplasia and abnormal vascular morphogenesis. Journal of Cell Biology 2001; 153: 543–553.
Bloch W, Huggel K, Sasaki T, Grose R, Bugnon P, Addicks K et al. The angiogenesis inhibitor endostatin impairs blood vessel maturation during wound healing. FASEB Journal 2000; 14: 2373–2376.
Armulik A, Genove G, Betsholtz C . Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell 2011; 21: 193–215.
Carmeliet P, Lampugnani MG, Moons L, Breviario F, Compernolle V, Bono F et al. Targeted deficiency or cytosolic truncation of the VE-cadherin gene in mice impairs VEGF-mediated endothelial survival and angiogenesis. Cell 1999; 98: 147–157.
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Lampugnani MG . The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. Journal of Cell Science 2008; 121: 2115–2122.
Orlova VV, Economopoulou M, Lupu F, Santoso S, Chavakis T . Junctional adhesion molecule-C regulates vascular endothelial permeability by modulating VE-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contacts. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2006; 203: 2703–2714.
Paik JH, Skoura A, Chae SS, Cowan AE, Han DK, Proia RL et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor regulation of N-cadherin mediates vascular stabilization. Genes & Development 2004; 18: 2392–2403.
Gerhardt H, Wolburg H, Redies C . N-cadherin mediates pericytic-endothelial interaction during brain angiogenesis in the chicken. Developmental Dynamics 2000; 218: 472–479.
Luo Y, High FA, Epstein JA, Radice GL . N-cadherin is required for neural crest remodeling of the cardiac outflow tract. Developmental Biology 2006; 299: 517–528.
Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM . The control of vascular integrity by endothelial cell junctions: molecular basis and pathological implications. Dev Cell 2009; 16: 209–221.
Vestweber D . VE-cadherin: the major endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and blood vessel formation. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2008; 28: 223–232.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK . Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011; 10: 417–427.
Huang FJ, You WK, Bonaldo P, Seyfried TN, Pasquale EB, Stallcup WB . Pericyte deficiencies lead to aberrant tumor vascularizaton in the brain of the NG2 null mouse. Developmental Biology 2010; 344: 1035–1046.
Abramsson A, Lindblom P, Betsholtz C . Endothelial and nonendothelial sources of PDGF-B regulate pericyte recruitment and influence vascular pattern formation in tumors. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2003; 112: 1142–1151.
Weis S, Cui J, Barnes L, Cheresh D . Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis. Journal of Cell Biology 2004; 167: 223–229.
Gavard J, Gutkind JS . VEGF controls endothelial-cell permeability by promoting the beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of VE-cadherin. Nature Cell Biology 2006; 8: 1223–1234.
Greenberg JI, Shields DJ, Barillas SG, Acevedo LM, Murphy E, Huang J et al. A role for VEGF as a negative regulator of pericyte function and vessel maturation. Nature 2008; 456: 809–813.
Stockmann C, Doedens A, Weidemann A, Zhang N, Takeda N, Greenberg JI et al. Deletion of vascular endothelial growth factor in myeloid cells accelerates tumorigenesis. Nature 2008; 456: 814–818.
Johansen JS, Williamson MK, Rice JS, Price PA . Identification of proteins secreted by human osteoblastic cells in culture. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research 1992; 7: 501–512.
Renkema GH, Boot RG, Au FL, Donker-Koopman WE, Strijland A, Muijsers AO et al. Chitotriosidase, a chitinase, and the 39-kDa human cartilage glycoprotein, a chitin-binding lectin, are homologues of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases secreted by human macrophages. European Journal of Biochemistry 1998; 251: 504–509.
Fusetti F, Pijning T, Kalk KH, Bos E, Dijkstra BW . Crystal structure and carbohydrate-binding properties of the human cartilage glycoprotein-39. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003; 278: 37753–37760.
Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ . Identification of a 38-kDa heparin-binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1995; 270: 13076–13083.
