Abstract
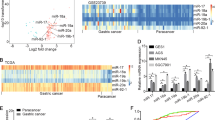
Inflammation has an important role in cancer development through various mechanisms. It has been shown that dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) that function as oncogenes or tumor suppressors contributes to tumorigenesis. However, the relationship between inflammation and cancer-related miRNA expression in tumorigenesis has not yet been fully understood. Using K19-C2mE and Gan mouse models that develop gastritis and gastritis-associated tumors, respectively, we found that 21 miRNAs were upregulated, and that 29 miRNAs were downregulated in gastric tumors in an inflammation-dependent manner. Among these miRNAs, the expression of miR-7, a possible tumor suppressor, significantly decreased in both gastritis and gastric tumors. Moreover, the expression of miR-7 in human gastric cancer was inversely correlated with the levels of interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α, suggesting that miR-7 downregulation is related to the severity of inflammatory responses. In the normal mouse stomach, miR-7 expression was at a basal level in undifferentiated gastric epithelial cells, and was induced during differentiation. Moreover, transfection of a miR-7 precursor into gastric cancer cells suppressed cell proliferation and soft agar colony formation. These results suggest that suppression of miR-7 expression is important for maintaining the undifferentiated status of gastric epithelial cells, and thus contributes to gastric tumorigenesis. Although epigenetic changes were not found in the CpG islands around miR-7-1 of gastritis and gastric tumor cells, we found that activated macrophage-derived small molecule(s) (<3 kDa) are responsible for miR-7 repression in gastric cancer cells. Furthermore, the miR-7 expression level significantly decreased in the inflamed gastric mucosa of Helicobacter-infected mice, whereas it increased in the stomach of germfree K19-C2mE and Gan mice wherein inflammatory responses were suppressed. Taken together, these results indicate that downregulation of tumor suppressor miR-7 is a novel mechanism by which the inflammatory response promotes gastric tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Ambros V . (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355.
Bartel DP . (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297.
Chen H, Shalom-Feuerstein R, Riley J, Zhang SD, Tucci P, Agostini M et al. (2010). miR-7 and miR-214 are specifically expressed during neuroblastoma differentiation, cortical development and embryonic stem cells differentiation, and control neurite outgrowth in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394: 921–927.
Cheng H, Bjerknes M, Amar J . (1984). Methods for the determination of epithelial cell kinetic parameters of human colonic epithelium isolated from surgical and biopsy. Gastroenterology 86: 78–85.
Chou YT, Lin HH, Lien YC, Wang YH, Hong CF, Kao YR et al. (2010). EGFR promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer Res 70: 8822–8831.
Coussens LM, Werb Z . (2002). Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420: 860–867.
Di Leva G, Croce CM . (2010). Roles of small RNAs in tumor formation. Trends Mol Med 16: 257–267.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . (2006). Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269.
Ichtchenko K, Bittner MA, Krasnoperov V, Little AR, Chepurny O, Holz RW et al. (1999). A novel ubiquitously expressed α-latrotoxin receptor is a member of the CIRL family of G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 274: 5491–5498.
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk ML, Struhl K . (2010). STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol Cell 39: 493–506.
Itadani H, Oshima H, Oshima M, Kotani H . (2009). Mouse gastric tumor models with prostaglandin E2 pathway activation show similar gene expression profiles to intestinal-type human gastric cancer. BMC Genomics 10: 615.
Jiang L, Liu X, Chen Z, Jin Y, Heidbreder CE, Kolokythas A et al. (2010). MicroRNA-7 targets IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biochem J 432: 199–205.
Katsuoka F, Motohashi H, Ishii T, Aburatani H, Engel JD, Yamamoto M . (2005). Genetic evidence that small maf proteins are essential for the activation of antioxidant response element-dependent genes. Mol Cell Biol 25: 8044–8051.
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y, Abounader R, Hawkinson M et al. (2008). MicroRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 68: 3566–3572.
Kondo Y, Shen L, Cheng AS, Ahmed S, Boumber Y, Charo C et al. (2008). Gene silencing in cancer by histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation independent of promoter methylation. Nat Genet 40: 741–750.
Korshunova I, Caroni P, Kolkova K, Berezin V, Bock E, Walmod PS . (2008). Characterization of BASP-1 mediated neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Res 86: 2201–2213.
Niwa T, Tsukamoto T, Toyoda T, Mori A, Tanaka H, Maekita T et al. (2010). Inflammatory processes triggered by Helicobacter pylori infection cause aberrant DNA methylation in gastric epithelial cells. Cancer Res 70: 1430–1440.
