Abstract
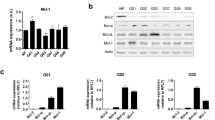
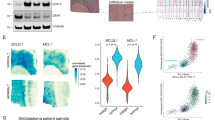
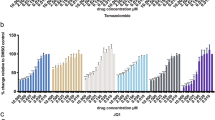
Defects in the apoptotic signaling cascades contribute to the poor therapeutic response of malignant gliomas. As glioblastomas are characterized by high expression levels of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, we studied the effects of the novel Bcl-2 inhibitor, ABT-737, on malignant glioma cells. ABT-737 treatment released the pro-apoptotic Bax protein from its binding partner Bcl-2 and potently induced apoptotic cell death in glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. The local administration of ABT-737 prolonged the survival in an intracranial glioma xenograft model. Downregulation of Mcl-1 and overexpression of Bcl-2 sensitized the cells to ABT-737-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, ABT-737 potentiated the cytotoxicity of the chemotherapeutic drugs vincristine and etoposide, and of the death ligand TRAIL. As glioma stem cells may play a crucial role for the tumor progression and the resistance to treatment in glioblastomas, we investigated the effects of ABT-737 on the subpopulation of glioma cells exhibiting stem cell characteristics. Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by ABT-737 were less efficient in glioma stem cells than in non-stem cell-like glioma cells. As the resistance of glioma stem cells was associated with high Mcl-1 expression levels, ABT-737 treatment combined with downregulation of Mcl-1 could represent a promising novel approach in glioblastoma treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Huang DC, Strasser A, Willis S, Chen L, Wei A et al. (2005). Subversion of the Bcl-2 life/death switch in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 70: 469–477.
Ahmadi R, Urig S, Hartmann M, Helmke BM, Koncarevic S, Allenberger B et al. (2006). Antiglioma activity of 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridineplatinum(II) complexes in a rat model—effects on cellular redox metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med 40: 763–778.
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al. (2006). Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444: 756–760.
Campos B, Wan F, Zeppernick F, Ernst A, Tagscherer KE, Ahmadi R et al. (2008). Differentiation therapy impacts on malignancy-related properties of brain tumor stem cell-derived tumors (submitted).
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA et al. (2006). Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 9: 351–365.
Chauhan D, Velankar M, Brahmandam M, Hideshima T, Podar K, Richardson P et al. (2007). A novel Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor ABT-737 as therapy in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 26: 2374–2380.
Chawla-Sarkar M, Bae SI, Reu FJ, Jacobs BS, Lindner DJ, Borden EC . (2004). Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs (XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 11: 915–923.
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S . (2007). Mcl-1 downregulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 67: 782–791.
Cragg MS, Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Huang DC, Strasser A . (2007). Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med 4: 1681–1690.
Del Bufalo D, Trisciuoglio D, Biroccio A, Marcocci L, Buglioni S, Candiloro A et al. (2001). Bcl-2 overexpression decreases BCNU sensitivity of a human glioblastoma line through enhancement of catalase activity. J Cell Biochem 83: 473–483.
Del Gaizo Moore V, Brown JR, Certo M, Love TM, Novina CD, Letai A . (2007). Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J Clin Invest 117: 112–121.
Del Gaizo Moore V, Schlis KD, Sallan SE, Armstrong SA, Letai A . (2008). BCL-2 dependence and ABT-737 sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 111: 2300–2309.
Deng J, Carlson N, Takeyama K, Dal Cin P, Shipp M, Letai A . (2007a). BH3 profiling identifies three distinct classes of apoptotic blocks to predict response to ABT-737 and conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Cell 12: 171–185.
Deng J, Shimamura T, Perera S, Carlson NE, Cai D, Shapiro GI et al. (2007b). Proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family protein BIM connects death signaling from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition to the mitochondrion. Cancer Res 67: 11867–11875.
Dictus C, Tronnier V, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C . (2007). Comparative analysis of in vitro conditions for rat adult neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci Methods 161: 250–258.
Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A, Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G et al. (2006). Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death Differ 13: 1238–1241.
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM . (2002a). Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression. Oncogene 21: 2283–2294.
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM . (2002b). Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med 8: 808–815.
Gillies RJ, Didier N, Denton M . (1986). Determination of cell number in monolayer cultures. Anal Biochem 159: 109–113.
Glaser T, Wagenknecht B, Groscurth P, Krammer PH, Weller M . (1999). Death ligand/receptor-independent caspase activation mediates drug-induced cytotoxic cell death in human malignant glioma cells. Oncogene 18: 5044–5053.
Gong Y, Somwar R, Politi K, Balak M, Chmielecki J, Jiang X et al. (2007). Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med 4: 1655–1668.
Green DR . (2006). At the gates of death. Cancer Cell 9: 328–330.
Hann CL, Daniel VC, Sugar EA, Dobromilskaya I, Murphy SC, Cope L et al. (2008). Therapeutic efficacy of ABT-737, a selective inhibitor of BCL-2, in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 68: 2321–2328.
