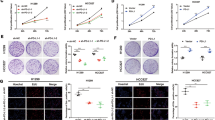
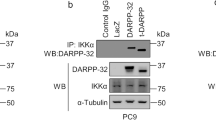
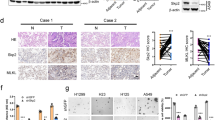
Abstract
Protein kinase C (PKC)ɛ, a member of the novel PKC family, has key roles in mitogenesis and survival in normal and cancer cells. PKCɛ is frequently overexpressed in epithelial cancers, particularly in lung cancer. Using a short-hairpin RNA approach, here we established that PKCɛ is required for non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) growth in vitro as well as tumor growth when inoculated into athymic mice. Moreover, sustained delivery of a PKCɛ-selective inhibitor peptide, ɛV1-2, reduced xenograft growth in mice. Both RNA interference depletion and pharmacological inhibition of PKCɛ caused a marked elevation in the number of apoptotic cells in NSCLC tumors. PKCɛ-depleted NSCLC cells show elevated expression of pro-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family, caspase recruitment domain-containing proteins and tumor necrosis factor ligands/receptor superfamily members. Moreover, a Gene Set Enrichment Analysis revealed that a vast majority of the genes changed in PKCɛ-depleted cells were also deregulated in human NSCLC. Our results strongly suggest that PKCɛ is required for NSCLC cell survival and maintenance of NSCLC tumor growth. Therefore, PKCɛ may represent an attractive therapeutic target for NSCLC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae KM, Wang H, Jiang G, Chen MG, Lu L, Xiao L . (2007). Protein kinase C epsilon is overexpressed in primary human non-small cell lung cancers and functionally required for proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells in a p21/Cip1-dependent manner. Cancer Res 67: 6053–6063.
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M, Cohen P . (2003). The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem J 371 (Pt 1): 199–204.
Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M, Shpiro N, Hastie CJ, McLauchlan H et al. (2007). The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J 408: 297–315.
Barr LF, Mabry M, Nelkin BD, Tyler G, May WS, Baylin SB . (1991). c-myc gene-induced alterations in protein kinase C expression: a possible mechanism facilitating myc-ras gene complementation. Cancer Res 51: 5514–5519.
Barry OP, Kazanietz MG . (2001). Protein kinase C isozymes, novel phorbol ester receptors and cancer chemotherapy. Curr Pharm Des 7: 1725–1744.
Basu A, Sivaprasad U . (2007). Protein kinase C epsilon makes the life and death decision. Cell Signal 19: 1633–1642.
Begley R, Liron T, Baryza J, Mochly-Rosen D . (2004). Biodistribution of intracellularly acting peptides conjugated reversibly to Tat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318: 949–954.
Benavides F, Blando J, Perez CJ, Garg R, Conti CJ, DiGiovanni J et al. (2011). Transgenic overexpression of PKC epsilon in the mouse prostate induces preneoplastic lesions. Cell Cycle 10: 268–277.
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J, Li C, Monti S, Vasa P et al. (2001). Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 13790–13795.
Black JD . (2000). Protein kinase C-mediated regulation of the cell cycle. Front Biosci 5: D406–D423.
Brodie C, Blumberg PM . (2003). Regulation of cell apoptosis by protein kinase c delta. Apoptosis 8: 19–27.
Budas GR, Koyanagi T, Churchill EN, Mochly-Rosen D . (2007). Competitive inhibitors and allosteric activators of protein kinase C isoenzymes: a personal account and progress report on transferring academic discoveries to the clinic. Biochem Soc Trans 35 (Pt 5): 1021–1026.
Caino MC, Meshki J, Kazanietz MG . (2009). Hallmarks for senescence in carcinogenesis: novel signaling players. Apoptosis 14: 392–408.
Caino MC, von Burstin VA, Lopez-Haber C, Kazanietz MG . (2011). Differential regulation of gene expression by protein kinase C isozymes as determined by genome-wide expression analysis. J Biol Chem 286: 11254–11264.
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P . (2000). Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351 (Pt 1): 95–105.
Felber M, Sonnemann J, Beck JF . (2007). Inhibition of novel protein kinase C-epsilon augments TRAIL-induced cell death in A549 lung cancer cells. Pathol Oncol Res 13: 295–301.
Fleischman LF, Chahwala SB, Cantley L . (1986). Ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science 231: 407–410.
Goekjian PG, Jirousek MR . (2001). Protein kinase C inhibitors as novel anticancer drugs. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 10: 2117–2140.
Gorin MA, Pan Q . (2009). Protein kinase C epsilon: an oncogene and emerging tumor biomarker. Mol Cancer 8: 9.
Gray MO, Karliner JS, Mochly-Rosen D . (1997). A selective epsilon-protein kinase C antagonist inhibits protection of cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 272: 30945–30951.
Griner EM, Kazanietz MG . (2007). Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 281.
Han EK, Cacace AM, Sgambato A, Weinstein IB . (1995). Altered expression of cyclins and c-fos in R6 cells that overproduce PKC epsilon. Carcinogenesis 16: 2423–2428.
