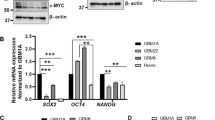
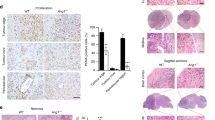
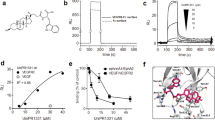
Abstract
Angiogenesis in glioblastoma is largely dependent on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signalling. Consistently, the VEGF coreceptor NRP1 promotes angiogenesis and tumour growth in gliomas. Here, we provide data showing that an innovative peptidic tool targeting the transmembrane domain of NRP1 efficiently blocks rat and human glioma growth in vivo. We show both in vivo and in vitro that the antitumour effect results from the anti-proliferative, anti-migratory and anti-angiogenic properties of the compound. The proposed NRP1 antagonizing peptide is therefore a promising novel class of anti-angiogenic drugs that might prolong glioma patient survival. Our results finally show for the first time that the transmembrane domain of important signalling receptors can be antagonized in vivo thereby providing a new avenue towards the development of atypical antagonists with strong therapeutic potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagci T, Wu JK, Pfannl R, Ilag LL, Jay DG . (2009). Autocrine semaphorin 3A signaling promotes glioblastoma dispersal. Oncogene 28: 3537–3550.
Bagri A, Tessier-Lavigne M . (2002). Neuropilins as semaphorin receptors: in vivofunctions in neuronal cell migration and axon guidance. Adv Exp Med Biol 515: 13–31.
Bargmann CI, Weinberg RA . (1988). Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J 7: 2043–2052.
Barr MP, Byrne AM, Duffy AM, Condron CM, Devocelle M, Harriott P et al. (2005). A peptide corresponding to the neuropilin-1-binding site on VEGF(165) induces apoptosis of neuropilin-1-expressing breast tumour cells. Br J Cancer 92: 328–333.
Bedjeguelal K, Bienayme H, Dumoulin A, Poigny S, Schmitt P, Tam E . (2006). Discovery of protein-protein binding disruptors using multi-component condensations small molecules. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 3998–4001.
Bennasroune A, Gardin A, Aunis D, Cremel G, Hubert P . (2004). Tyrosine kinase receptors as attractive targets of cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 50: 23–38.
Forbes LV, Gale RE, Pizzey A, Pouwels K, Nathwani A, Linch DC . (2002). An activating mutation in the transmembrane domain of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 21: 5981–5989.
Gamse JT, Shen YC, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raymond PA, Halpern ME et al. (2002). Otx5 regulates genes that show circadian expression in the zebrafish pineal complex. Nat Genet 30: 117–121.
Garcia-Verdugo JM, Doetsch F, Wichterle H, Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A . (1998). Architecture and cell types of the adult subventricular zone: in search of the stem cells. J Neurobiol 36: 234–248.
Giordano RJ, Anobom CD, Cardo-Vila M, Kalil J, Valente AP, Pasqualini R et al. (2005). Structural basis for the interaction of a vascular endothelial growth factor mimic peptide motif and its corresponding receptors. Chem Biol 12: 1075–1083.
Goldbrunner RH, Wagner S, Roosen K, Tonn JC . (2000). Models for assessment of angiogenesis in gliomas. J Neurooncol 50: 53–62.
Grobben B, De Deyn PP, Slegers H . (2002). Rat C6 glioma as experimental model system for the study of glioblastoma growth and invasion. Cell Tissue Res 310: 257–270.
Guttmann-Raviv N, Kessler O, Shraga-Heled N, Lange T, Herzog Y, Neufeld G . (2006). The neuropilins and their role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Lett 231: 1–11.
Hong TM, Chen YL, Wu YY, Yuan A, Chao YC, Chung YC et al. (2007). Targeting neuropilin 1 as an antitumor strategy in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13: 4759–4768.
Hu B, Guo P, Bar-Joseph I, Imanishi Y, Jarzynka MJ, Bogler O et al. (2007). Neuropilin-1 promotes human glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine pathway. Oncogene 26: 5577–5586.
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT . (2007). Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 610–622.
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS . (2006). Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3: 24–40.
Jia H, Bagherzadeh A, Hartzoulakis B, Jarvis A, Lohr M, Shaikh S et al. (2006). Characterization of a bicyclic peptide neuropilin-1 (NP-1) antagonist (EG3287) reveals importance of vascular endothelial growth factor exon 8 for NP-1 binding and role of NP-1 in KDR signaling. J Biol Chem 281: 13493–13502.
Jocic Z, Staton RD . (1993). Reduplication after right middle cerebral artery infarction. Brain Cogn 23: 222–230.
Kelland LR . (2004). Of mice and men: values and liabilities of the athymic nude mouse model in anticancer drug development. Eur J Cancer 40: 827–836.
Kienlen-Campard P, Tasiaux B, Van Hees J, Li M, Huysseune S, Sato T et al. (2008). Amyloidogenic processing but not amyloid precursor protein (APP) intracellular C-terminal domain production requires a precisely oriented APP dimer assembled by transmembrane GxxxG motifs. J Biol Chem 283: 7733–7744.
