Abstract
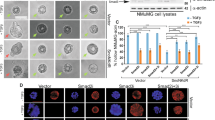
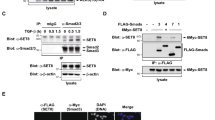
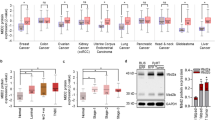
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and components of the extracellular matrix, thereby profoundly affecting the microenvironment of cells including cancerous ones. We studied MMP-10 induction by TGF-β in mammary epithelial cells and found that the induction was dependent on the myocyte enhancer factor (MEF)-2 transcription factor. TGF-β upregulated the gene promoter through the MEF2 site, and knockdown of the MEF2A transcription factor negatively affected MMP-10 induction, whereas its overexpression had a positive effect on the induction. In response to TGF-β, acetylation and concomitant binding of MEF2A to the promoter region increased, thus suggesting a critical role of MEF2A in transactivation of MMP-10 by TGF-β. Consistent with the fact that class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) interact with MEF2 and suppress transcription, knockdown of HDACs increased and their overexpression inhibited MMP-10 expression. Intriguingly, TGF-β promoted proteasome-dependent degradation of HDACs. Consistent with this, acetylation of core histones was increased around the MEF2 site of the MMP-10 promoter by TGF-β and alleviated by overexpression of HDACs. Collectively, it is possible that TGF-β transcriptionally upregulated MMP-10 through activation of MEF2A, concomitant with acetylation of core histones increasing around the promoter, as a consequence of degradation of the class IIa HDACs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelelli C, Magli A, Ferrari D, Ganassi M, Matafora V, Parise F et al. (2008). Differentiation-dependent lysine 4 acetylation enhances MEF2C binding to DNA in skeletal muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 915–928.
Aung PP, Oue N, Mitani Y, Nakayama H, Yoshida K, Noguchi T et al. (2006). Systematic search for gastric cancer-specific genes based on SAGE data: melanoma inhibitory activity and matrix metalloproteinase-10 are novel prognostic factors in patients with gastric cancer. Oncogene 25: 2546–2557.
Bierie B, Moses HL . (2006). Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 506–520.
Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S, Mandal A, Chakraborti T . (2003). Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem 253: 269–285.
Chang S, Young BD, Li S, Qi X, Richardson JA, Olson EN . (2006). Histone deacetylase 7 maintains vascular integrity by repressing matrix metalloproteinase 10. Cell 126: 321–334.
Cho NH, Hong KP, Hong SH, Kang S, Chung KY, Cho SH . (2004). MMP expression profiling in recurred stage IB lung cancer. Oncogene 23: 845–851.
Clark IM, Swingler TE, Sampieri CL, Edwards DR . (2008). The regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40: 1362–1378.
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A . (2001). TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet 29: 117–129.
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH . (1998). Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 95: 737–740.
Gill JH, Kirwan IG, Seargent JM, Martin SW, Tijani S, Anikin VA et al. (2004). MMP-10 is overexpressed, proteolytically active, and a potential target for therapeutic intervention in human lung carcinomas. Neoplasia 6: 777–785.
Impola U, Uitto VJ, Hietanen J, Hakkinen L, Zhang L, Larjava H et al. (2004). Differential expression of matrilysin-1 (MMP-7), 92 kD gelatinase (MMP-9), and metalloelastase (MMP-12) in oral verrucous and squamous cell cancer. J Pathol 202: 14–22.
Inoue Y, Imamura T . (2008). Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases. Cancer Sci 99: 2107–2112.
Ishikawa F, Nose K, Shibanuma M . (2008). Downregulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha and its role in regulation of gene expression by TGF-beta in mammary epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 314: 2131–2140.
Izzi L, Attisano L . (2004). Regulation of the TGFbeta signalling pathway by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Oncogene 23: 2071–2078.
Jakowlew SB . (2006). Transforming growth factor-beta in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25: 435–457.
Kang JS, Alliston T, Delston R, Derynck R . (2005). Repression of Runx2 function by TGF-beta through recruitment of class II histone deacetylases by Smad3. EMBO J 24: 2543–2555.
Kanome T, Itoh N, Ishikawa F, Mori K, Kim-Kaneyama JR, Nose K et al. (2007). Characterization of Jumping translocation breakpoint (JTB) gene product isolated as a TGF-beta1-inducible clone involved in regulation of mitochondrial function, cell growth and cell death. Oncogene 26: 5991–6001.
Kato Y, Zhao M, Morikawa A, Sugiyama T, Chakravortty D, Koide N et al. (2000). Big mitogen-activated kinase regulates multiple members of the MEF2 protein family. J Biol Chem 275: 18534–18540.
Kerkela E, Ala-aho R, Lohi J, Grenman R, V MK, Saarialho-Kere U . (2001). Differential patterns of stromelysin-2 (MMP-10) and MT1-MMP (MMP-14) expression in epithelial skin cancers. Br J Cancer 84: 659–669.
Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, Oki T, Nakajima H, Nosaka T et al. (2003). Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning: powerful tools in functional genomics. Exp Hematol 31: 1007–1014.
Lemercier C, Verdel A, Galloo B, Curtet S, Brocard MP, Khochbin S . (2000). mHDA1/HDAC5 histone deacetylase interacts with and represses MEF2A transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 275: 15594–15599.
Levy L, Hill CS . (2005). Smad4 dependency defines two classes of transforming growth factor \{beta\} (TGF-\{beta\}) target genes and distinguishes TGF-\{beta\}-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition from its antiproliferative and migratory responses. Mol Cell Biol 25: 8108–8125.
Liu D, Kang JS, Derynck R . (2004). TGF-beta-activated Smad3 represses MEF2-dependent transcription in myogenic differentiation. EMBO J 23: 1557–1566.
