Abstract
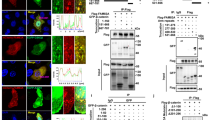
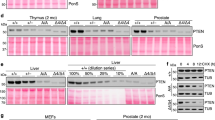
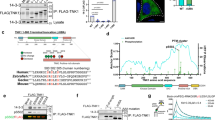
XB130 is a recently cloned 130 kDa-adaptor protein and Src kinase substrate, structurally similar to actin-filament-associated protein. Here we show that XB130 is predominantly expressed in the thyroid. Given that XB130 is a thyroid-specific tyrosine kinase substrate, we asked whether it is targeted by RET/PTC, a genetically rearranged, constitutively active, thyroid-specific tyrosine kinase that plays a pathogenic role in papillary thyroid cancer. RET/PTC induced robust tyrosine phosphorylation of XB130, which promoted its subsequent association with the p85α subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase). We identified tyrosine 54 of XB130 as the major target of RET/PTC-mediated phosphorylation and a critical binding site for the SH2 domains of p85α. Importantly, downregulation of XB130 in TPC1 papillary thyroid cancer cells, harboring the RET/PTC1 kinase, strongly reduced Akt activity without altering ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and concomitantly inhibited cell-cycle progression and survival in suspension. In conclusion, XB130 is a novel substrate of the RET/PTC kinase that links RET/PTC signaling to PI 3-kinase activation, and thereby plays an important role in sustaining proliferation and survival of thyroid tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P et al. (1996). Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J 15: 6541–6551.
Arighi E, Borrello MG, Sariola H . (2005). RET tyrosine kinase signaling in development and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16: 441–467.
Backer JM, Myers Jr MG, Shoelson SE, Chin DJ, Sun XJ, Miralpeix M et al. (1992). Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J 11: 3469–3479.
Besset V, Scott RP, Ibanez CF . (2000). Signaling complexes and protein-protein interactions involved in the activation of the Ras and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways by the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 275: 39159–39166.
Carlomagno F, Vitagliano D, Guida T, Ciardiello F, Tortora G, Vecchio G et al. (2002). ZD6474, an orally available inhibitor of KDR tyrosine kinase activity, efficiently blocks oncogenic RET kinases. Cancer Res 62: 7284–7290.
Carpenter CL, Auger KR, Chanudhuri M, Yoakim M, Schaffhausen B, Shoelson S et al. (1993). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is activated by phosphopeptides that bind to the SH2 domains of the 85-kDa subunit. J Biol Chem 268: 9478–9483.
Castellone MD, Cirafici AM, De Vita G, De Falco V, Malorni L, Tallini G et al. (2003). Ras-mediated apoptosis of PC CL 3 rat thyroid cells induced by RET/PTC oncogenes. Oncogene 22: 246–255.
De Falco V, Guarino V, Malorni L, Cirafici AM, Troglio F, Erreni M et al. (2005). RAI(ShcC/N-Shc)-dependent recruitment of GAB 1 to RET oncoproteins potentiates PI 3-K signalling in thyroid tumors. Oncogene 24: 6303–6313.
de Martimprey H, Bertrand JR, Fusco A, Santoro M, Couvreur P, Vauthier C et al. (2008). siRNA nanoformulation against the ret/PTC1 junction oncogene is efficient in an in vivo model of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Nucleic Acids Res 36: e2.
Escobedo JA, Navankasattusas S, Kavanaugh WM, Milfay D, Fried VA, Williams LT . (1991). cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell 65: 75–82.
Flynn DC, Leu TH, Reynolds AB, Parsons JT . (1993). Identification and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding a 110-kilodalton actin filament-associated pp60src substrate. Mol Cell Biol 13: 7892–7900.
Giordano TJ, Kuick R, Thomas DG, Misek DE, Vinco M, Sanders D et al. (2005). Molecular classification of papillary thyroid carcinoma: distinct BRAF, RAS, and RET/PTC mutation-specific gene expression profiles discovered by DNA microarray analysis. Oncogene 24: 6646–6656.
Grieco M, Santoro M, Berlingieri MT, Melillo RM, Donghi R, Bongarzone I et al. (1990). PTC is a novel rearranged form of the ret proto-oncogene and is frequently detected in vivo in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Cell 60: 557–563.
Han B, Bai XH, Lodyga M, Xu J, Yang BB, Keshavjee S et al. (2004). Conversion of mechanical force into biochemical signaling. J Biol Chem 279: 54793–54801.
Harlan JE, Hajduk PJ, Yoon HS, Fesik SW . (1994). Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nature 371: 168–170.
Haslam RJ, Koide HB, Hemmings BA . (1993). Pleckstrin domain homology. Nature 363: 309–310.
Hayashi H, Ichihara M, Iwashita T, Murakami H, Shimono Y, Kawai K et al. (2000). Characterization of intracellular signals via tyrosine 1062 in RET activated by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Oncogene 19: 4469–4475.
Hemmings BA . (1997). PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 gets its message across. Science 277: 534.
Iavarone C, Acunzo M, Carlomagno F, Catania A, Melillo RM, Carlomagno SM et al. (2006). Activation of the Erk8 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase by RET/PTC3, a constitutively active form of the RET proto-oncogene. J Biol Chem 281: 10567–10576.
Iwashita T, Asai N, Murakami H, Matsuyama M, Takahashi M . (1996). Identification of tyrosine residues that are essential for transforming activity of the ret proto-oncogene with MEN2A or MEN2B mutation. Oncogene 12: 481–487.
Jung HS, Kim DW, Jo YS, Chung HK, Song JH, Park JS et al. (2005). Regulation of protein kinase B tyrosine phosphorylation by thyroid-specific oncogenic RET/PTC kinases. Mol Endocrinol 19: 2748–2759.