Nguyen HT, Dalmasso G, Yan Y, Laroui H, Dahan S, Mayer L et al. (2010). MicroRNA-7 modulates CD98 expression during intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 285: 1479–1489.
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng G, Baltimore D . (2007). MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 1604–1609.
Oshima H, Hioki K, Popivanova BK, Oguma K, van Rooijen N, Ishikawa TO et al. (2011). Prostaglandin E2 signaling and bacterial infection recruit tumor-promoting macrophages to mouse gastric tumors. Gastroenterology 140: 596–607.
Oshima H, Itadani H, Kotani H, Taketo MM, Oshima M . (2009). Induction of prostaglandin E2 pathway promotes gastric hamartoma development with suppression of bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Cancer Res 69: 2729–2733.
Oshima H, Matsunaga A, Fujimura T, Tsukamoto T, Taketo MM, Oshima M . (2006). Carcinogeniesis in mouse stomach by simultaneous activation of the Wnt signaling and prostaglandin E2 pathway. Gastroenterology 131: 1086–1095.
Oshima H, Oshima M, Inaba K, Taketo MM . (2004). Hyperplastic gastric tumors induced by activated macrophages in COX-2/mPGES-1 transgenic mice. EMBO J 23: 1669–1678.
Pull SL, Doherty JM, Mills JC, Gordon JI, Stappenbeck TS . (2005). Activated macrophages are an adaptive element of the colonic epithelial progenitor niche necessary for regenerative responses to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 99–104.
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R . (2004). Recognition of commensal microflora by Toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 118: 229–241.
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK, Kumar R . (2008). MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res 68: 8195–8200.
Sachdeva M, Zhu S, Wu F, Wu H, Walia V, Kumar S et al. (2009). p53 represses c-Myc through induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 3207–3212.
Saydam O, Senol O, Wurdinger T, Mizrak A, Ozdener GB, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO et al. (2011). miRNA-7 attenuation in Schwannoma tumors stimulates growth by upregulating three oncogenic signaling pathways. Cancer Res 71: 852–861.
Sonkoly E, Pivarcsi A . (2011). MicroRNAs in inflammation and response to injuries induced by environmental pollution. Mutat Res 717: 46–53.
Sonoshita M, Takaku K, Sasaki N, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F, Narumiya S et al. (2001). Acceleration of intestinal polyposis through prostaglandin receptor EP2 in ApcΔ716 knockout mice. Nat Med 7: 1048–1051.
Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Nojima M, Kai M, Yamano H, Yoshikawa K et al. (2010). Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect. Carcinogenesis 31: 2066–2073.
Takeshima H, Yamashita S, Shimazu T, Niwa T, Ushijima T . (2009). The presence of RNA polymerase II, active or stalled, predicts epigenetic fate of promoter CpG islands. Genome Res 19: 1974–1982.
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B et al. (2007). Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-α stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 179: 5082–5089.
Ventura A, Jacks T . (2009). MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 136: 586–591.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2257–2261.
Wang D, DuBois RN . (2010). Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 181–193.
Webster RJ, Giles KM, Price KJ, Zhang PM, Mattick JS, Leedman PJ . (2009). Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human cancer cells by microRNA-7. J Biol Chem 284: 5731–5741.
Wu H, Sun S, Tu K, Gao Y, Xie B, Krainer AR et al. (2010). A splicing-independent function of SF2/ASF in microRNA processing. Mol Cell 38: 67–77.
Yamashita S, Takahashi S, McDonell N, Watanabe N, Niwa T, Hosoya K et al. (2008). Methylation silencing of transforming growth factor-β receptor type II in rat prostate cancers. Cancer Res 68: 2112–2121.
Acknowledgements
We thank Manami Watanabe for her excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, D., Piao, YS., Yamashita, S. et al. Inflammation-induced repression of tumor suppressor miR-7 in gastric tumor cells. Oncogene 31, 3949–3960 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.558
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.558
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MiR-7 deficiency promotes Th1 polarization of CD4+T cells and enhances the antitumor effect in adoptive cell therapy for lung cancer
Immunologic Research (2024)
-
CD204-positive M2-like tumor-associated macrophages increase migration of gastric cancer cells by upregulating miR-210 to reduce NTN4 expression
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2024)
-
Role of non-coding RNA in immune microenvironment and anticancer therapy of gastric cancer
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Understanding the regulation of β-catenin expression and activity in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis: beyond destruction complex
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
Epigenetic silencing of miR-483-3p promotes acquired gefitinib resistance and EMT in EGFR-mutant NSCLC by targeting integrin β3
Oncogene (2018)