Abstract
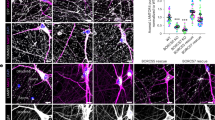
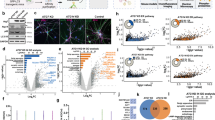
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization is central to apoptotic signaling and is directly regulated by the Bcl-2 family of proteins, consisting of anti-apoptotic members and pro-apoptotic members, although the precise mechanisms involved remain elusive. When cells are deficient in both pro-apoptotic multidomain members of this family (Bax and Bak), mitochondrial membrane permeabilization does not occur in response to various apoptotic stimuli. We have previously reported that the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC or porin) plays a role in apoptotic mitochondrial membrane permeabilization by interacting with Bcl-2 family members. Here, we have provided additional evidence that VDAC2 is required for pro-apoptotic activity of Bax in the absence of Bak. In the absence of Bak, VDAC2-deficient cells showed strong resistance to various apoptotic stimuli, whereas re-introduction of the Vdac2 gene restored their apoptotic response. Consistently, silencing of VDAC2 in Bak-deficient cells, but not Bax-deficient cells, also conferred resistance to various apoptotic stimuli. In the absence of VDAC2 and Bak, the activation of Bax (assessed by mitochondrial membrane integration, conformational changes and oligomerization) was markedly impaired. Taken together, these findings indicate that VDAC2 is required for pro-apoptotic activity of Bax in the absence of Bak.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Hamad S, Sivan S, Shoshan-Barmatz V . (2006). The expression level of the voltage-dependent anion channel controls life and death of the cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5787–5792.
Abu-Hamad S, Zaid H, Israelson A, Nahon E, Shoshan-Barmatz V . (2008). Hexokinase-I protection against apoptotic cell death is mediated via interaction with the voltage-dependent anion channel-1: mapping the site of binding. J Biol Chem 283: 13482–13490.
Anflous K, Armstrong DD, Craigen WJ . (2001). Altered mitochondrial sensitivity for ADP and maintenance of creatine-stimulated respiration in oxidative striated muscles from VDAC1-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 276: 1954–1960.
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes R, Martinou JC . (2000). Bax oligomerization is required for channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Biochem J 345 (Pt 2): 271–278.
Baehrecke EH . (2002). How death shapes life during development. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 779–787.
Baines CP, Kaiser RA, Sheiko T, Craigen WJ, Molkentin JD . (2007). Voltage-dependent anion channels are dispensable for mitochondrial-dependent cell death. Nat Cell Biol 9: 550–555.
Bellot G, Cartron PF, Er E, Oliver L, Juin P, Armstrong LC et al. (2007). TOM22, a core component of the mitochondria outer membrane protein translocation pore, is a mitochondrial receptor for the proapoptotic protein Bax. Cell Death Differ 14: 785–794.
Blachly-Dyson E, Forte M . (2001). VDAC channels. IUBMB Life 52: 113–118.
Cheng EH, Sheiko TV, Fisher JK, Craigen WJ, Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). VDAC2 inhibits BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. Science 301: 513–517.
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B, Martinou JC . (2000). Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol Cell Biol 20: 929–935.
Green DR, Kroemer G . (2004). The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 305: 626–629.
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Latterich M, Schneiter R et al. (2002). Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell 111: 331–342.
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter Jr GA, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ et al. (2006). Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311: 847–851.
Madesh M, Hajnóczky G . (2001). VDAC-dependent permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane by superoxide induces rapid and massive cytochrome c release. J Cell Biol 155: 1003–1015.
Morita S, Kojima T, Kitamura T . (2000). Plat-E: an efficient and stable system for transient packaging of retroviruses. Gene Ther 7: 1063–1066.
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Hsu YT, Youle RJ . (1999). Conformation of the Bax C-terminus regulates subcellular location and cell death. EMBO J 18: 2330–2341.
Neise D, Graupner V, Gillissen BF, Daniel PT, Schulze-Osthoff K, Jänicke RU et al. (2008). Activation of the mitochondrial death pathway is commonly mediated by a preferential engagement of Bak. Oncogene 27: 1387–1396.
Nomura M, Shimizu S, Sugiyama T, Narita M, Ito T, Matsuda H et al. (2003). 14-3-3 interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic Bax. J Biol Chem 278: 2058–2065.
Ott M, Norberg E, Walter KM, Schreiner P, Kemper C, Rapaport D et al. (2007). The mitochondrial TOM complex is required for tBid/Bax-induced cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem 282: 27633–27639.
Rapaport D . (2003). Finding the right organelle. Targeting signals in mitochondrial outer-membrane proteins. EMBO Rep 4: 948–952.
Sampson MJ, Decker WK, Beaudet AL, Ruitenbeek W, Armstrong D, Hicks MJ et al. (2001). Immotile sperm and infertility in mice lacking mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel type 3. J Biol Chem 276: 39206–39212.
Sampson MJ, Lovell RS, Craigen WJ . (1996). Isolation, characterization, and mapping of two mouse mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel isoforms. Genomics 33: 283–288.
Sampson MJ, Lovell RS, Craigen WJ . (1997). The murine voltage-dependent anion channel gene family. J Biol Chem 272: 18966–18973.
Setoguchi K, Otera H, Mihara K . (2006). Cytosolic factor- and TOM-independent import of C-tail-anchored mitochondrial outer membrane proteins. EMBO J 25: 5635–5647.
Shimizu S, Matsuoka Y, Shinohara Y, Yoneda Y, Tsujimoto Y . (2001). Essential role of voltage-dependent anion channel in various forms of apoptosis in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 152: 237–250.
Shimizu S, Narita M, Tsujimoto Y . (1999). Bcl-2 family of proteins target mitochondrial channel VDAC to regulate apoptogenic cytochrome c release. Nature 399: 483–487.
Shoshan-Barmatz V, Israelson A, Brdiczka D, Sheu SS . (2006). The voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC): function in intracellular signaling, cell life and cell death. Curr Pharm Des 12: 2249–2270.
Tsujimoto Y . (2003). Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J Cell Physiol 195: 158–167.
Wang X . (2001). The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15: 2922–2933.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ et al. (2001). Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292: 727–730.
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ . (1997). Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139: 1281–1292.
Zong WX, Lindsten T, Ross AJ, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB . (2001). BH3-only proteins that bind pro-survival Bcl-2 family members fail to induce apoptosis in the absence of Bax and Bak. Genes Dev 15: 1481–1486.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Kitamura for providing of Plat-E cells. This study was supported in part by SORST of the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST), a grant for Creative Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, a grant for the 21st Century COE Program from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, and a grant for Comprehensive Research on Aging and Health from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamagata, H., Shimizu, S., Nishida, Y. et al. Requirement of voltage-dependent anion channel 2 for pro-apoptotic activity of Bax. Oncogene 28, 3563–3572 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.213
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.213
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCHF5 controls BAK apoptotic activity independently of BH3-only proteins
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Pore-forming proteins as drivers of membrane permeabilization in cell death pathways
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2023)
-
Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2023)
-
VDAC2 enables BAX to mediate apoptosis and limit tumor development
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Solid-state NMR, electrophysiology and molecular dynamics characterization of human VDAC2
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2015)