Abstract
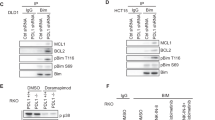
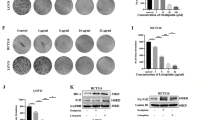
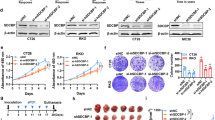
During development inhibitor of DNA-bind-2 (Id2) regulates proliferation and differentiation. Id2 expression has been detected in cancer cells, yet its cellular function and validity as a therapeutic target remains largely unknown. Immunohistochemical analysis of colorectal cancer (CRC) specimens revealed that Id2 was undetectable in normal colonic mucosa, but occurs in 40% of primary tumors and in most CRC liver metastases (P<0.0001). Additionally, Id2 was expressed in all CRC cell lines assayed. CRC cells with reduced Id2 expression demonstrated reduced proliferation. Analysis of CRC cell cycle regulatory proteins showed that reducing Id2 levels reduces cyclin D1 levels and increased p21 levels. Reduction of Id2 expression also enhanced tumor cell apoptosis, increasing levels of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim/Bod, and cleavage of caspase-7 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. In vivo studies show tumors derived from cells with decreased Id2 levels formed smaller tumors with fewer metastases compared with tumors with normal levels (P<0.05). Furthermore, intraperitoneal administration of Id2 small interfering RNA (siRNA) conjugated with the neutral liposome 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine decreased tumor burden in mice compared with control treatment (P=0.006). We conclude that Id2 is upregulated in CRC, and is important in promoting cell survival. In vivo targeting of Id2 by siRNA establishes that it is a valid therapeutic target where its expression occurs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
colorectal carcinoma
- Id2:
-
inhibitor of DNA-bind-2
- Rb:
-
Retinoblastoma protein
- shRNA:
-
short hairpin RNA
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
References
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Logsdon CD . (2006). Effect of cromolyn on S100P interactions with RAGE and pancreatic cancer growth and invasion in mouse models. J Natl Cancer Inst 98: 1806–1818.
Asirvatham AJ, Carey JP, Chaudhary J . (2007). ID1-, ID2-, and ID3-regulated gene expression in E2A positive or negative prostate cancer cells. Prostate 67: 1411–1420.
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H . (1990). The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 61: 49–59.
Benezra R, Rafii S, Lyden D . (2001). The Id proteins and angiogenesis. Oncogene 20: 8334–8341.
Broude EV, Swift ME, Vivo C, Chang BD, Davis BM, Kalurupalle S et al. (2007). p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1) mediates retinoblastoma protein degradation. Oncogene 26: 6954–6958.
Camp ER, Yang A, Liu W, Fan F, Somcio R, Hicklin DJ et al. (2006). Roles of nitric oxide synthase inhibition and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibition on vascular morphology and function in an in vivo model of pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12: 2628–2633.
Cannarile MA, Lind NA, Rivera R, Sheridan AD, Camfield KA, Wu BB et al. (2006). Transcriptional regulator Id2 mediates CD8+ T cell immunity. Nat Immunol 7: 1317–1325.
Gray MJ, Wey JS, Belcheva A, McCarty MF, Trevino JG, Evans DB et al. (2005). Neuropilin-1 suppresses tumorigenic properties in a human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line lacking neuropilin-1 coreceptors. Cancer Res 65: 3664–3670.
Hsu SY, Lin P, Hsueh AJ . (1998). BOD (Bcl-2-related ovarian death gene) is an ovarian BH3 domain-containing proapoptotic Bcl-2 protein capable of dimerization with diverse antiapoptotic Bcl-2 members. Mol Endocrinol 12: 1432–1440.
Hughes TA, Brady HJ . (2005). E2F1 up-regulates the expression of the tumour suppressor axin2 both by activation of transcription and by mRNA stabilisation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329: 1267–1274.
Iavarone A, Garg P, Lasorella A, Hsu J, Israel MA . (1994). The helix-loop-helix protein Id-2 enhances cell proliferation and binds to the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev 8: 1270–1284.
Jen Y, Manova K, Benezra R . (1996). Expression patterns of Id1, Id2, and Id3 are highly related but distinct from that of Id4 during mouse embryogenesis. Dev Dyn 207: 235–252.
Kleeff J, Ishiwata T, Friess H, Buchler MW, Israel MA, Korc M . (1998). The helix-loop-helix protein Id2 is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 58: 3769–3772.
Landen Jr CN., Chavez-Reyes A, Bucana C, Schmandt R, Deavers MT, Lopez-Berestein G et al. (2005). Therapeutic EphA2 gene targeting in vivo using neutral liposomal small interfering RNA delivery. Cancer Res 65: 6910–6918.
Langley RR, Ramirez KM, Tsan RZ, Van Arsdall M, Nilsson MB, Fidler IJ . (2003). Tissue-specific microvascular endothelial cell lines from H-2K(b)-tsA58 mice for studies of angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res 63: 2971–2976.
