Abstract
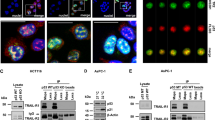
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α factor (LITAF) is a multiple functional molecule whose sequence is identical to the small integral membrane protein of the lysosome/late endosome. LITAF was initially identified as a transcription factor that activates transcription of proinflammatory cytokine in macrophages in response to LPS. Mutations of the LITAF gene are associated with a genetic disease, called Charcot–Marie–Tooth syndrome. Recently, we have reported that mRNA levels of LITAF and TNF superfamily member 15 (TNFSF15) are upregulated by 5′ adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK). The present study further assesses their biological functions. Thus, we show that 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside (AICAR), a pharmacological activator of AMPK, increases the abundance of LITAF and TNFSF15 in LNCaP and C4-2 prostate cancer cells, which is abrogated by small hairpin RNA (shRNA) or the dominant-negative mutant of AMPK α1 subunit. Our data further demonstrate that AMPK activation upregulates the transcription of LITAF. Intriguingly, silencing LITAF by shRNA enhances proliferation, anchorage-independent growth of these cancer cells and tumor growth in the xenograft model. In addition, our study reveals that LITAF mediates the effect of AMPK by binding to a specific sequence in the promoter region. Furthermore, we show that TNFSF15 remarkably inhibits the growth of prostate cancer cells and bovine aortic endothelial cells in vitro, with a more potent effect toward the latter. In conjuncture, intratumoral injection of TNFSF15 significantly reduces the size of tumors and number of blood vessels and induces changes that are characteristic of tumor cell differentiation. Therefore, our studies for the first time establish the regulatory axis of AMPK–LITAF–TNFSF15 and also suggest that LITAF may function as a tumor suppressor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- AICAR:
-
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside
- BAEC:
-
bovine aortic endothelial cell
- CMT1C:
-
Charcot–Marie–Tooth type 1C disease, an autosomal genetic disease with demyelinating periphery nervous system
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- LKB1:
-
liver kinase B, also named serine/threonine kinase 11 (STK11)
- LITAF:
-
lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor α factor
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- SIMPLE:
-
small integral membrane protein of the lysosome/late endosome
- TNFSF15:
-
tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 15
References
Bayry J . (2010). Immunology: TL1A in the inflammatory network in autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6: 67–68.
Beauvais K, Furby A, Latour P . (2006). Clinical, electrophysiological and molecular genetic studies in a family with X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy presenting a novel mutation in GJB1 promoter and a rare polymorphism in LITAF/SIMPLE. Neuromuscul Disord 16: 14–18.
Bennett CL, Shirk AJ, Huynh HM, Street VA, Nelis E, Van Maldergem L et al. (2004). SIMPLE mutation in demyelinating neuropathy and distribution in sciatic nerve. Ann Neurol 55: 713–720.
Chang JY, He RY, Lin HP, Hsu LJ, Lai FJ, Hong Q et al. (2010). Signaling from membrane receptors to tumor suppressor WW domain-containing oxidoreductase. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235: 796–804.
Hardie DG . (2007). AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 774–785.
Haridas V, Shrivastava A, Su J, Yu GL, Ni J, Liu D et al. (1999). VEGI, a new member of the TNF family activates nuclear factor-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase and modulates cell growth. Oncogene 18: 6496–6504.
Hong YH, Lillehoj HS, Lee SH, Park DW, Lillehoj EP . (2006). Molecular cloning and characterization of chicken lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha factor (LITAF). Dev Comp Immunol 30: 919–929.
Hou W, Medynski D, Wu S, Lin X, Li LY . (2005). VEGI-192, a new isoform of TNFSF15, specifically eliminates tumor vascular endothelial cells and suppresses tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res 11: 5595–5602.
Latour P, Gonnaud PM, Ollagnon E, Chan V, Perelman S, Stojkovic T et al. (2006). SIMPLE mutation analysis in dominant demyelinating Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: three novel mutations. J Peripher Nerv Syst 11: 148–155.
Ludes-Meyers JH, Kil H, Bednarek AK, Drake J, Bedford MT, Aldaz CM . (2004). WWOX binds the specific proline-rich ligand PPXY: identification of candidate interacting proteins. Oncogene 23: 5049–5055.
Luo Z, Zang M, Guo W . (2010). AMPK as a metabolic tumor suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growth. Future Oncol 6: 457–470.
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V et al. (2007). Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 109: 271–280.
Myokai F, Takashiba S, Lebo R, Amar S . (1999). A novel lipopolysaccharide-induced transcription factor regulating tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression: molecular cloning, sequencing, characterization, and chromosomal assignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4518–4523.
Nelson JD, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K . (2006). Protocol for the fast chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method. Nat Protoc 1: 179–185.
