Abstract
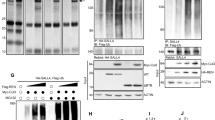
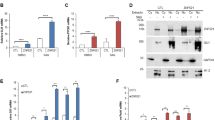
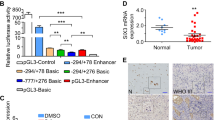
Hedgehog pathway regulates tissue patterning and cell proliferation. Gli1 transcription factor is the major effector of Hedgehog signaling and its deregulation is often associated to medulloblastoma formation. Proteolytic processes represent a critical mechanism by which this pathway is turned off. Here, we characterize the regulation of an ubiquitin-mediated mechanism of Gli1 degradation, promoted by the coordinated action of the E3 ligase Itch and the adaptor protein Numb. We show that Numb activates the catalytic activity of Itch, releasing it from an inhibitory intramolecular interaction between its homologous to E6-AP C-terminus and WW domains. The consequent activation of Itch, together with the recruitment of Gli1 through direct binding with Numb, allows Gli1 to enter into the complex, resulting in Gli1 ubiquitination and degradation. This process is mediated by a novel Itch-dependent degron, composed of a combination of two PPXYs and a phospho-serine/proline motifs, localized in Gli1 C-terminal region, indicating the role of two different WW docking sites in Gli1 ubiquitination. Remarkably, Gli1 protein mutated in these modules is no longer regulated by Itch and Numb, and determines enhanced Gli1-dependent medulloblastoma growth, migration and invasion abilities, as well as in vitro transforming activity. Our data reveal a novel mechanism of regulation of Gli1 stability and function, which influences Hedgehog/Gli1 oncogenic potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Hh:
-
Hedgehog
- MB:
-
medulloblastoma
- HECT:
-
homologous to E6-AP C-terminus
- RING:
-
really interesting new gene
- WT:
-
wild-type
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
References
Argenti B, Gallo R, Di Marcotullio L, Ferretti E, Napolitano M, Canterini S et al. (2005). Hedgehog antagonist REN(KCTD11) regulates proliferation and apoptosis of developing granule cell progenitors. J Neurosci 25: 8338–8346.
Bar EE, Chaudhr A, Farah MH, Eberhart CG . (2007). Hedgehog signaling promotes medulloblastoma survival via Bc/II. Am J Pathol 170: 347–355.
Bedford MT, Sarbassova D, Xu J, Leder P, Yaffer MB . (2000). A novel Pro–Arg motif recognized by WW domains. J Biol Chem 275: 10359–10369.
Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A, Melino G . (2008). The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligase: multiple players in cancer development. Cancer Cell 14: 10–21.
Boname JM, Stevenson PG . (2001). MHC class I ubiquitination by a viral PHD/LAP finger protein. Immunity 15: 627–636.
Canettieri G, Coni S, Della Guardia M, Nocerino V, Antonucci L, Di Magno L et al. (2009). The coactivator CRTC1 promotes cell proliferation and transformation via AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 1445–1450.
Canettieri G, Di Marcotullio L, Greco A, Coni S, Antonucci L, Infante P et al. (2010). Histone deacetylase and Cullin3-RENKCTD11 ubiquitin ligase interplay regulates Hedgehog signalling through Gli acetylation. Nat Cell Biol 12: 132–142.
Cayouette M, Raff M . (2002). Asymmetric segregation of Numb: a mechanism for neural specification from Drosophila to mammals. Nat Neurosci 5: 1265–1269.
Chang L, Kamata H, Solinas G, Luo JL, Maeda S, Venuprasad K et al. (2006). The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell 124: 601–613.
Courbard JR, Fiore F, Adelaide J, Borg JP, Birnbaum D, Ollendorff V . (2002). Interaction between two ubiquitin–protein isopeptide ligases of different classes, CBLC and AIP4/ITCH. J Biol Chem 277: 45267–45275.
Di Marcotullio L, Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Argenti B, Mincione C, Zazzeroni F et al. (2004). REN(KCTD11) is a suppressor of Hedgehog signaling and is deleted in human medulloblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 10833–10838.
Di Marcotullio L, Ferretti E, Greco A, De Smaele E, Po A, Sico MA et al. (2006). Numb is a suppressor of Hedgehog signalling and targets Gli1 for Itch-dependent ubiquitination. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1415–1423.
Espanel X, Sudol M . (1999). A single point mutation in a group I WW domain shifts its specificity to that of group II WW domains. J Biol Chem 274: 17284–17289.
