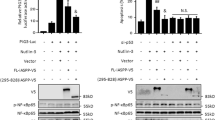
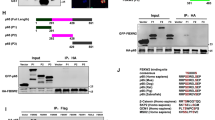
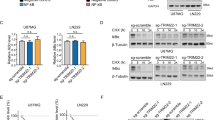
Abstract
As a tumor suppressor protein, the inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) has an important role in many cellular processes including cell cycle progression, proliferation, apoptosis, DNA damage response, tumor angiogenesis and contact inhibition. Here, we report that ING4 functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce nuclear factor-κB (NFκB)/p65 degradation. The plant homeodomain finger of ING4 interacted with p65 to undergo robust ubiquitination and degradation. ING4 bound to p65 and delivered the Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin to Lys-62 residue of p65, leading to ubiquitination of p65 and degradation. Lys-62 residue of p65 was required for ING4-mediated ubiquitination of p65 and degradation. Further analysis shows that C239 of ING4 was critical for ING4-induced p65 degradation. These findings demonstrate that ING4 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to induce ubiquitination of p65 and degradation, which is critical to terminate NFκB activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Coles AH, Jones SN . The ING gene family in the regulation of cell growth and tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 2009; 218: 45–57.
Zhang X, Xu LS, Wang ZQ, Wang KS, Li N, Cheng ZH et al. ING4 induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and enhances the chemosensitivity to DNA-damage agents in HepG2 cells. FEBS Lett 2004; 570: 7–12.
Xie Y, Zhang H, Sheng W, Xiang J, Ye Z, Yang J et al. Adenovirus-mediated ING4 expression suppresses lung carcinoma cell growth via induction of cell cycle alteration and apoptosis and inhibition of tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett 2008; 271: 105–116.
Cai L, Li X, Zheng S, Wang Y, Wang Y, Li H et al. Inhibitor of growth 4 is involved in melanomagenesis and induces growth suppression and apoptosis in melanoma cell line M14. Melanoma Res 2009; 19: 1–7.
Li X, Zhang Q, Cai L, Wang Y, Wang Q, Huang X et al. Inhibitor of growth 4 induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 via Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondria apoptosis pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2009; 135: 829–835.
Russell M, Berardi P, Gong W, Riabowol K . Grow-ING, ING proteins link cancer, senescence and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 2006; 312: 951–961.
Kim S, Chin K, Gray JW, Bishop JM . A screen for genes that suppress loss of contact inhibition: identification of ING4 as a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 16251–16256.
Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H, Demircan K, Gunduz E, Cengiz B, Ouchida M et al. Frequent deletion and down-regulation of ING4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 12p13, in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Gene 2005; 356: 109–117.
Nozell S, Laver T, Moseley D, Nowoslawski L, De Vos M, Atkinson GP et al. The ING4 tumor suppressor attenuates NF-kappaB activity at the promoters of target genes. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 6632–6645.
Unoki M, Shen JC, Zheng ZM, Harris CC . Novel splice variants of ING4 and their possible roles in the regulation of cell growth and motility. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 34677–34686.
Garkavtsev I, Kozin SV, Chernova O, Xu L, Winkler F, Brown E et al. The candidate tumour suppressor protein ING4 regulates brain tumour growth and angiogenesis. Nature 2004; 428: 328–332.
Hung T, Binda O, Champagne KS, Kuo AJ, Johnson K, Chang HY et al. ING4 mediates crosstalk between histone H3K4 trimethylation and H3 acetylation to attenuate cellular transformation. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 248–256.
Zhang X, Wang KS, Wang ZQ, Xu LS, Wang QW, Chen F et al. Nuclear localization signal of ING4 plays a key role in its binding to p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 331: 1032–1038.
Ozer A, Wu LC, Bruick RK . The candidate tumor suppressor ING4 represses activation of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 7481–7486.
Baldwin ASJ . The transcription factor NFκB and human disease. J Clin Invest 2001; 107: 3–6.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Signaling to NFκB. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 2195–2224.
