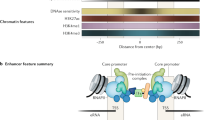
Abstract
Various studies have detailed the role of E2F proteins in both transcription activation and repression. Further study has shown that distinct promoter elements, but comprising the same E2F-recognition motif, confer positive or negative E2F control and that this reflects binding of either activator or repressor E2F proteins, respectively. We now show that the specificity of binding of an activator or repressor E2F protein is determined by adjacent sequences that bind a cooperating transcription factor. We propose that the functional E2F element is a module comprising not only the E2F-binding site but also the adjacent site for the cooperating transcription factor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aparicio O, Geisberg JV, Sekinger EA, Yang A, Moqtaderi Z, Struhl K . (2005). Chromatin immunoprecipitation for determining the association of proteins with specific genomic sequences in vivo. Curr Protoc Mol Biol, Chapter 21: Unit 21.3.
Araki K, Nakajima Y, Eto K, Ikeda MA . (2003). Distinct recruitment of E2F family members to specific E2F-binding sites mediates activation and repression of the E2F1 promoter. Oncogene 22: 7632–7641.
Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL et al. (1998). p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 395: 124–125.
Bryne JC, Valen E, Tang MH, Marstrand T, Winther O, da Piedade I et al. (2008). JASPAR, the open access database of transcription factor-binding profiles: new content and tools in the 2008 update. Nucleic Acids Res 36: D102–D106.
Christensen J, Cloos P, Toftegaard U, Klinkenberg D, Bracken AP, Trinh E et al. (2005). Characterization of E2F8, a novel E2F-like cell cycle regulated repressor of E2F activated transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 33: 5458–5470.
Croxton R, Ma Y, Song L, Haura EB, Cress WD . (2002). Direct repression of the Mcl-1 promoter by E2F1. Oncogene 21: 1359–1369.
de Bruin A, Maiti B, Jakoi L, Timmers C, Buerki R, Leone G . (2003). Identification and characterization of E2F7, a novel mammalian E2F family member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem 278: 42041–42049.
DeGregori J, Johnson DG . (2006). Distinct and overlapping roles for E2F family members in transcription, proliferation and apoptosis. Curr Mol Med 6: 739–748.
DeGregori J, Leone G, Miron A, Jakoi L, Nevins JR . (1997). Distinct roles for E2F proteins in cell growth control and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 7245–7250.
Di Stefano L, Jensen MR, Helin K . (2003). E2F7, a novel E2F featuring DP-independent repression of a subset of E2F-regulated genes. EMBO J 22: 6289–6298.
Dyson N . (1998). The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev 12: 2245–2262.
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad BM, Dettling M, Dudoit S et al. (2004). Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5: R80.
Giangrande P, Zhu W, Schlisio S, Sun XH, Mori S, Gaubatz S et al. (2004). A role for E2F6 in distinguishing G1/S and G2/M specific transcription. Genes Dev 18: 2941–2951.
Giangrande PH, Hallstrom TC, Tunyaplin C, Calame K, Nevins JR . (2003). Identification of the E box factor TFE3 as a functional partner for the E2F3 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 23: 3707–3720.
Hallstrom TC, Mori S, Nevins JR . (2007). An E2F1-dependent gene expression program that determines the balance between proliferation and cell death. Cancer Cell 13: 11–22.
Hallstrom TC, Nevins JR . (2003). Specificity in the activation and control of transcription factor E2F-dependent apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 10848–10853.
Hallstrom TC, Nevins JR . (2006). Jab1 is a specificity factor for E2F1-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 20: 613–623.
Ikeda M-A, Jakoi L, Nevins JR . (1996). A unique role for the Rb protein in controlling E2F accumulation during cell growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 3215–3220.
Irwin M, Martin MC, Phillips AC, Seelan RS, Smith DI, Liu W et al. (2000). Role for the p53 homologue p73 in E2F-1-induced apoptosis. Nature 407: 645–648.
Ishida S, Huang E, Zuzan H, Spang R, Leone G, West M et al. (2001). Role for E2F in control of both DNA replication and mitotic functions as revealed from DNA microarray analysis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 4684–4699.
Kong L-J, Chang JT, Bild AH, Nevins JR . (2007). Compensation and specificity of function within the E2F family. Oncogene 26: 321–327.
Kowalik TF, DeGregori J, Leone G, Nevins JR . (1998). E2F1-specific induction of apoptosis and p53 accumulation is modulated by mdm2. Cell Growth Differ 9: 113–118.
Kowalik TF, DeGregori J, Schwarz JK, Nevins JR . (1995). E2F1 overexpression in quiescent fibroblasts leads to induction of cellular DNA synthesis and apoptosis. J Virol 69: 2491–2500.
Kuhn RM, Karolchik D, Zweig AS, Wang T, Smith KE, Rosenbloom KR et al. (2009). The UCSC Genome Browser Database: update 2009. Nucleic Acids Res 37: D755–D761.
Lissy NA, Davis PK, Irwin M, Kaelin WG, Dowdy SF . (2000). A common E2F-1 and p73 pathway mediates cell death induced by TCR activation. Nature 407: 642–644.
Logan N, Graham A, Zhao XD, Fisher RI, Maiti B, Leone G et al. (2005). E2F-8: an E2F family member with a similar organization of DNA binding domains to E2F-7. Oncogene 24: 5000–5004.
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A et al. (2006). TRANSFAC and its moduel TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 34: D108–D110.
