Abstract
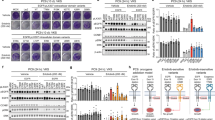
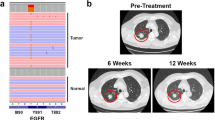
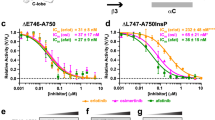
Targeted therapy against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) represents a major therapeutic advance in lung cancer treatment. Somatic mutations of the EGFR gene, most commonly L858R (exon 21) and short in-frame exon 19 deletions, have been found to confer enhanced sensitivity toward the inhibitors gefitinib and erlotinib. We have recently identified an EGFR mutation E884K, in combination with L858R, in a patient with advanced lung cancer who progressed on erlotinib maintenance therapy, and subsequently had leptomeningeal metastases that responded to gefitinib. The somatic E884K substitution appears to be relatively infrequent and resulted in a mutant lysine residue that disrupts an ion pair with residue R958 in the EGFR kinase domain C-lobe, an interaction that is highly conserved within the human kinome as demonstrated by our sequence analysis and structure analysis. Our studies here, using COS-7 transfection model system, show that E884K works in concert with L858R in-cis, in a dominant manner, to change downstream signaling, differentially induce Mitogen-activated protein kinase (extracellular signaling-regulated kinase 1/2) signaling and associated cell proliferation and differentially alter sensitivity of EGFR phosphorylation inhibition by ERBB family inhibitors in an inhibitor-specific manner. Mutations of the conserved ion pair E884–R958 may result in conformational changes that alter kinase substrate recognition. The analogous E1271K-MET mutation conferred differential sensitivity toward preclinical MET inhibitors SU11274 (unchanged) and PHA665752 (more sensitive). Systematic bioinformatics analysis of the mutation catalog in the human kinome revealed the presence of cancer-associated mutations involving the conserved E884 homologous residue, and adjacent residues at the ion pair, in known proto-oncogenes (KIT, RET, MET and FAK) and tumor-suppressor gene (LKB1). Targeted therapy using small-molecule inhibitors should take into account potential cooperative effects of multiple kinase mutations, and their specific effects on downstream signaling and inhibitor sensitivity. Improved efficacy of targeted kinase inhibitors may be achieved by targeting the dominant activating mutations present.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COSMIC:
-
catalogue of somatic mutations in cancer
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- MAPK (ERK1/2):
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase (extracellular signaling-regulated kinase 1/2)
- STAT3:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TKI:
-
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
References
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale A, Wang L et al. (2007). MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 20932–20937.
Bellon SF, Kaplan-Lefko P, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Moriguchi J, Rex K et al. (2008). c-Met inhibitors with novel binding mode show activity against several hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma related mutations. J Biol Chem 283: 2675–2683.
Brodsky LI, Vasiliev AV, Kalaidzidis YL, Osipov YS, Tatuzov RL, Feranchuk SI . (1992). GeneBee: the program package for biopolymer structure analysis. Dimacs 8: 127–139.
Chen Z, Feng J, Saldivar JS, Gu D, Bockholt A, Sommer SS (2008). EGFR somatic doublets in lung cancer are frequent and generally arise from a pair of driver mutations uncommonly seen as singlet mutations: one-third of doublets occur at five pairs of amino acids. Oncogene 27: 4336–4343.
Choong NW, Dietrich S, Seiwert TY, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Davies GC et al. (2006). Gefitinib response of erlotinib-refractory lung cancer involving meninges—role of EGFR mutation. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3: 50–57; quiz 51 p following 57.
Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ . (2004). The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20: 426–427.
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Martone T, Maffe A, Maggiora P, Stefani AD et al. (2000). Somatic mutations of the MET oncogene are selected during metastatic spread of human HNSC carcinomas. Oncogene 19: 1547–1555.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO et al. (2007). MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316: 1039–1043.
Frohling S, Scholl C, Levine RL, Loriaux M, Boggon TJ, Bernard OA et al. (2007). Identification of driver and passenger mutations of FLT3 by high-throughput DNA sequence analysis and functional assessment of candidate alleles. Cancer Cell 12: 501–513.
Guo A, Villen J, Kornhauser J, Lee KA, Stokes MP, Rikova K et al. (2008). Signaling networks assembled by oncogenic EGFR and c-Met. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 692–697.
Hubbard SR . (1997). Crystal structure of the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in complex with peptide substrate and ATP analog. Embo J 16: 5572–5581.
Jackman DM, Holmes AJ, Lindeman N, Wen PY, Kesari S, Borras AM et al. (2006). Response and resistance in a non-small-cell lung cancer patient with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and leptomeningeal metastases treated with high-dose gefitinib. J Clin Oncol 24: 4517–4520.
Jagadeeswaran R, Ma PC, Seiwert TY, Jagadeeswaran S, Zumba O, Nallasura V et al. (2006). Functional analysis of c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Res 66: 352–361.
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P et al. (2007). LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature 448: 807–810.
Jin L, Pluskey S, Petrella EC, Cantin SM, Gorga JC, Rynkiewicz MJ et al. (2004). The three-dimensional structure of the ZAP-70 kinase domain in complex with staurosporine: implications for the design of selective inhibitors. J Biol Chem 279: 42818–42825.
Jones TA, Zou JY, Cowan SW, Kjeldgaard M . (1991). Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A 47 (Part 2): 110–119.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M et al. (2005). EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 352: 786–792.
