Abstract
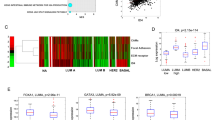
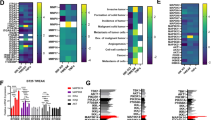
Activity of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase is positively correlated with tumor metastasis; however, its detailed role in the mechanism of tumor invasion is still not completely understood. Here, we show that Axl enhances the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), required for Axl-mediated invasion both in vitro and in vivo. We found that the highly selective MEK1/2 inhibitors U0126 and PD98059, and the expressed dominant-negative form of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), completely block Axl-mediated MMP-9 activation. In contrast, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 and wortmannin had little effect on activation. Interestingly, however, the Axl ligand Gas6 is not involved in Axl-mediated MMP-9 activation. Mutation of Glu59Axl and Thr77Axl dramatically reduced Gas6–Axl binding but continued to induce MMP-9 activation. In addition, overexpression of Axl-activated ERK and enhanced nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) transactivation and brahma-related gene-1 (Brg-1) translocation. Exposure to the NF-κB inhibitor silibinin, which inhibits IκBα kinase activity, or overexpression of the dominant-negative mutant IκB and Brg-1 strikingly inhibited Axl-mediated MMP-9 activation. These data indicate that coordination of ERK signaling and NF-κB and Brg-1 activation are indispensable to regulation of Axl-dependent MMP-9 gene transcription. Together with previous data, our results provide a plausible mechanism for Axl-mediated tumor invasion and establish a functional link between the Axl and MMP-9 signaling pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banine F, Bartlett C, Gunawardena R, Muchardt C, Yaniv M, Knudsen ES et al. (2005). SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factors induce changes in DNA methylation to promote transcriptional activation. Cancer Res 65: 3542–3547.
Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, Hendrix M et al. (2000). Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature 406: 536–540.
Budagian V, Bulanova E, Orinska Z, Thon L, Mamat U, Bellosta P et al. (2005). A promiscuous liaison between IL-15 receptor and Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in cell death control. EMBO J 24: 4260–4270.
Chung BI, Malkowicz SB, Nguyen TB, Libertino JA, McGarvey TW . (2003). Expression of the proto-oncogene Axl in renal cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol 22: 533–540.
Craven RJ, Xu LH, Weiner TM, Fridell YW, Dent GA, Srivastava S et al. (1995). Receptor tyrosine kinases expressed in metastatic colon cancer. Int J Cancer 60: 791–797.
Demarchi F, Verardo R, Varnum B, Brancolini C, Schneider C . (2001). Gas6 anti-apoptotic signaling requires NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem 276: 31738–31744.
Dhanalakshmi S, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Agarwal R . (2002). Silibinin inhibits constitutive and TNFalpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB and sensitizes human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 21: 1759–1767.
DiRenzo J, Shang Y, Phelan M, Sif S, Myers M, Kingston R et al. (2000). BRG-1 is recruited to estrogen-responsive promoters and cooperates with factors involved in histone acetylation. Mol Cell Biol 20: 7541–7549.
Fingleton B . (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases: roles in cancer and metastasis. Front Biosci 11: 479–491.
Fridell YW, Jin Y, Quilliam LA, Burchert A, McCloskey P, Spizz G et al. (1996). Differential activation of the Ras/extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinase pathway is responsible for the biological consequences induced by the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 16: 135–145.
Genersch E, Hayess K, Neuenfeld Y, Haller H . (2000). Sustained ERK phosphorylation is necessary but not sufficient for MMP-9 regulation in endothelial cells: involvement of Ras-dependent and -independent pathways. J Cell Sci 113 (Part 23): 4319–4330.
Hafizi S, Dahlback B . (2006). Signalling and functional diversity within the Axl subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 295–304.
Hasanbasic I, Cuerquis J, Varnum B, Blostein MD . (2004). Intracellular signaling pathways involved in Gas6-Axl-mediated survival of endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287: H1207–H1213.
Holland SJ, Powell MJ, Franci C, Chan EW, Friera AM, Atchison RE et al. (2005). Multiple roles for the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in tumor formation. Cancer Res 65: 9294–9303.
Ito T, Ito M, Naito S, Ohtsuru A, Nagayama Y, Kanematsu T et al. (1999). Expression of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in human thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 9: 563–567.
Jacob AN, Kalapurakal J, Davidson WR, Kandpal G, Dunson N, Prashar Y et al. (1999). A receptor tyrosine kinase, UFO/Axl, and other genes isolated by a modified differential display PCR are overexpressed in metastatic prostatic carcinoma cell line DU145. Cancer Detect Prev 23: 325–332.
Jin S, Lu D, Ye S, Ye H, Zhu L, Feng Z et al. (2005). A simplified probe preparation for ELISA-based NF-kappaB activity assay. J Biochem Biophys Methods 65: 20–29.
Lakka SS, Jasti SL, Gondi C, Boyd D, Chandrasekar N, Dinh DH et al. (2002). Downregulation of MMP-9 in ERK-mutated stable transfectants inhibits glioma invasion in vitro. Oncogene 21: 5601–5608.
