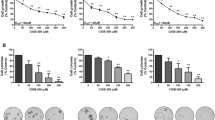
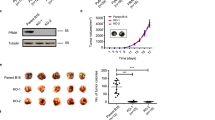
Abstract
Metastasis is the major reason for breast cancer-related deaths. Although there is a host of indirect evidence for a role of protein kinase C (PKC) α in primary breast cancer growth, its role in the molecular pathways leading to metastasis has not been studied comprehensively. By treating mice with αV5-3, a novel peptide inhibitor selective for PKCα, we were able to determine how PKCα regulates metastasis of mammary cancer cells using a syngeneic and orthotopic model. The primary tumor growth was not affected by αV5-3 treatment. However, the mortality rate was reduced and metastasis in the lung decreased by more than 90% in the αV5-3-treated mice relative to the control-treated mice. αV5-3 treatment reduced intravasation by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activities. αV5-3 treatment also reduced lung seeding of tumor cells and decreased cell migration, effects that were accompanied by a reduction in nuclear factor kappa B activity and cell surface levels of the CXCL12 receptor, CXCR4. αV5-3 treatment caused no apparent toxicity in non-tumor-bearing naïve mice. Rather, inhibiting PKCα protected against liver damage and increased the number of immune cells in tumor-bearing mice. Importantly, αV5-3 showed superior efficacy relative to anti-CXCR4 antibody in reducing metastasis in vivo. Together, these data show that pharmacological inhibition of PKCα effectively reduces mammary cancer metastasis by targeting intravasation and lung seeding steps in the metastatic process and suggest that PKCα-specific inhibitors, such as αV5-3, can be used to study the mechanistic roles of PKCα specifically and may provide a safe and effective treatment for the prevention of lung metastasis of breast cancer patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affara NI, Coussens LM . (2007). IKKalpha at the crossroads of inflammation and metastasis. Cell 129: 25–26.
Alsayed Y, Ngo H, Runnels J, Leleu X, Singha UK, Pitsillides CM et al. (2007). Mechanisms of regulation of CXCR4/SDF-1 (CXCL12)-dependent migration and homing in multiple myeloma. Blood 109: 2708–2717.
Assender JW, Gee JM, Lewis I, Ellis IO, Robertson JF, Nicholson RI . (2007). Protein kinase C isoform expression as a predictor of disease outcome on endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 60: 1216–1221.
Begley R, Liron T, Baryza J, Mochly-Rosen D . (2004). Biodistribution of intracellularly acting peptides conjugated reversibly to Tat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318: 949–954.
Borner C, Wyss R, Regazzi R, Eppenberger U, Fabbro D . (1987). Immunological quantitation of phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase of human mammary carcinoma cells: inverse relationship to estrogen receptors. Int J Cancer 40: 344–348.
Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S, Mandal A, Chakraborti T . (2003). Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem 253: 269–285.
Chen L, Wright LR, Chen CH, Oliver SF, Wender PA, Mochly-Rosen D . (2001). Molecular transporters for peptides: delivery of a cardioprotective epsilonPKC agonist peptide into cells and intact ischemic heart using a transport system, R(7). Chem Biol 8: 1123–1129.
Christofori G . (2007). Cancer: division of labour. Nature 446: 735–736.
Cindoruk M, Kerem M, Karakan T, Salman B, Akin O, Alper M et al. (2007). Peroxisome proliferators-activated alpha agonist treatment ameliorates hepatic damage in rats with obstructive jaundice: an experimental study. BMC Gastroenterol 7: 44.
Faivre S, Kroemer G, Raymond E . (2006). Current development of mTOR inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 671–688.
Frankel LB, Lykkesfeldt AE, Hansen JB, Stenvang J . (2007). Protein kinase C alpha is a marker for antiestrogen resistance and is involved in the growth of tamoxifen resistant human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 104: 165–179.
Griner EM, Kazanietz MG . (2007). Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 281–294.
Gross S, Piwnica-Worms D . (2005). Real-time imaging of ligand-induced IKK activation in intact cells and in living mice. Nat Methods 2: 607–614.
