Abstract
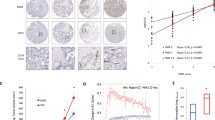
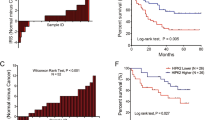
Tumor growth is the orchestration of various oncogenes and tumor suppressors, and the regulation of these genes offers a rational therapeutic approach to cancer treatment. In this study, we found a new regulator of tumor growth, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIα (PI4KIIα), the mechanism of which is involved in angiogenesis and hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1α regulation. Results obtained from a human cancer tissue microarray showed that PI4KIIα protein expression increases markedly in seven types of cancers compared with normal tissues. Suppression of PI4KIIα leads to retarded tumor growth in nude mice. Downregulation of PI4KIIα in cancer cells eliminates tumor cell-induced endothelial cell tubulogenesis and migration, and results in impaired angiogenesis. Further investigation showed that PI4KIIα can directly regulate HIF-1α expression and that the expression of these two proteins is correlated in vivo. At the same time, downregulation of PI4KIIα markedly reduces HER-2 autophosphorylation, and PI4KIIα specifically triggers HIF-1α accumulation through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)- and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK)-dependent pathway, suggesting that PI4KIIα may regulate HIF-1α through the HER-2/PI3K, ERK cascade. In summary, we discovered a pivotal role for PI4KIIα in the regulation of tumor growth. Our results shed new light on understanding the novel functions of PI4KIIα in cancer and suggest that PI4KIIα may be a promising specific target for tumor therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craige B, Salazar G, Faundez V . (2008). Phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase type II alpha contains an AP-3-sorting motif and a kinase domain that are both required for endosome traffic. Mol Biol Cell 19: 1415–1426.
Di PG, De CP . (2006). Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443: 651–657.
Drabkin D . (1949). The standardization of hemoglobin measurement. Am J Med Sci 217: 710–711.
Ferrara N . (2002). VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 795–803.
Folkman J . (1971). Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285: 1182–1186.
Folkman J, Haudenschild C . (1980). Angiogenesis in vitro. Nature 288: 551–556.
Garcia-Cardena G, Folkman J . (1998). Is there a role for nitric oxide in tumor angiogenesis? J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 560–561.
Gehrmann T, Heilmeyer Jr LM . (1998). Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases. Eur J Biochem 253: 357–370.
Gewinner C, Wang ZC, Richardson A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Etemadmoghadam D, Bowtell D et al. (2009). Evidence that inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase type II is a tumor suppressor that inhibits PI3K signaling. Cancer Cell 16: 115–125.
Grant DS, Kinsella JL, Fridman R, Auerbach R, Piasecki BA, Yamada Y et al. (1992). Interaction of endothelial cells with a laminin A chain peptide (SIKVAV) in vitro and induction of angiogenic behavior in vivo. J Cell Physiol 153: 614–625.
Guo J, Wenk MR, Pellegrini L, Onofri F, Benfenati F, De CP . (2003). Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIalpha is responsible for the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity associated with synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 3995–4000.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . (1996). Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86: 353–364.
Heilmeyer Jr LM, Vereb Jr G, Vereb G, Kakuk A, Szivak I . (2003). Mammalian phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases. IUBMB Life 55: 59–65.
Hellwig-Burgel T, Rutkowski K, Metzen E, Fandrey J, Jelkmann W . (1999). Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Blood 94: 1561–1567.
Hsuan JJ . (1993). Oncogene regulation by growth factors. Anticancer Res 13: 2521–2532.
Huang LE, Bunn HF . (2003). Hypoxia-inducible factor and its biomedical relevance. J Biol Chem 278: 19575–19578.
Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Leung SW, Roe R, Semenza GL . (1997). Transactivation and inhibitory domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Modulation of transcriptional activity by oxygen tension. J Biol Chem 272: 19253–19260.
Kauffmann-Zeh A, Klinger R, Kauffmann-Zeh A, Endemann G, Waterfield MD, Wetzker R et al. (1994). Regulation of human type II phosphatidylinositol kinase activity by epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation and receptor association. J Biol Chem 269: 31243–31251.
Koesters R, von Knebel DM . (2003). The Wnt signaling pathway in solid childhood tumors. Cancer Lett 198: 123–138.
Kubota Y, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Lawley TJ . (1988). Role of laminin and basement membrane in the morphological differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures. J Cell Biol 107: 1589–1598.
Kung AL, Wang S, Klco JM, Kaelin WG, Livingston DM . (2000). Suppression of tumor growth through disruption of hypoxia-inducible transcription. Nat Med 6: 1335–1340.
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW . (2004). Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 36: 1–12.