Klosen P, Maessen X, van den Bosch de Aguilar P . (1993). PEG embedding for immunocytochemistry: application to the analysis of immunoreactivity loss during histological processing. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 455–463.
Lemmon MA, Flanagan JM, Treutlein HR, Zhang J, Engelman DM . (1992). Sequence specificity in the dimerization of transmembrane alpha-helices. Biochemistry 31: 12719–12725.
Marchesi VT . (2005). An alternative interpretation of the amyloid Abeta hypothesis with regard to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 9093–9098.
Meyers GA, Orlow SJ, Munro IR, Przylepa KA, Jabs EW . (1995). Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) transmembrane mutation in Crouzon syndrome with Acanthosis nigricans. Nat Genet 11: 462–464.
Nasarre C, Koncina E, Labourdette G, Cremel G, Roussel G, Aunis D et al. (2009). Neuropilin-2 acts as a modulator of Sema3A-dependent glioma cell migration. Cell Adh Migr 3: 383–389.
Nasarre P, Kusy S, Constantin B, Castellani V, Drabkin HA, Bagnard D et al. (2005). Semaphorin SEMA3F has a repulsing activity on breast cancer cells and inhibits E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Neoplasia 7: 180–189.
Orian-Rousseau V, Ponta H . (2008). Adhesion proteins meet receptors: a common theme? Adv Cancer Res 101: 63–92.
Roth L, Nasarre C, Dirrig-Grosch S, Aunis D, Cremel G, Hubert P et al. (2008). Transmembrane domain interactions control biological functions of neuropilin-1. Mol Biol Cell 19: 646–654.
Senes A, Engel DE, DeGrado WF . (2004). Folding of helical membrane proteins: the role of polar, GxxxG-like and proline motifs. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14: 465–479.
Slimani H, Guenin E, Briane D, Coudert R, Charnaux N, Starzec A et al. (2006). Lipopeptide-based liposomes for DNA delivery into cells expressing neuropilin-1. J Drug Target 14: 694–706.
Starzec A, Vassy R, Martin A, Lecouvey M, Di Benedetto M, Crepin M et al. (2006). Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of peptide inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Life Sci 79: 2370–2381.
Taguchi A, Soma T, Tanaka H, Kanda T, Nishimura H, Yoshikawa H et al. (2004). Administration of CD34+ cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model. J Clin Invest 114: 330–338.
Tessitore A, Sinisi AA, Pasquali D, Cardone M, Vitale D, Bellastella A et al. (1999). A novel case of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A associated with two de novo mutations of the RET protooncogene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84: 3522–3527.
Tirand L, Frochot C, Vanderesse R, Thomas N, Trinquet E, Pinel S et al. (2006). A peptide competing with VEGF165 binding on neuropilin-1 mediates targeting of a chlorin-type photosensitizer and potentiates its photodynamic activity in human endothelial cells. J Control Release 111: 153–164.
Uitenbroek DG . (1997). Binomial SISA. http://www.quantitativeskills.com/sisa/distributions/binomial.htm.
Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M, Perret GY . (2004). Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in women with breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. Cancer Res 64: 2941–2955.
Wang AC, Dai X, Luu B, Conrad DJ . (2001). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma regulates airway epithelial cell activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24: 688–693.
Webster MK, Donoghue DJ . (1996). Constitutive activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 by the transmembrane domain point mutation found in achondroplasia. EMBO J 15: 520–527.
Weiner DB, Liu J, Cohen JA, Williams WV, Greene MI . (1989). A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature 339: 230–231.
Williams G, Eickholt BJ, Maison P, Prinjha R, Walsh FS, Doherty P . (2005). A complementary peptide approach applied to the design of novel semaphorin/neuropilin antagonists. J Neurochem 92: 1180–1190.
Xu L, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Chung DC, Lauwers GY . et al. (2009). Direct evidence that bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody, up-regulates SDF1alpha, CXCR4, CXCL6, and neuropilin 1 in tumors from patients with rectal cancer. Cancer Res 69: 7905–7910.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Sophie Reibel-Foisset and Mr Nicolas Lethenet for excellent assistance with in vivo experiments and animal care. This work was supported by INSERM, ACI JC (No. 5327), ARC, ANR Emergence bio, FRC/Rotary international to Dominique Bagnard. Cécile Nasarre was supported by Pharmaxon and La Ligue Contre le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasarre, C., Roth, M., Jacob, L. et al. Peptide-based interference of the transmembrane domain of neuropilin-1 inhibits glioma growth in vivo. Oncogene 29, 2381–2392 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Investigating the role of peptides in effective therapies against cancer
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
Manipulating oligodendrocyte intrinsic regeneration mechanism to promote remyelination
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Neuropilin-1 is associated with clinicopathology of gastric cancer and contributes to cell proliferation and migration as multifunctional co-receptors
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2016)
-
Semaphorin 3A upregulates FOXO 3a-dependent MelCAM expression leading to attenuation of breast tumor growth and angiogenesis
Oncogene (2015)
-
Nanoparticles coated with the tumor-penetrating peptide iRGD reduce experimental breast cancer metastasis in the brain
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2015)