Harvey JR, Mellor P, Eldaly H, Lennard TW, Kirby JA, Ali S . (2007). Inhibition of CXCR4-mediated breast cancer metastasis: a potential role for heparinoids? Clin Cancer Res 13: 1562–1570.
Helbig G, Christopherson II KW, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD et al. (2003). NF-kappaB promotes breast cancer cell migration and metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem 278: 21631–21638.
Inagaki K, Begley R, Ikeno F, Mochly-Rosen D . (2005). Cardioprotection by epsilon-protein kinase C activation from ischemia: continuous delivery and antiarrhythmic effect of an epsilon-protein kinase C-activating peptide. Circulation 111: 44–50.
Kawakami A, Aikawa M, Nitta N, Yoshida M, Libby P, Sacks FM . (2007). Apolipoprotein CIII-induced THP-1 cell adhesion to endothelial cells involves pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein- and protein kinase C alpha-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27: 219–225.
Ke Z, Lin H, Fan Z, Cai TQ, Kaplan RA, Ma C et al. (2006). MMP-2 mediates ethanol-induced invasion of mammary epithelial cells over-expressing ErbB2. Int J Cancer 119: 8–16.
Kim J, Choi YL, Vallentin A, Hunrichs BS, Hellerstein MK, Peehl DM et al. (2008). Centrosomal PKCbetaII and pericentrin are critical for human prostate cancer growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 68: 6831–6839.
Kim YM, Jang JW, Lee OH, Yeon J, Choi EY, Kim KW et al. (2000). Endostatin inhibits endothelial and tumor cellular invasion by blocking the activation and catalytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase. Cancer Res 60: 5410–5413.
Kraft AS, Anderson WB, Cooper HL, Sando JJ . (1982). Decrease in cytosolic calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity following phorbol ester treatment of EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 257: 13193–13196.
Martiny-Baron G, Fabbro D . (2007). Classical PKC isoforms in cancer. Pharmacol Res 55: 477–486.
Mi Z, Guo H, Wai PY, Gao C, Kuo PC . (2006). Integrin-linked kinase regulates osteopontin-dependent MMP-2 and uPA expression to convey metastatic function in murine mammary epithelial cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 27: 1134–1145.
Mimeault M, Batra SK . (2007). Functions of tumorigenic and migrating cancer progenitor cells in cancer progression and metastasis and their therapeutic implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26: 203–214.
Mochly-Rosen D, Gordon AS . (1998). Anchoring proteins for protein kinase C: a means for isozyme selectivity. FASEB J 12: 35–42.
Molckovsky A, Siu LL . (2008). First-in-class, first-in-human phase I results of targeted agents: highlights of the 2008 American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting. J Hematol Oncol 1: 20.
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME et al. (2001). Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410: 50–56.
Noel A, Jost M, Maquoi E . (2008). Matrix metalloproteinases at cancer tumor-host interface. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19: 52–60.
O'Brian C, Vogel VG, Singletary SE, Ward NE . (1989). Elevated protein kinase C expression in human breast tumor biopsies relative to normal breast tissue. Cancer Res 49: 3215–3217.
Pan Q, Bao LW, Kleer CG, Sabel MS, Griffith KA, Teknos TN et al. (2005). Protein kinase C epsilon is a predictive biomarker of aggressive breast cancer and a validated target for RNA interference anticancer therapy. Cancer Res 65: 8366–8371.
Peter M, Ameer-Beg SM, Hughes MK, Keppler MD, Prag S, Marsh M et al. (2005). Multiphoton-FLIM quantification of the EGFP-mRFP1 FRET pair for localization of membrane receptor-kinase interactions. Biophys J 88: 1224–1237.
Podsypanina K, Du YC, Jechlinger M, Beverly LJ, Hambardzumyan D, Varmus H . (2008). Seeding and propagation of untransformed mouse mammary cells in the lung. Science 321: 1841–1844.
Ron D, Luo J, Mochly-Rosen D . (1995). C2 region-derived peptides inhibit translocation and function of beta protein kinase C in vivo. J Biol Chem 270: 24180–24187.