Hsiao WL, Housey GM, Johnson MD, Weinstein IB . (1989). Cells that overproduce protein kinase C are more susceptible to transformation by an activated H-ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 9: 2641–2647.
Inagaki K, Begley R, Ikeno F, Mochly-Rosen D . (2005). Cardioprotection by epsilon-protein kinase C activation from ischemia: continuous delivery and antiarrhythmic effect of an epsilon-protein kinase C-activating peptide. Circulation 111: 44–50.
Jansen AP, Verwiebe EG, Dreckschmidt NE, Wheeler DL, Oberley TD, Verma AK . (2001). Protein kinase C-epsilon transgenic mice: a unique model for metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 61: 808–812.
Koyanagi T, Noguchi K, Ootani A, Inagaki K, Robbins RC, Mochly-Rosen D . (2007). Pharmacological inhibition of epsilon PKC suppresses chronic inflammation in murine cardiac transplantation model. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43: 517–522.
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J . (2010). Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 141: 1117–1134.
Lu D, Huang J, Basu A . (2006). Protein kinase C\{epsilon\} activates prote. J Biol Chem 281: 22799–22807.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M . (2003). RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 459–465.
Matyas GR, Fishman PH . (1989). Lipid signalling pathways in normal and ras-transfected NIH/3T3 cells. Cell Signal 1: 395–404.
McJilton MA, Van Sikes C, Wescott GG, Wu D, Foreman TL, Gregory CW et al. (2003). Protein kinase C epsilon interacts with Bax and promotes survival of human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 22: 7958–7968.
Mischak H, Goodnight JA, Kolch W, Martiny-Baron G, Schaechtle C, Kazanietz MG et al. (1993). Overexpression of protein kinase C-delta and -epsilon in NIH 3T3 cells induces opposite effects on growth, morphology, anchorage dependence, and tumorigenicity. J Biol Chem 268: 6090–6096.
Mochly-Rosen D, Kauvar LM . (1998). Modulating protein kinase C signal transduction. Adv Pharmacol 44: 91–145.
Nakagawa M, Oliva JL, Kothapalli D, Fournier A, Assoian RK, Kazanietz MG . (2005). Phorbol ester-induced G1 phase arrest selectively mediated by protein kinase C delta-dependent induction of p21. J Biol Chem 280: 33926–33934.
Okhrimenko H, Lu W, Xiang C, Hamburger N, Kazimirsky G, Brodie C . (2005). Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates the apoptosis and survival of glioma cells. Cancer Res 65: 7301–7309.
Oliva JL, Caino MC, Senderowicz AM, Kazanietz MG . (2008). S-Phase-specific activation of PKC alpha induces senescence in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283: 5466–5476.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. (2004). EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304: 1497–1500.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I et al. (2004). EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 13306–13311.
Parker PJ, Murray-Rust J . (2004). PKC at a glance. J Cell Sci 117 (Pt 2): 131–132.
Perletti GP, Folini M, Lin HC, Mischak H, Piccinini F, Tashjian Jr AH. . (1996). Overexpression of protein kinase C epsilon is oncogenic in rat colonic epithelial cells. Oncogene 12: 847–854.
Preiss J, Loomis CR, Bishop WR, Stein R, Niedel JE, Bell RM . (1986). Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem 261: 8597–8600.
Rusch V, Baselga J, Cordon-Cardo C, Orazem J, Zaman M, Hoda S et al. (1993). Differential expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in primary non-small cell lung cancers and adjacent benign lung. Cancer Res 53 (10 Suppl): 2379–2385.
Sekido Y, Fong KM, Minna JD . (2003). Molecular genetics of lung cancer. Annu Rev Med 54: 73–87.
Serova M, Ghoul A, Benhadji KA, Cvitkovic E, Faivre S, Calvo F et al. (2006). Preclinical and clinical development of novel agents that target the protein kinase C family. Semin Oncol 33: 466–478.
Slupsky JR, Kamiguti AS, Harris RJ, Cawley JC, Zuzel M . (2007). Central role of protein kinase C epsilon in constitutive activation of ERK1/2 and Rac1 in the malignant cells of hairy cell leukemia. Am J Pathol 170: 745–754.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 15545–15550.
Toker A . (1998). Signaling through protein kinase C. Front Biosci 3: D1134–D1147.
Acknowledgements
D M-R is the founder of KAI Pharmaceuticals, a company that uses PKC regulators in the clinic. However, none of the work in her lab is supported by the company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caino, M., Lopez-Haber, C., Kim, J. et al. Proteins kinase Cɛ is required for non-small cell lung carcinoma growth and regulates the expression of apoptotic genes. Oncogene 31, 2593–2600 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.428
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.428
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Distinctive requirement of PKCε in the control of Rho GTPases in epithelial and mesenchymally transformed lung cancer cells
Oncogene (2019)
-
PKCα is required for Akt-mTORC1 activation in non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) with EGFR mutation
Oncogene (2019)
-
COX-2 mediates pro-tumorigenic effects of PKCε in prostate cancer
Oncogene (2018)
-
Inflammation-Related Genetic Variants Predict Toxicity Following Definitive Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2014)
-
Protein kinase C and cancer: what we know and what we do not
Oncogene (2014)