Rehli M, Krause SW, Andreesen R . Molecular characterization of the gene for human cartilage gp-39 (CHI3L1), a member of the chitinase protein family and marker for late stages of macrophage differentiation. Genomics 1997; 43: 221–225.
Kzhyshkowska J, Gratchev A, Goerdt S . Human chitinases and chitinase-like proteins as indicators for inflammation and cancer. Biomarker insights 2007; 2: 128–146.
Hu B, Trinh K, Figueira WF, Price PA . Isolation and sequence of a novel human chondrocyte protein related to mammalian members of the chitinase protein family. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996; 271: 19415–19420.
Nyirkos P, Golds EE . Human synovial cells secrete a 39 kDa protein similar to a bovine mammary protein expressed during the non-lactating period. Biochemical Journal 1990; 269: 265–268.
Jensen BV, Johansen JS, Price PA . High levels of serum HER-2/neu and YKL-40 independently reflect aggressiveness of metastatic breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 2003; 9: 4423–4434.
Cintin C, Johansen JS, Christensen IJ, Price PA, Sorensen S, Nielsen HJ . Serum YKL-40 and colorectal cancer. British Journal of Cancer 1999; 79: 1494–1499.
Hogdall EV, Johansen JS, Kjaer SK, Price PA, Christensen L, Blaakaer J et al. High plasma YKL-40 level in patients with ovarian cancer stage III is related to shorter survival. Oncology Reports 2003; 10: 1535–1538.
Bergmann OJ, Johansen JS, Klausen TW, Mylin AK, Kristensen JS, Kjeldsen E et al. High serum concentration of YKL-40 is associated with short survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Clinical Cancer Research 2005; 11: 8644–8652.
Hottinger AF, Iwamoto FM, Karimi S, Riedel E, Dantis J, Park J et al. YKL-40 and MMP-9 as serum markers for patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Annals of neurology 2011; 70: 163–169.
Pelloski CE, Mahajan A, Maor M, Chang EL, Woo S, Gilbert M et al. YKL-40 expression is associated with poorer response to radiation and shorter overall survival in glioblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research 2005; 11: 3326–3334.
Shao R, Hamel K, Petersen L, Cao QJ, Arenas RB, Bigelow C et al. YKL-40, a secreted glycoprotein, promotes tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2009; 28: 4456–4468.
Francescone RA, Scully S, Faibish M, Taylor SL, Oh D, Moral L et al. Role of YKL-40 in the angiogenesis, radioresistance, and progression of glioblastoma. The Journal of biological chemistry 2011; 286: 15332–15343.
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 157–173.
Francescone R, Scully S, Bentley B, Yan W, Taylor SL, Oh D et al. Glioblastoma-derived Tumor Cells Induce Vasculogenic Mimicry through Flk-1 Protein Activation. The Journal of biological chemistry 2012; 287: 24821–24831.
Faibish M, Francescone R, Bentley B, Yan W, Shao R . A YKL-40-neutralizing antibody blocks tumor angiogenesis and progression: a potential therapeutic agent in cancers. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2011; 10: 742–751.
Chambers RC, Leoni P, Kaminski N, Laurent GJ, Heller RA . Global expression profiling of fibroblast responses to transforming growth factor-beta1 reveals the induction of inhibitor of differentiation-1 and provides evidence of smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. American Journal of Pathology 2003; 162: 533–546.
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA . Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2002; 3: 349–363.
Elenbaas B, Weinberg RA . Heterotypic signaling between epithelial tumor cells and fibroblasts in carcinoma formation. Experimental Cell Research 2001; 264: 169–184.
Helfrich I, Scheffrahn I, Bartling S, Weis J, von Felbert V, Middleton M et al. Resistance to antiangiogenic therapy is directed by vascular phenotype, vessel stabilization, and maturation in malignant melanoma. The Journal of experimental medicine 2010; 207: 491–503.
Chen XL, Nam JO, Jean C, Lawson C, Walsh CT, Goka E et al. VEGF-induced vascular permeability is mediated by FAK. Dev Cell 2012; 22: 146–157.
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS . Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005; 438: 967–974.