Sahai E . (2007). Illuminating the metastatic process. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 737–749.
Shin Y, Yoon SH, Choe EY, Cho SH, Woo CH, Rho JY et al. (2007). PMA-induced up-regulation of MMP-9 is regulated by a PKCalpha-NF-kappaB cascade in human lung epithelial cells. Exp Mol Med 39: 97–105.
Sledge Jr GW, Gokmen-Polar Y . (2006). Protein kinase C-beta as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Semin Oncol 33: S15–S18.
Sliva D . (2004). Signaling pathways responsible for cancer cell invasion as targets for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: 327–336.
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D et al. (2004). CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64: 8604–8612.
Stebbins EG, Mochly-Rosen D . (2001). Binding specificity for RACK1 resides in the V5 region of beta II protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 276: 29644–29650.
Steffan NM, Bren GD, Frantz B, Tocci MJ, O'Neill EA, Paya CV . (1995). Regulation of IkB alpha phosphorylation by PKC- and Ca(2+)-dependent signal transduction pathways. J Immunol 155: 4685–4691.
Taichman RS, Cooper C, Keller ET, Pienta KJ, Taichman NS, McCauley LK . (2002). Use of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 pathway in prostate cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Res 62: 1832–1837.
Tester AM, Ruangpanit N, Anderson RL, Thompson EW . (2000). MMP-9 secretion and MMP-2 activation distinguish invasive and metastatic sublines of a mouse mammary carcinoma system showing epithelial-mesenchymal transition traits. Clin Exp Metastasis 18: 553–560.
Thorne SH, Contag CH . (2005). Using in vivo bioluminescence imaging to shed light on cancer biology. Proc IEEE 93: 750–762.
Tonetti DA, Morrow M, Kidwai N, Gupta A, Badve S . (2003). Elevated protein kinase C alpha expression may be predictive of tamoxifen treatment failure. Br J Cancer 88: 1400–1402.
Ways DK, Kukoly CA, deVente J, Hooker JL, Bryant WO, Posekany KJ et al. (1995). MCF-7 breast cancer cells transfected with protein kinase C-alpha exhibit altered expression of other protein kinase C isoforms and display a more aggressive neoplastic phenotype. J Clin Invest 95: 1906–1915.
Yee JK, Moores JC, Jolly DJ, Wolff JA, Respess JG, Friedmann T . (1987). Gene expression from transcriptionally disabled retroviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 5197–5201.
Zorzi D, Laurent A, Pawlik TM, Lauwers GY, Vauthey JN, Abdalla EK . (2007). Chemotherapy-associated hepatotoxicity and surgery for colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg 94: 274–286.
Zucker S, Cao J, Chen WT . (2000). Critical appraisal of the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Oncogene 19: 6642–6650.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Erinn Bruno Rankin in Dr Amato Giaccia's lab at the Department of Radiation Oncology at Stanford University for generous technical support and Dr Adrienne Gordon for critical reading of the paper. This work was supported in part by PHS Grant Number CA09151, awarded by the National Cancer Institute, DHHS (to JK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
DMR is the founder of KAI Pharmaceuticals. However, none of the work at her laboratory was supported by the company and the company had no access to information about unpublished research. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Thorne, S., Sun, L. et al. Sustained inhibition of PKCα reduces intravasation and lung seeding during mammary tumor metastasis in an in vivo mouse model. Oncogene 30, 323–333 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.415
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.415
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MLK3 regulates FRA-1 and MMPs to drive invasion and transendothelial migration in triple-negative breast cancer cells
Oncogenesis (2017)
-
Activated human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells suppress metastatic features of MDA-MB-231 cells by secreting IFN-β
Cell Death & Disease (2016)
-
Protein kinase C and cancer: what we know and what we do not
Oncogene (2014)
-
Tetraspanin proteins promote multiple cancer stages
Nature Reviews Cancer (2014)
-
A peptide that inhibits function of Myristoylated Alanine-Rich C Kinase Substrate (MARCKS) reduces lung cancer metastasis
Oncogene (2014)