Lay JD, Hong CC, Huang JS, Yang YY, Pao CY, Liu CH et al. (2007). Sulfasalazine suppresses drug resistance and invasiveness of lung adenocarcinoma cells expressing AXL. Cancer Res 67: 3878–3887.
Liu Y, Denlinger CE, Rundall BK, Smith PW, Jones DR . (2006). Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces Akt-mediated phosphorylation of p300, which promotes acetylation and transcriptional activation of RelA/p65. J Biol Chem 281: 31359–31368.
Ma Z, Shah RC, Chang MJ, Benveniste EN . (2004). Coordination of cell signaling, chromatin remodeling, histone modifications, and regulator recruitment in human matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5496–5509.
Melaragno MG, Fridell YW, Berk BC . (1999). The Gas6/Axl system: a novel regulator of vascular cell function. Trends Cardiovasc Med 9: 250–253.
Meric F, Lee WP, Sahin A, Zhang H, Kung HJ, Hung MC . (2002). Expression profile of tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8: 361–367.
Nakano T, Tani M, Ishibashi Y, Kimura K, Park YB, Imaizumi N et al. (2003). Biological properties and gene expression associated with metastatic potential of human osteosarcoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 20: 665–674.
Nemoto T, Ohashi K, Akashi T, Johnson JD, Hirokawa K . (1997). Overexpression of protein tyrosine kinases in human esophageal cancer. Pathobiology 65: 195–203.
Neubauer A, O'Bryan JP, Fiebeler A, Schmidt C, Huhn D, Liu ET . (1993). Axl, a novel receptor tyrosine kinase isolated from chronic myelogenous leukemia. Semin Hematol 30: 34.
Roberts CW, Orkin SH . (2004). The SWI/SNF complex—chromatin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 133–142.
Sasaki T, Knyazev PG, Clout NJ, Cheburkin Y, Gohring W, Ullrich A et al. (2006). Structural basis for Gas6-Axl signalling. EMBO J 25: 80–87.
Shieh YS, Lai CY, Kao YR, Shiah SG, Chu YW, Lee HS et al. (2005). Expression of axl in lung adenocarcinoma and correlation with tumor progression. Neoplasia 7: 1058–1064.
Singh RA, Zhang JZ . (2004). Differential activation of ERK, p38, and JNK required for Th1 and Th2 deviation in myelin-reactive T cells induced by altered peptide ligand. J Immunol 173: 7299–7307.
Sun W, Fujimoto J, Tamaya T . (2004). Coexpression of Gas6/Axl in human ovarian cancers. Oncology 66: 450–457.
Tai KY, Shiah SG, Shieh YS, Kao YR, Chi CY, Huang E et al. (2007). DNA methylation and histone modification regulate silencing of epithelial cell adhesion molecule for tumor invasion and progression. Oncogene 26: 3989–3997.
Vajkoczy P, Knyazev P, Kunkel A, Capelle HH, Behrndt S, von Tengg-Kobligk H et al. (2006). Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and invasion and prolongs survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5799–5804.
van Ginkel PR, Gee RL, Shearer RL, Subramanian L, Walker TM, Albert DM et al. (2004). Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl promotes ocular melanoma cell survival. Cancer Res 64: 128–134.
Wang W . (2003). The SWI/SNF family of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers: similar mechanisms for diverse functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 274: 143–169.
Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW, Lai CH, Huang CL, Lo SS et al. (2002). Clinical significance of AXL kinase family in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 22: 1071–1078.
Yao J, Xiong S, Klos K, Nguyen N, Grijalva R, Li P et al. (2001). Multiple signaling pathways involved in activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by heregulin-beta1 in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 20: 8066–8074.
Zeigler ME, Chi Y, Schmidt T, Varani J . (1999). Role of ERK and JNK pathways in regulating cell motility and matrix metalloproteinase 9 production in growth factor-stimulated human epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol 180: 271–284.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Health Research Institutes (Zhunan, Taiwan) grant no. 96A1-CASP01-014 (to C-W Wu). We thank Dr Christian Muchardt (Institute Pasteur, Paris) and Dr Weidong Wang (National Institute on Aging, Baltimore) for providing the BJ-5-Brg-1 and BJ-5-Brg-1(K798R) plasmids; Dr Anthony N Imbalzano for contacting Dr Muchardt and Dr Wang and Dr Jian Jian Li (Purdue University, Indiana) for providing the pCEP4–ERK1(K71R), pCEP4–ERK2(K52R) and pEGFP–IκBα(S32A, S36A) plasmids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, KY., Shieh, YS., Lee, CS. et al. Axl promotes cell invasion by inducing MMP-9 activity through activation of NF-κB and Brg-1. Oncogene 27, 4044–4055 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.57
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
AXL receptor tyrosine kinase modulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor signaling
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Role of miR-944/MMP10/AXL- axis in lymph node metastasis in tongue cancer
Communications Biology (2023)
-
A pathway map of AXL receptor-mediated signaling network
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Inhibition of the Axl pathway impairs breast and prostate cancer metastasis to the bones and bone remodeling
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2021)
-
AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications
Molecular Cancer (2019)