Krause DS, Van Etten RA . (2005). Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med 353: 172–187.
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Ali-Seyed M, Gunduz M, Xia W, Wei Y et al. (2005). Nuclear interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer Cell 7: 575–589.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW et al. (2004). Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350: 2129–2139.
Ma PC, Jagadeeswaran R, Jagadeesh S, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Fox EA et al. (2005a). Functional expression and mutations of c-Met and its therapeutic inhibition with SU11274 and small interfering RNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 65: 1479–1488.
Ma PC, Kijima T, Maulik G, Fox EA, Sattler M, Griffin JD et al. (2003a). c-MET mutational analysis in small cell lung cancer: novel juxtamembrane domain mutations regulating cytoskeletal functions. Cancer Res 63: 6272–6281.
Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J, Salgia R . (2003b). c-Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22: 309–325.
Ma PC, Schaefer E, Christensen JG, Salgia R . (2005b). A selective small molecule c-MET Inhibitor, PHA665752, cooperates with rapamycin. Clin Cancer Res 11: 2312–2319.
Ma PC, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Jagadeeswaran R, Husain AN, Salgia R . (2007). Downstream signalling and specific inhibition of c-MET/HGF pathway in small cell lung cancer: implications for tumour invasion. Br J Cancer 97: 368–377.
Mazzone M, Comoglio PM . (2006). The Met pathway: master switch and drug target in cancer progression. FASEB J 20: 1611–1621.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. (2004). EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304: 1497–1500.
Peruzzi B, Bottaro DP . (2006). Targeting the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12: 3657–3660.
Pevarello P, Brasca MG, Amici R, Orsini P, Traquandi G, Corti L et al. (2004). 3-Aminopyrazole inhibitors of CDK2/cyclin A as antitumor agents. 1. Lead finding. J Med Chem 47: 3367–3380.
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H et al. (2007). Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 131: 1190–1203.
Scapin G, Patel SB, Lisnock J, Becker JW, LoGrasso PV . (2003). The structure of JNK3 in complex with small molecule inhibitors: structural basis for potency and selectivity. Chem Biol 10: 705–712.
Shigematsu H, Gazdar AF . (2006). Somatic mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in lung cancers. Int J Cancer 118: 257–262.
Shinomiya N, Gao CF, Xie Q, Gustafson M, Waters DJ, Zhang YW et al. (2004). RNA interference reveals that ligand-independent met activity is required for tumor cell signaling and survival. Cancer Res 64: 7962–7970.
Smolen GA, Sordella R, Muir B, Mohapatra G, Barmettler A, Archibald H et al. (2006). Amplification of MET may identify a subset of cancers with extreme sensitivity to the selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor PHA-665752. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2316–2321.
Stamos J, Sliwkowski MX, Eigenbrot C . (2002). Structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain alone and in complex with a 4-anilinoquinazoline inhibitor. J Biol Chem 277: 46265–46272.
Tam IY, Chung LP, Suen WS, Wang E, Wong MC, Ho KK et al. (2006). Distinct epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutation patterns in non-small cell lung cancer patients with different tobacco exposure and clinicopathologic features. Clin Cancer Res 12: 1647–1653.
Tang Z, Du R, Jiang S, Wu C, Barkauskas DS, Richey J et al. (2008). Dual MET-EGFR combinatorial inhibition against T790M-EGFR-mediated erlotinib-resistant lung cancer. Br J Cancer 99: 911–922, 2008.
Thomas RK, Baker AC, Debiasi RM, Winckler W, Laframboise T, Lin WM et al. (2007). High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer. Nat Genet 39: 347–351.
Wood ER, Truesdale AT, McDonald OB, Yuan D, Hassell A, Dickerson SH et al. (2004). A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res 64: 6652–6659.
Zhang X, Gureasko J, Shen K, Cole PA, Kuriyan J . (2006). An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 125: 1137–1149.
Zhu X, Kim JL, Newcomb JR, Rose PE, Stover DR, Toledo LM et al. (1999). Structural analysis of the lymphocyte-specific kinase Lck in complex with non-selective and Src family selective kinase inhibitors. Structure 7: 651–661.
Acknowledgements
Patrick C Ma is supported by NIH/National Cancer Institute-K08 Career Development Award (5K08CA102545-04), American Cancer Society (Ohio)-Institutional Research Grant (IRG-91-022, Case Comprehensive Cancer Center) and Ohio Cancer Research Associates (Give New Ideas A Chance) Grant Award. Titus J Boggon is an American Society of Hematology Junior Faculty Scholar. Edward T Petri is supported by an NIH/National Cancer Institute T32 training Grant (5T32CA009085-32). We thank Dr Zhenghe J Wang (Department of Genetics, Case Western Reserve University) for critically reading the manuscript and for helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Z., Jiang, S., Du, R. et al. Disruption of the EGFR E884–R958 ion pair conserved in the human kinome differentially alters signaling and inhibitor sensitivity. Oncogene 28, 518–533 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.411
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.411
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel EPHB4 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Mutations and Kinomic Pathway Analysis in Lung Cancer
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Global connectivity of hub residues in Oncoprotein structures encodes genetic factors dictating personalized drug response to targeted Cancer therapy
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Two cases of leptomeningeal metastases from lung adenocarcinoma which progressed during gefitinib therapy but responded to erlotinib
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2012)