Kaplan DR, Miller FD . (1997). Signal transduction by the neurotrophin receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 213–221.
Knauf JA, Kuroda H, Basu S, Fagin JA . (2003). RET/PTC-induced dedifferentiation of thyroid cells is mediated through Y1062 signaling through SHC-RAS-MAP kinase. Oncogene 22: 4406–4412.
Lodyga M, Bai XH, Mourgeon E, Han B, Keshavjee S, Liu M . (2002). Molecular cloning of actin filament-associated protein: a putative adaptor in stretch-induced Src activation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283: L265–L274.
Maeda K, Murakami H, Yoshida R, Ichihara M, Abe A, Hirai M et al. (2004). Biochemical and biological responses induced by coupling of Gab1 to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in RET-expressing cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323: 345–354.
Mai KT, Vaccani JP, Thomas J, Odell PF . (2001). Immunostaining for ret oncogene proteins in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a correlation of ret immunoreactivity and potential of lymph node metastasis. Thyroid 11: 859–863.
Mariggio S, Filippi BM, Iurisci C, Dragani LK, De Falco V, Santoro M et al. (2007). Cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha regulates cell growth in RET/PTC-transformed thyroid cells. Cancer Res 67: 11769–11778.
Marte BM, Downward J . (1997). PKB/Akt: connecting phosphoinositide 3-kinase to cell survival and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci 22: 355–358.
Melillo RM, Carlomagno F, De Vita G, Formisano P, Vecchio G, Fusco A et al. (2001). The insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 recruits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to Ret: evidence for a competition between Shc and IRS-1 for the binding to Ret. Oncogene 20: 209–218.
Melillo RM, Castellone MD, Guarino V, De Falco V, Cirafici AM, Salvatore G et al. (2005). The RET/PTC-RAS-BRAF linear signaling cascade mediates the motile and mitogenic phenotype of thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Invest 115: 1068–1081.
Miyagi E, Braga-Basaria M, Hardy E, Vasko V, Burman KD, Jhiang S et al. (2004). Chronic expression of RET/PTC 3 enhances basal and insulin-stimulated PI3 kinase/AKT signaling and increases IRS-2 expression in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Mol Carcinog 41: 98–107.
Pelicci G, Troglio F, Bodini A, Melillo RM, Pettirossi V, Coda L et al. (2002). The neuron-specific Rai (ShcC) adaptor protein inhibits apoptosis by coupling Ret to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7351–7363.
Pierotti MA, Santoro M, Jenkins RB, Sozzi G, Bongarzone I, Grieco M et al. (1992). Characterization of an inversion on the long arm of chromosome 10 juxtaposing D10S170 and RET and creating the oncogenic sequence RET/PTC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1616–1620.
Rordorf-Nikolic T, Van Horn DJ, Chen D, White MF, Backer JM . (1995). Regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase by tyrosyl phosphoproteins. Full activation requires occupancy of both SH2 domains in the 85-kDa regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem 270: 3662–3666.
Santoro M, Chiappetta G, Cerrato A, Salvatore D, Zhang L, Manzo G et al. (1996). Development of thyroid papillary carcinomas secondary to tissue-specific expression of the RET/PTC1 oncogene in transgenic mice. Oncogene 12: 1821–1826.
Santoro M, Dathan NA, Berlingieri MT, Bongarzone I, Paulin C, Grieco M et al. (1994a). Molecular characterization of RET/PTC3; a novel rearranged version of the RETproto-oncogene in a human thyroid papillary carcinoma. Oncogene 9: 509–516.
Santoro M, Melillo RM, Grieco M, Berlingieri MT, Vecchio G, Fusco A . (1993). The TRK and RET tyrosine kinase oncogenes cooperate with ras in the neoplastic transformation of a rat thyroid epithelial cell line. Cell Growth Differ 4: 77–84.
Santoro M, Wong WT, Aroca P, Santos E, Matoskova B, Grieco M et al. (1994b). An epidermal growth factor receptor/ret chimera generates mitogenic and transforming signals: evidence for a ret-specific signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 14: 663–675.
Takahashi M, Buma Y, Iwamoto T, Inaguma Y, Ikeda H, Hiai H . (1988). Cloning and expression of the ret proto-oncogene encoding a tyrosine kinase with two potential transmembrane domains. Oncogene 3: 571–578.
Xu J, Bai XH, Lodyga M, Han B, Xiao H, Keshavjee S et al. (2007). XB130, a novel adaptor protein for signal transduction. J Biol Chem 282: 16401–16412.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr B Han and Dr D Winer for technical assistance. We thank AJ Ryan, AstraZeneca for the ZD6474 inhibitor. We also thank Dr S Asa and JM Hershman for human thyroid cell lines, Dr G Pelicci for GST-fusion proteins and Dr M Chiariello for the Src mutant. This work was supported by operating grants (MOP-13270, MOP-42546) from Canadian Institutes of Health Research, a grant from the Italian Association for Cancer Research, MIUR, Alleanza contro iL Cancro and the European Union Contract FP6-36495 (GENRISK-T).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lodyga, M., De Falco, V., Bai, Xh. et al. XB130, a tissue-specific adaptor protein that couples the RET/PTC oncogenic kinase to PI 3-kinase pathway. Oncogene 28, 937–949 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.447
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.447
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of XB130 adaptor protein mediates trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)
-
XB130 promotes proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Roles of XB130, a novel adaptor protein, in cancer
Journal of Clinical Bioinformatics (2011)
-
Identification of AFAP1L1 as a prognostic marker for spindle cell sarcomas
Oncogene (2011)
-
The RET/PTC3 oncogene activates classical NF-κB by stabilizing NIK
Oncogene (2011)