Lasorella A, Boldrini R, Dominici C, Donfrancesco A, Yokota Y, Inserra A et al. (2002). Id2 is critical for cellular proliferation and is the oncogenic effector of N-myc in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 62: 301–306.
Lasorella A, Iavarone A, Israel MA . (1996). Id2 specifically alters regulation of the cell cycle by tumor suppressor proteins. Mol Cell Biol 16: 2570–2578.
Lasorella A, Noseda M, Beyna M, Yokota Y, Iavarone A . (2000). Id2 is a retinoblastoma protein target and mediates signalling by Myc oncoproteins. Nature 407: 592–598.
Lasorella A, Rothschild G, Yokota Y, Russell RG, Iavarone A . (2005). Id2 mediates tumor initiation, proliferation, and angiogenesis in rb mutant mice. Mol Cell Biol 25: 3563–3574.
Lasorella A, Uo T, Iavarone A . (2001). Id proteins at the cross-road of development and cancer. Oncogene 20: 8326–8333.
Lofstedt T, Jogi A, Sigvardsson M, Gradin K, Poellinger L, Pahlman S et al. (2004). Induction of ID2 expression by hypoxia-inducible factor-1: a role in dedifferentiation of hypoxic neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 279: 39223–39231.
Lukas J, Bartkova J, Rohde M, Strauss M, Bartek J . (1995). Cyclin D1 is dispensable for G1 control in retinoblastoma gene-deficient cells independently of cdk4 activity. Mol Cell Biol 15: 2600–2611.
O'Connor L, Strasser A, O'Reilly LA, Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S et al. (1998). Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. Embo J 17: 384–395.
Oliver FJ, de la Rubia G, Rolli V, Ruiz-Ruiz MC, de Murcia G, Murcia JM . (1998). Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and its cleavage in apoptosis. Lesson from an uncleavable mutant. J Biol Chem 273: 33533–33539.
Pagliuca A, Gallo P, De Luca P, Lania L . (2000). Class A helix-loop-helix proteins are positive regulators of several cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors' promoter activity and negatively affect cell growth. Cancer Res 60: 1376–1382.
Parikh AA, Fan F, Liu WB, Ahmad SA, Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N et al. (2004). Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: expression, regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 164: 2139–2151.
Prabhu S, Ignatova A, Park ST, Sun XH . (1997). Regulation of the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 by E2A and Id proteins. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5888–5896.
Rockman SP, Currie SA, Ciavarella M, Vincan E, Dow C, Thomas RJ et al. (2001). Id2 is a target of the beta-catenin/T cell factor pathway in colon carcinoma. J Biol Chem 276: 45113–45119.
Rothschild G, Zhao X, Iavarone A, Lasorella A . (2006). E Proteins and Id2 converge on p57Kip2 to regulate cell cycle in neural cells. Mol Cell Biol 26: 4351–4361.
Russell RG, Lasorella A, Dettin LE, Iavarone A . (2004). Id2 drives differentiation and suppresses tumor formation in the intestinal epithelium. Cancer Res 64: 7220–7225.
Weinberg RA . (1995). The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81: 323–330.
Weinberg RA . (1996). E2F and cell proliferation: a world turned upside down. Cell 85: 457–459.
Wilson JW, Deed RW, Inoue T, Balzi M, Becciolini A, Faraoni P et al. (2001). Expression of Id helix-loop-helix proteins in colorectal adenocarcinoma correlates with p53 expression and mitotic index. Cancer Res 61: 8803–8810.
Yang AD, Fan F, Camp ER, van Buren G, Liu W, Somcio R et al. (2006). Chronic oxaliplatin resistance induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4147–4153.
Zhang X, Ling MT, Wong YC, Wang X . (2007). Evidence of a novel antiapoptotic factor: role of inhibitor of differentiation or DNA binding (Id-1) in anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Sci 98: 308–314.
Acknowledgements
We thank Rita Hernandez (Department of Surgical Oncology) and Christine Wogan (Department of Scientific Publications) for manuscript editing and preparation. Supported by NIH-5 T32 CA09599 (GVB, NAD, ADY and PG), Program Project Development Grant from the Ovarian Cancer Research Fund, Inc. (AKS), the Zarrow Foundation (AKS) and William C Liedtke, Jr Chair in Cancer Research (LME).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, M., Dallas, N., Van Buren, G. et al. Therapeutic targeting of Id2 reduces growth of human colorectal carcinoma in the murine liver. Oncogene 27, 7192–7200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.356
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.356
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ID2 promotes tumor progression and metastasis in thyroid cancer
Endocrine (2024)
-
Loss of E-cadherin leads to Id2-dependent inhibition of cell cycle progression in metastatic lobular breast cancer
Oncogene (2022)
-
Peroxiredoxin 4 suppresses anoikis and augments growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the β-catenin/ID2 pathway
Cellular Oncology (2019)
-
Vessel co-option mediates resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy in liver metastases
Nature Medicine (2016)
-
The ID proteins: master regulators of cancer stem cells and tumour aggressiveness
Nature Reviews Cancer (2014)