Lambeng N, Wallez Y, Rampon C, Cand F, Christe G, Gulino-Debrac D et al. Vascular endothelial-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in angiogenic and quiescent adult tissues. Circ Res 2005; 96: 384–391.
Nakamura Y, Patrushev N, Inomata H, Mehta D, Urao N, Kim HW et al. Role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in vascular endothelial growth factor signaling and cell-cell adhesions in endothelial cells. Circ Res 2008; 102: 1182–1191.
Lin MI, Yu J, Murata T, Sessa WC . Caveolin-1-deficient mice have increased tumor microvascular permeability, angiogenesis, and growth. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2849–2856.
Shrivastava-Ranjan P, Rollin PE, Spiropoulou CF . Andes virus disrupts the endothelial cell barrier by induction of vascular endothelial growth factor and downregulation of VE-cadherin. Journal of virology 2010; 84: 11227–11234.
Gorbunova E, Gavrilovskaya IN, Mackow ER . Pathogenic hantaviruses Andes virus and Hantaan virus induce adherens junction disassembly by directing vascular endothelial cadherin internalization in human endothelial cells. Journal of virology 2010; 84: 7405–7411.
Shay-Salit A, Shushy M, Wolfovitz E, Yahav H, Breviario F, Dejana E et al. VEGF receptor 2 and the adherens junction as a mechanical transducer in vascular endothelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002; 99: 9462–9467.
Liu J, Liao S, Huang Y, Samuel R, Shi T, Naxerova K et al. PDGF-D improves drug delivery and efficacy via vascular normalization, but promotes lymphatic metastasis by activating CXCR4 in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 3638–3648.
Jayson GC, Parker GJ, Mullamitha S, Valle JW, Saunders M, Broughton L et al. Blockade of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta by CDP860, a humanized, PEGylated di-Fab', leads to fluid accumulation and is associated with increased tumor vascularized volume. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 973–981.
Hellberg C, Ostman A, Heldin CH . PDGF and vessel maturation, Recent results in cancer research. Fortschritte der Krebsforschung 2010; 180: 103–114.
Erber R, Thurnher A, Katsen AD, Groth G, Kerger H, Hammes HP et al. Combined inhibition of VEGF and PDGF signaling enforces tumor vessel regression by interfering with pericyte-mediated endothelial cell survival mechanisms. FASEB Journal 2004; 18: 338–340.
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N, Bergsland E, Hanahan D . Benefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2003; 111: 1287–1295.
Gerhardt H, Semb H . Pericytes: gatekeepers in tumour cell metastasis? Journal of molecular medicine (Berlin, Germany) 2008; 86: 135–144.
Yonenaga Y, Mori A, Onodera H, Yasuda S, Oe H, Fujimoto A et al. Absence of smooth muscle actin-positive pericyte coverage of tumor vessels correlates with hematogenous metastasis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Oncology 2005; 69: 159–166.
Yan W, Bentley B, Shao R . Distinct Angiogenic Mediators Are Required for Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor- and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-induced Angiogenesis: The Role of Cytoplasmic Tyrosine Kinase c-Abl in Tumor Angiogenesis. Molecular biology of the cell 2008; 19: 2278–2288.
Yan W, Cao QJ, Arenas RB, Bentley B, Shao R . GATA3 inhibits breast cancer metastasis through the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010; 285: 14042–14051.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NCI R01 CA120659 and CEAR grant, John Adams Innovation Institute, Massachusetts (RS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francescone, R., Ngernyuang, N., Yan, W. et al. Tumor-derived mural-like cells coordinate with endothelial cells: role of YKL-40 in mural cell-mediated angiogenesis. Oncogene 33, 2110–2122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.160
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
HOXA-AS2 promotes type I endometrial carcinoma via miRNA-302c-3p-mediated regulation of ZFX
Cancer Cell International (2020)
-
Tumor vasculature remolding by thalidomide increases delivery and efficacy of cisplatin
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Increased expression of Chitinase 3-like 1 and microvessel density predicts metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Tumor Biology (2014)