Niemann A, Berger P, Suter U . (2006). Pathomechanisms of mutant proteins in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neuromol Med 8: 217–242.
Pan X, Wang Y, Zhang M, Pan W, Qi ZT, Cao GW . (2004). Effects of endostatin-vascular endothelial growth inhibitor chimeric recombinant adenoviruses on antiangiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 10: 1409–1414.
Parr C, Gan CH, Watkins G, Jiang WG . (2006). Reduced vascular endothelial growth inhibitor (VEGI) expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Angiogenesis 9: 73–81.
Picornell Y, Mei L, Taylor K, Yang H, Targan SR, Rotter JI . (2007). TNFSF15 is an ethnic-specific IBD gene. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13: 1333–1338.
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (1997). A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 389: 300–305.
Sethi G, Sung B, Aggarwal BB . (2009). Therapeutic potential of VEGI/TL1A in autoimmunity and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 647: 207–215.
Stucchi A, Reed K, O'Brien M, Cerda S, Andrews C, Gower A et al. (2006). A new transcription factor that regulates TNF-alpha gene expression, LITAF, is increased in intestinal tissues from patients with CD and UC. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12: 581–587.
Tang X, Fenton MJ, Amar S . (2003). Identification and functional characterization of a novel binding site on TNF-alpha promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 4096–4101.
Tang X, Marciano DL, Leeman SE, Amar S . (2005). LPS induces the interaction of a transcription factor, LPS-induced TNF-alpha factor, and STAT6(B) with effects on multiple cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 5132–5137.
Tang X, Metzger D, Leeman S, Amar S . (2006). LPS-induced TNF-alpha factor (LITAF)-deficient mice express reduced LPS-induced cytokine: evidence for LITAF-dependent LPS signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 13777–13782.
Tang X, Molina M, Amar S . (2007). p53 short peptide (p53pep164) regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-β/cytokine expression. Cancer Res 67: 1308–1316.
Xiang X, Saha AK, Wen R, Ruderman NB, Luo Z . (2004). AMP-activated protein kinase activators can inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells by multiple mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321: 161–167.
Xiang X, Zang M, Waelde CA, Wen R, Luo Z . (2002). Phosphorylation of 338SSYY341 regulates specific interaction between Raf-1 and MEK1. J Biol Chem 277: 44996–45003.
Young HA, Tovey MG . (2006). TL1A: a mediator of gut inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 8303–8304.
Yue TL, Ni J, Romanic AM, Gu JL, Keller P, Wang C et al. (1999). TL1, a novel tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine, induces apoptosis in endothelial cells. Involvement of activation of stress protein kinases (stress-activated protein kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase) and caspase-3-like protease. J Biol Chem 274: 1479–1486.
Zhai Y, Ni J, Jiang GW, Lu J, Xing L, Lincoln C et al. (1999a). VEGI, a novel cytokine of the tumor necrosis factor family, is an angiogenesis inhibitor that suppresses the growth of colon carcinomas in vivo. FASEB J 13: 181–189.
Zhai Y, Yu J, Iruela-Arispe L, Huang WQ, Wang Z, Hayes AJ et al. (1999b). Inhibition of angiogenesis and breast cancer xenograft tumor growth by VEGI, a novel cytokine of the TNF superfamily. Int J Cancer 82: 131–136.
Zhang BB, Zhou G, Li C . (2009). AMPK: an emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 9: 407–416.
Zhou J, Huang W, Tao R, Ibaragi S, Lan F, Ido Y et al. (2009). Inactivation of AMPK alters gene expression and promotes growth of prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 28: 1993–2002.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NIH grants (R01 CA118918 to ZL, R01 DE014079 to SA and CA124490 to CC). We thank Dr Zhixiong Xiao (BUMC) for providing p53 shRNA pSuperRetro construct as a generous gift. We are also thankful to Miss Siu Wong for her assistance in animal dissection, to Dr Wen Guo for helping us with confirmatory qPCR analysis and to Dr Mengwei Zang for her advice on statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Yang, Z., Tsuji, T. et al. LITAF and TNFSF15, two downstream targets of AMPK, exert inhibitory effects on tumor growth. Oncogene 30, 1892–1900 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.575
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.575
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How metformin affects various malignancies by means of microRNAs: a brief review
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
LITAF Enhances Radiosensitivity of Human Glioma Cells via the FoxO1 Pathway
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
The regulation effect of AMPK in immune related diseases
Science China Life Sciences (2018)
-
GILP family: a stress-responsive group of plant proteins containing a LITAF motif
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2018)
-
Interferon-γ produced by tumor-infiltrating NK cells and CD4+ T cells downregulates TNFSF15 expression in vascular endothelial cells
Angiogenesis (2014)