Hou Y, Mortimer L, Chadee K . Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteinase 5 binds integrin on colonic cells and stimulates NFκB-mediated pro-inflammatory responses. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 35497–35504.
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y . Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NFκB activity. Annu Rev Immunol 2000; 18: 621–663.
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K . Structure, regulation and function of NFκB. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1994; 10: 405–455.
Saccani S, Marazzi I, Beg AA, Natoli G . Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor kappaB response. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 107–113.
Tanaka T, Grusby MJ, Kaisho T . PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-kappa B activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nature Immunol 2007; 8: 558–591.
Laney JD, Hochstrasser M . Substrate targeting in the ubiquitin system. Cell 1999; 97: 427–430.
Natoli G, Chiocca S . Nuclear ubiquitin ligases, NFκB degradation, and the control of inflammation. Sci Signal 2008; 1: pe1.
Byron SA, Min E, Thal TS, Hostetter G, Watanabe AT, Azorsa DO et al. Negative regulation of NF-κB by the ING4 tumor suppressor in breast cancer. PLoS One 2012; 7: e46823.
Coles AH, Gannon H, Cerny A, Kurt-Jones E, Jones SN . Inhibitor of growth-4 promotes IkappaB promoter activation to suppress NF-kappaB signaling and innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 11423–11428.
Shen JC, Unoki M, Ythier D, Duperray A, Varticovski L, Kumamoto K et al. Inhibitor of growth 4 suppresses cell spreading and cell migration by interacting with a novel binding partner, liprin alpha1. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2552–2558.
Wang QS, Li M, Zhang LY, Jin Y, Tong DD, Yu Y et al. Down-regulation of ING4 is associated with initiation and progression of lung cancer. Histopathology 2010; 57: 271–281.
Uchida D, Hatakeyama S, Matsushima A, Han H, Ishido S, Hotta H et al. AIRE functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 167–172.
Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CA . RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem 2009; 78: 399–434.
Joazeiro CA, Weissman AM . RING finger proteins: mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 2000; 102: 549–552.
Pickart CM, Fushman D . Polyubiquitin chains: polymeric protein signals. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2004; 8: 610–616.
Coscoy L, Ganem D . PHD domains and E3 ubiquitin ligases: viruses make the connection. Trends Cell Biol 2003; 13: 7–12.
Ivanov AV, Peng H, Yurchenko V, Yap KL, Negorev DG, Schultz DC et al. PHD domain-mediated E3 ligase activity directs intramolecular sumoylation of an adjacent bromodomain required for gene silencing. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 823–837.
Xu P, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, Cheng D, Xie Y, Robert J et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals the function of unconventional ubiquitin chains in proteasomal degradation. Cell 2009; 3: 133–1345.
Hou YZ, Gao FQ, Wang QH, Zhao JF, Flagg T, Zhang Y et al. Bcl2 impedes DNA mismatch repair by directly regulating the hMSH2-hMSH6 heterodimeric complex. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 9279–9287.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Start Fund of Jiangsu University (12JDG071). National Natural Science Foundation of China (81173592), Tianjin Applied Basic Research and Frontier Technological Program (11JCZDJC21100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, Q. et al. Inhibitor of growth 4 induces NFκB/p65 ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Oncogene 33, 1997–2003 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.135
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.135
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of ferroptosis on tumor progression and immunotherapy
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
MTSS1 suppresses mammary tumor-initiating cells by enhancing RBCK1-mediated p65 ubiquitination
Nature Cancer (2020)
-
Identification of the inhibitor of growth protein 4 (ING4) as a potential target in prostate cancer therapy
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2020)
-
Inhibitor of Growth 4 (ING4) is a positive regulator of rRNA synthesis
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Rapamycin-upregulated miR-29b promotes mTORC1-hyperactive cell growth in TSC2-deficient cells by downregulating tumor suppressor retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ)
Oncogene (2019)