Ma K, Chan JK, Zhu G, Wu Z . (2005). Myocyte enhancer factor 2 acetylation by p300 enhances its DNA binding activity, transcriptional activity, and myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 25: 3575–3582.
Massague J, Gomis RR . (2006). The logic of TGFbeta signaling. FEBS Lett 580: 2811–2820.
Mathew R, Khanna R, Kumar R, Mathur M, Shukla NK, Ralhan R . (2002). Stromelysin-2 overexpression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: potential clinical implications. Cancer Detect Prev 26: 222–228.
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Olson EN . (2002). MEF2: a calcium-dependent regulator of cell division, differentiation and death. Trends Biochem Sci 27: 40–47.
Miska EA, Karlsson C, Langley E, Nielsen SJ, Pines J, Kouzarides T . (1999). HDAC4 deacetylase associates with and represses the MEF2 transcription factor. EMBO J 18: 5099–5107.
Miyata Y, Iwata T, Maruta S, Kanda S, Nishikido M, Koga S et al. (2007). Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-10 in renal cell carcinoma and its prognostic role. Eur Urol 52: 791–797.
Mori K, Asakawa M, Hayashi M, Imura M, Ohki T, Hirao E et al. (2006). Oligomerizing potential of a focal adhesion LIM protein Hic-5 organizing a nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling complex. J Biol Chem 281: 22048–22061.
Muraoka-Cook RS, Kurokawa H, Koh Y, Forbes JT, Roebuck LR, Barcellos-Hoff MH et al. (2004). Conditional overexpression of active transforming growth factor beta1 in vivo accelerates metastases of transgenic mammary tumors. Cancer Res 64: 9002–9011.
Nakamura H, Fujii Y, Ohuchi E, Yamamoto E, Okada Y . (1998). Activation of the precursor of human stromelysin 2 and its interactions with other matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J Biochem 253: 67–75.
Nelson JD, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K . (2006). Protocol for the fast chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method. Nat Protoc 1: 179–185.
Ornatsky OI, Cox DM, Tangirala P, Andreucci JJ, Quinn ZA, Wrana JL et al. (1999). Post-translational control of the MEF2A transcriptional regulatory protein. Nucleic Acids Res 27: 2646–2654.
Pardali K, Moustakas A . (2007). Actions of TGF-beta as tumor suppressor and pro-metastatic factor in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775: 21–62.
Piek E, Ju WJ, Heyer J, Escalante-Alcalde D, Stewart CL, Weinstein M et al. (2001). Functional characterization of transforming growth factor beta signaling in Smad2- and Smad3-deficient fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276: 19945–19953.
Quinn ZA, Yang CC, Wrana JL, McDermott JC . (2001). Smad proteins function as co-modulators for MEF2 transcriptional regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 29: 732–742.
Ramos-DeSimone N, Hahn-Dantona E, Sipley J, Nagase H, French DL, Quigley JP . (1999). Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) via a converging plasmin/stromelysin-1 cascade enhances tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 274: 13066–13076.
Shalizi A, Gaudilliere B, Yuan Z, Stegmuller J, Shirogane T, Ge Q et al. (2006). A calcium-regulated MEF2 sumoylation switch controls postsynaptic differentiation. Science 311: 1012–1017.
Sparrow DB, Miska EA, Langley E, Reynaud-Deonauth S, Kotecha S, Towers N et al. (1999). MEF-2 function is modified by a novel co-repressor, MITR. EMBO J 18: 5085–5098.
Thuault S, Valcourt U, Petersen M, Manfioletti G, Heldin CH, Moustakas A . (2006). Transforming growth factor-beta employs HMGA2 to elicit epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 174: 175–183.
Weeks BH, He W, Olson KL, Wang XJ . (2001). Inducible expression of transforming growth factor beta1 in papillomas causes rapid metastasis. Cancer Res 61: 7435–7443.
Windsor LJ, Grenett H, Birkedal-Hansen B, Bodden MK, Engler JA, Birkedal-Hansen H . (1993). Cell type-specific regulation of SL-1 and SL-2 genes. Induction of the SL-2 gene but not the SL-1 gene by human keratinocytes in response to cytokines and phorbolesters. J Biol Chem 268: 17341–17347.
Yang SH, Galanis A, Sharrocks AD . (1999). Targeting of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases to MEF2 transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 19: 4028–4038.
Zhao M, New L, Kravchenko VV, Kato Y, Gram H, di Padova F et al. (1999). Regulation of the MEF2 family of transcription factors by p38. Mol Cell Biol 19: 21–30.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Eric N Olson (University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, USA) for his generous gift of the MMP-10 promoter luciferase constructs. We also thank Ms E Kaneko and Ms T Kaneko for contributing to this work as a project for their bachelor's degree. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (19570185) and the High-Technology Research Center Project from the Ministry for Education, Culture Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan, and also by the High-Tech Research Centre Project for Private Universities: a matching fund subsidy from MEXT, 2007–2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, F., Miyoshi, H., Nose, K. et al. Transcriptional induction of MMP-10 by TGF-β, mediated by activation of MEF2A and downregulation of class IIa HDACs. Oncogene 29, 909–919 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.387
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.387
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MEF2A transcriptionally upregulates the expression of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 in colorectal cancer to promote tumor progression
Oncogene (2021)
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-10: a novel biomarker for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Respiratory Research (2015)
-
Loss of anchorage primarily induces non-apoptotic cell death in a human mammary epithelial cell line under atypical focal adhesion kinase signaling
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via ROS-dependent ERK–NF-κB pathways
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2012)
-
Expression of myocyte enhancer factor-2 and downstream genes in ground squirrel skeletal muscle during hibernation
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2010)