Fang D, Elly C, Gao B, Fang N, Altman Y, Joazeiro C et al. (2002). Dysregulation of T lymphocyte function in itchy mice: a role for Itch in TH2 differentiation. Nat Immunol 3: 281–287.
Fang D, Kerppola TK . (2004). Ubiquitin-mediated fluorescence complementation reveals that Jun ubiquitinated by Itch/AIP4 is localized to lysosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 14782–14787.
Gallagher E, Gao M, Liu YC, Karin M . (2006). Activation of E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch through a phosphorylation-induced conformational change. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 1717–1722.
Galvin KE, Ye H, Erstad DJ, Feddersen R, Wetmore C . (2008). Gli1 induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in hippocampal but not tumor-derived neural stem cells. Stem Cells 26: 1027–1036.
Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP . (1997). Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277: 1109–1113.
Guerreiro AS, Fattet S, Fischer B, Shalaby T, Jackson SP, Schoenwaelder SM et al. (2008). Targeting the PI3K p110alpha isoform inhibits medulloblastoma proliferation, chemoresistance, and migration. Clin Cancer Res 14: 6761–6769.
Gulino A, Di Marcotullio L, Screpanti I . (2010). The multiple functions of Numb. Exp Cell Res 316: 900–906.
Haas AL, Siepmann TJ . (1997). Pathways of ubiquitin conjugation. FASEB J 11: 1257–1268.
Hatakeyama S, Yada M, Matsumoto M, Ishida N, Nakayama KI . (2001). Ubox proteins as a new family of ubiquitin–protein ligases. J Biol Chem 276: 33111–33120.
Huntzicker EG, Estay IS, Zhen H, Lokteva LA, Jackson PK, Oro AE . (2006). Dual degradation signals control Gli protein stability and tumor formation. Genes Dev 20: 276–281.
Ingham PW, Placzek M . (2006). Orchestrating ontogenesis: variations on a theme by sonic-hedgehog. Nat Rev Genet 7: 841–850.
Ingham RJ, Gish G, Pawson T . (2004). The Nedd4 family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: functional diversity within a common modular architecture. Oncogene 23: 1972–1984.
Ikeda A, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R, Ikeda M . (2003). Itchy, a Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase, downregulates latent membrane protein 2A activity in B-cell signaling. J Virol 77: 5529–5534.
Jia J, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Tong C, Wang B, Hou F et al. (2005). Phosphorylation by double-time/CKIepsilon and CKIalpha targets cubitus interruptus for Slimb/beta-TRCP-mediated proteolytic processing. Dev Cell 9: 819–830.
Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M . (2006). Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev 22: 159–180.
Kimura H, Stephen D, Joyner A, Curran T . (2005). Gli1 is important for medulloblastoma formation in Ptc1+/− mice. Oncogene 24: 4026–4036.
Laner-Plamberger S, Kaser A, Paulischta M, Hauser-Kronberger C, Eichberger T, Frischauf AM . (2009). Cooperation between GLI and JUN enhances transcription of JUN and selected GLI target genes. Oncogene 28: 1639–1651.
Liu YC . (2004). Ubiquitin ligases and the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol 22: 81–127.
Lohr NJ, Molleston JP, Strauss KA, Torres-Martinez W, Sherman EA, Squires RH et al. (2010). Human ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase deficiency causes syndromic multisystem autoimmune disease. Am J Hum Genet 86: 447–453.
Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Lu KP . (1999). Function of WW domains as phosphoserine or posphothreonine-binding modules. Science 283: 1325–1328.
Macias MJ, Wiesner S, Sudol M . (2002). WW and SH3 domains, two different scaffolds to recognize proline-rich ligands. FEBS Lett 513: 30–37.
MacDonald TJ, Brown KM, LaFleur B, Peterson K, Lawlor C, Chen Y et al. (2001). Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet 29: 143–152.
Magnifico A, Ettenberg S, Yang C, Mariano J, Tiwari S, Fang S et al. (2003). WW domain HECT E3s target Cbl RING finger E3s for proteasomal degradation. J Biol Chem 278: 43169–43177.
McGill A, McGlade CJ . (2003). Mammalian Num proteins promote Notch1 receptor ubiquitination and degradation of the Notch1 intracellular domain. J Biol Chem 278: 23196–23203.