Melillo G, Musso T, Sica A, Taylor LS, Cox GW, Varesio L . (1995). A hypoxia-responsive element mediates a novel pathway of activation of the inducible nitric oxide synthase promoter. J Exp Med 182: 1683–1693.
Minogue S, Anderson JS, Waugh MG, dos Santos M, Corless S, Cramer R et al. (2001). Cloning of a human type ii phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase reveals a novel lipid kinase family. J Biol Chem 276: 16635–16640.
Minogue S, Waugh MG, De Matteis MA, Stephens DJ, Berditchevski F, Hsuan JJ . (2006). Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase is required for endosomal trafficking and degradation of the EGF receptor. J Cell Sci 119: 571–581.
Pan W, Choi SC, Wang H, Qin Y, Volpicelli-Daley L, Swan L et al. (2008). Wnt3a-mediated formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 321: 1350–1353.
Qin Y, Li L, Pan W, Wu D . (2009). Regulation of phosphatidylinositol kinases and metabolism by Wnt3a and Dvl2. J Biol Chem 284: 22544–22548.
Roskoski Jr R . (2004). The ErbB/HER receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319: 1–11.
Salazar G, Zlatic S, Craige B, Peden AA, Pohl J, Faundez V . (2009). Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome protein complexes associate with phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type II alpha in neuronal and non-neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 284: 1790–1802.
Scott GK, Dodson JM, Montgomery PA, Johnson RM, Sarup JC, Wong WL et al. (1991). p185HER2 signal transduction in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 266: 14300–14305.
Semenza GL . (2001). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol Med 7: 345–350.
Semenza GL . (2002). HIF-1 and tumor progression: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 8: S62–S67.
Simons JP, Al-Shawi R, Minogue S, Waugh MG, Wiedemann C, Evangelou S et al. (2009). Loss of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2alpha activity causes late onset degeneration of spinal cord axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 11535–11539.
Tan C, Cruet-Hennequart S, Troussard A, Fazli L, Costello P, Sutton K et al. (2004). Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by integrin-linked kinase (ILK). Cancer Cell 5: 79–90.
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J, Semenza GL, Van OE . (2002). Insulin stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/target of rapamycin-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277: 27975–27981.
Wang YJ, Wang J, Sun HQ, Martinez M, Sun YX, Macia E et al. (2003). Phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate regulates targeting of clathrin adaptor AP-1 complexes to the Golgi. Cell 114: 299–310.
Waugh MG, Minogue S, Anderson JS, Balinger A, Blumenkrantz D, Calnan DP et al. (2003). Localization of a highly active pool of type II phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in a p97/valosin-containing-protein-rich fraction of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J 373: 57–63.
Weber G, Shen F, Prajda N, Yeh YA, Yang H, Herenyiova M et al. (1996). Increased signal transduction activity and down-regulation in human cancer cells. Anticancer Res 16: 3271–3282.
Xu Z, Huang G, Kandror KV . (2006). Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIalpha is targeted specifically to cellugyrin-positive glucose transporter 4 vesicles. Mol Endocrinol 20: 2890–2897.
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, Iizuka N, Monden M, Yamamoto S et al. (2004). Expression level of valosin-containing protein (p97) is correlated with progression and prognosis of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 11: 697–704.
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM et al. (2000). Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 60: 1541–1545.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shane Minogue and Konstantin V Kandror for gifted plasmids and Pietro De Camilli for PI4KIIα antibody, Wei Liang, Xiyun Yan and Yi Zhu for sharing materials, and Guoheng Xu and Qinwei Yin for valuable discussions. We are grateful to Nanping Wang for his great support. We also thank Junfeng Hao and Xudong Zhao for technical assistance. The work was supported by the ‘863’ National High-Technology Development Program of China (0A200202D03), the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB911001, 2005CB522804) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (90606020, 30770512).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
A patent has been applied by the Institute of Biophysics, CAS, CHINA (CC, JML).
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Lu, Y., Zhang, J. et al. PI4KIIα is a novel regulator of tumor growth by its action on angiogenesis and HIF-1α regulation. Oncogene 29, 2550–2559 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.14
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.14
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic targeting of the PI4K2A/PKR lysosome network is critical for misfolded protein clearance and survival in cancer cells
Oncogene (2020)
-
Novel phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases III beta (PI4KIIIβ) inhibitors discovered by virtual screening using free energy models
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2020)
-
PI4KIIα regulates insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis via a PKD-dependent pathway
Biophysics Reports (2018)
-
Overexpression of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIIα is associated with undifferentiated status and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
Molecular insights into the membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIα
Nature Communications (2014)