Moroni MC, Hickman ES, Denchi EL, Caprara G, Colli E, Cecconi F et al. (2001). Apaf-1 is a transcriptional target for E2F and p53. Nat Cell Biol 3: 552–558.
Muller H, Bracken AP, Vernell R, Moroni MC, Christians F, Grassilli E et al. (2001). E2Fs regulate the expression of genes involved in differentiation, development, proliferation, and apoptosis. Genes Dev 15: 267–285.
Nahle Z, Polakoff J, Davuluri RV, McCurrach ME, Jacobson MD, Narita M et al. (2002). Direct coupling of the cell cycle and cell death machinery by E2F. Nat Cell Biol 4: 859–864.
Nevins JR . (1998). Toward an understanding of the functional complexity of the E2F and Retinoblastoma families. Cell Growth Differ 9: 585–593.
Pilpel Y, Sudarsanam P, Church GM . (2001). Identifying regulatory networks by combinatorial analysis of promoter elements. Nat Genet 29: 153–159.
Polager S, Kalma Y, Berkovich E, Ginsberg D . (2002). E2Fs up-regulate expression of genes involved in DNA replication, DNA repair and mitosis. Oncogene 21: 437–446.
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T, Terragni J, Young RA et al. (2002). E2F integrates cell cycle progression with DNA repair, replication, and G(2)/M checkpoints. Genes Dev 16: 245–256.
Rogoff HA, Pickering MT, Frame FM, Debatis ME, Sanchez Y, Jones S et al. (2004). Apoptosis associated with deregulated E2F activity is dependent on E2F1 and Atm/Nbs1/Chk2. Mol Cell Biol 24: 2968–2977.
Schlisio S, Halperin T, Vidal M, Nevins JR . (2002). Interaction of YY1 with E2Fs, mediated by RYBP, provides a mechanism for specificity of E2F function. EMBO J 21: 5775–5786.
Sears RC, Nevins JR . (2002). Signaling networks that link cell proliferation and cell fate. J Biol Chem 277: 11617–11620.
Sherr CJ . (1996). Cancer cell cycles. Science 274: 1672–1677.
Smale ST . (2001). Core promoters: active contributors to combinatorial gene regulation. Genes Dev 15: 2503–2508.
Stanojevic D, Small S, Levine M . (1991). Regulation of a segmentation stripe by overlapping activators and repressors in the Drosophila embryo. Science 254: 1385–1387.
Stiewe T, Putzer BM . (2000). Role of the p53 homologue p73 in E2F1-induced apoptosis. Nat Genet 26: 464–469.
Takahashi Y, Rayman JB, Dynlacht BD . (2000). Analysis of promoter binding by the E2F and Rb families in vivo: distinct E2F proteins mediate activation and repression. Genes Dev 14: 804–816.
Tao Y, Kassatly RF, Cress WD, Horowitz JM . (1997). Subunit composition determines E2F DNA-binding site specificity. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6994–7007.
Tommasi S, Pfeifer GP . (1995). in vivo structure of the human cdc2 promoter: release of a p130-E2F-4 complex from sequences immediately upstream of the transcription initiation site coincides with induction of cdc2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 15: 6901–6913.
Trimarchi JM, Fairchild B, Wen J, Lees JA . (2001). The E2F6 transcription factor is a component of the mammalian Bmi1-containing polycomb complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98: 1519–1524.
Trimarchi JM, Lees JA . (2002). Sibling rivalry in the E2F family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 11–20.
Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC et al. (1999). CDC25A phosphatase is a target of E2F and is required for efficient E2f-induced S phase. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6379–6395.
Wells J, Boyd KE, Fry CJ, Bartley SM, Farnham PJ . (2000). Target gene specificity of E2F and pocket protein family members in living cells. Mol Cell Biol 20: 5797–5807.
Wysocka A, Herr W . (2003). The herpes simplex virus VP16-induced complex: the makings of a regulatory switch. Trends Biochem Sci 28: 294–304.
Yamamoto KR, Darimont BD, Wagner RL, Iniguez-Lluhi JA . (1998). Building transcriptional regulatory complexes: signals and surfaces. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 63: 587–598.
Yan Z, DeGregori J, Shohet RV, Leone G, Stillman B, Nevins JR et al. (1998). Cdc6 is regulated by E2F and is essential for DNA replication in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3603–3608.
Zheng N, Fraenkel E, Pabo CO, Pavletich NP . (1999). Structural basis of DNA recognition by the heterodimeric cell cycle transcription factor E2F-DP. Genes Dev 13: 666–674.
Zhu W, Giangrande P, Nevins JR . (2004). E2Fs link the control of G1/S and G2/M. EMBO J 23: 4615–4626.
Ziebold U, Reza T, Caron A, Lees JA . (2001). E2F3 contributes both to the inappropriate proliferation and to the apoptosis arising in Rb mutant embryos. Genes Dev 15: 386–391.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Nevins laboratory for valuable input throughout the course of this study and for comments on the paper. The project described was supported by award number R01CA104663 from the National Cancer Institute. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freedman, J., Chang, J., Jakoi, L. et al. A combinatorial mechanism for determining the specificity of E2F activation and repression. Oncogene 28, 2873–2881 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.153
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.153
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multi-omic approach identifies a transcriptional network coupling innate immune response to proliferation in the blood of COVID-19 cancer patients
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
E2F transcription factor-1 regulates oxidative metabolism
Nature Cell Biology (2011)
-
Role of cis-regulatory elements on the ring-specific hrp3 promoter in the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Parasitology Research (2010)