Melino G, Gallagher E, Aqeilan RI, Knight R, Peschiaroli A, Rossi M et al. (2008). Itch: a HECT-type E3 ligase regulating immunity, skin and cancer. Cell Death Differ 15: 1103–1112.
Mouchantaf R, Azakir B, McPherson P, Millard S, Wood S, Angers A . (2006). The ubiquitin ligase itch is auto-ubiquitylated in vivo and in vitro but is protected from degradation by interacting with the deubiquitylating enzyme FAM/USP9X. J Biol Chem 281: 38738–38747.
Mund T, Pelham HRB . (2009). Conrol of the activity of WW-HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligase by NDFIP proteins. EMBO Rep 10: 501–507.
Omerovic J, Santangelo L, Puggioni EM, Marrocco J, Dall'Armi C, Palombo C et al. (2007). The E3 ligase Aip4/Itch ubiquitinates and targets ErbB-4 for degradation. FASEB J 21: 2849–2862.
Perry WL, Hustad CM, Swing DA, O'Sullivan TN, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG . (1998). The itchy locus encodes a novel ubiquitin protein ligase that is disrupted in a18H mice. Nat Genet 18: 143–146.
Peschiaroli A, Dorrello NV, Guardavaccaro D, Venere M, Halazonetis T, Sherman N et al. (2006). SCFbeta TrCP-mediated degradation of Claspin regulates recovery from the DNA replication checkpoint response. Mol Cell 23: 319–329.
Pickart CM . (2001). Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem 70: 503–533.
Qiu L, Joazeiro C, Fang N, Wang HY, Elly C, Altman Y et al. (2000). Recognition and ubiquitination of Notch by Itch, a hect-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 275: 35734–35737.
Rossi M, De Laurenzi V, Munarriz E, Green DR, Liu YC et al. (2005). The ubiquitin–protein ligase Itch regulates p73 stability. EMBO J 24: 836–848.
Ruiz i Altaba A, Sanchez P, Dahamane N . (2002). Gli and Hedgehog in cancer: tumors, embryos and stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 361–372.
Ruppert JM, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . (1991). The zinc finger protein GLI transforms primary cells in cooperation with adenovirus E1A. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1724–1728.
Shembade N, Harhaj NS, Parvatiyar K, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Matesic LE et al. (2008). The E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates inflammatory signaling pathways by controlling the function of the ubiquitin editing enzyme A20. Nat Immunol 9: 254–262.
Sudol M . (1996). Structure and function of the WW domain. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 65: 113–132.
Sudol M, Recinos CC, Abraczinskas J, Humbert J, Farooq A . (2005). WW or WoW: the WW domains in a union of bliss. IUBMB Life 57: 773–778.
Traweger A, Fang D, Liu YC, Stelzhammer W, Krizbai IA, Fresser F et al. (2002). The tight junction specific protein occludin is a functional target of the E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase itch. J Biol Chem 277: 10201–10208.
Van Sant C, Hagglund R, Lopez P, Roizman B . (2001). The infected cell protein 0 of herpes simplex virus 1 dynamically interacts with proteasomes, binds and activates the cdc34 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, and possesses in vitro E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 8815–8820.
Welchman RL, Gordon C, Mayer RJ . (2005). Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins as multifunctional signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 599–609.
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Wang B, Ou CY, Chien CT, Jiang J . (2006). A hedgehog-induced BTB protein modulates hedgehog signaling by degrading Ci/Gli transcription factor. Dev Cell 10: 719–729.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr A Oro for providing the various Gli1 mutants and G Giannini for advice and critical discussion. This work was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Telethon Grant GGP07118 and the Ministry of University and Research, (FIRB), the Ministry of Health, Fondazione Roma and Fondazione Mariani.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Marcotullio, L., Greco, A., Mazzà, D. et al. Numb activates the E3 ligase Itch to control Gli1 function through a novel degradation signal. Oncogene 30, 65–76 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.394
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.394
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BM-MSCs overexpressing the Numb enhance the therapeutic effect on cholestatic liver fibrosis by inhibiting the ductular reaction
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme USP44 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting Hedgehog signaling and PDL1 expression
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Smurf1 and Smurf2 mediated polyubiquitination and degradation of RNF220 suppresses Shh-group medulloblastoma
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Therapeutic Effectiveness of Anticancer Agents Targeting Different Signaling Molecules Involved in Asymmetric Division of Cancer Stem Cell
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2023)
-
NUMB facilitates autophagy initiation through targeting SCFβ-TrCP2 complex
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)