Huang S, Sinicrope FA . (2008). BH3 mimetic ABT-737 potentiates TRAIL-mediated apoptotic signaling by unsequestering Bim and Bak in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 68: 2944–2951.
Kajiwara Y, Yamasaki F, Hama S, Yahara K, Yoshioka H, Sugiyama K et al. (2003). Expression of survivin in astrocytic tumors: correlation with malignant grade and prognosis. Cancer 97: 1077–1083.
Kang MH, Kang YH, Szymanska B, Wilczynska-Kalak U, Sheard MA, Harned TM et al. (2007). Activity of vincristine, L-ASP and dexamethasone against acute lymphoblastic leukemia is enhanced by the BH3-mimetic ABT-737 in vitro and in vivo. Blood 110: 2057–2066.
Kang MH, Wan Z, Kang YH, Sposto R, Reynolds CP . (2008). Mechanism of synergy of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and ABT-737 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines: Mcl-1 inactivation. J Natl Cancer Inst 100: 580–595.
Karcher S, Steiner HH, Ahmadi R, Zoubaa S, Vasvari G, Bauer H et al. (2006). Different angiogenic phenotypes in primary and secondary glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 118: 2182–2189.
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S et al. (2006). Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 10: 375–388.
Krajewski S, Bodrug S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Gascoyne R, Berean K et al. (1995). Immunohistochemical analysis of Mcl-1 protein in human tissues. Differential regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 protein production suggests a unique role for Mcl-1 in control of programmed cell death in vivo. Am J Pathol 146: 1309–1319.
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Ehrmann J, Sikorska M, Lach B, Chatten J et al. (1997). Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2, Bcl-X, Mcl-1, and Bax in tumors of central and peripheral nervous system origin. Am J Pathol 150: 805–814.
Kraus JA, Wenghoefer M, Glesmann N, Mohr S, Beck M, Schmidt MC et al. (2001). TP53 gene mutations, nuclear p53 accumulation, expression of Waf/p21, Bcl-2, and CD95 (APO-1/Fas) proteins are not prognostic factors in de novo glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 52: 263–272.
Letai A . (2006). Restoring cancer's death sentence. Cancer Cell 10: 343–345.
Lin X, Morgan-Lappe S, Huang X, Li L, Zakula DM, Vernetti LA et al. (2006). ‘Seed’ analysis of off-target siRNAs reveals an essential role of Mcl-1 in resistance to the small-molecule Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) inhibitor ABT-737. Oncogene 26: 3972–3979.
Nagane M, Levitzki A, Gazit A, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ . (1998). Drug resistance of human glioblastoma cells conferred by a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor through modulation of Bcl-XL and caspase-3-like proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 5724–5729.
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ . (2000). Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 60: 847–853.
Olejniczak ET, Van Sant C, Anderson MG, Wang G, Tahir SK, Sauter G et al. (2007). Integrative genomic analysis of small-cell lung carcinoma reveals correlates of sensitivity to bcl-2 antagonists and uncovers novel chromosomal gains. Mol Cancer Res 5: 331–339.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. (2005). An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435: 677–681.
Pollack IF, Erff M, Ashkenazi A . (2001). Direct stimulation of apoptotic signaling by soluble Apo2l/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand leads to selective killing of glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res 7: 1362–1369.
Reed JC . (2006). Drug insight: cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3: 388–398.
Rieger J, Naumann U, Glaser T, Ashkenazi A, Weller M . (1998). APO2 ligand: a novel lethal weapon against malignant glioma? FEBS Lett 427: 124–128.
Riemenschneider MJ, Betensky RA, Pasedag SM, Louis DN . (2006). AKT activation in human glioblastomas enhances proliferation via TSC2 and S6 kinase signaling. Cancer Res 66: 5618–5623.
Roth W, Isenmann S, Naumann U, Kugler S, Bahr M, Dichgans J et al. (1999). Locoregional Apo2L/TRAIL eradicates intracranial human malignant glioma xenografts in athymic mice in the absence of neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265: 479–483.
Sanai N, Alvarez-Buylla A, Berger MS . (2005). Neural stem cells and the origin of gliomas. N Engl J Med 353: 811–822.
Sinicrope FA, Penington RC, Tang XM . (2004). Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis is inhibited by Bcl-2 but restored by the small molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor, HA 14-1, in human colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 10: 8284–8292.
Stupp R, Hegi ME . (2007). Targeting brain-tumor stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 25: 193–194.
Tahir SK, Yang X, Anderson MG, Morgan-Lappe SE, Sarthy AV, Chen J et al. (2007). Influence of Bcl-2 family members on the cellular response of small-cell lung cancer cell lines to ABT-737. Cancer Res 67: 1176–1183.
Trudel S, Stewart AK, Li Z, Shu Y, Liang SB, Trieu Y et al. (2007). The Bcl-2 family protein inhibitor, ABT-737, has substantial antimyeloma activity and shows synergistic effect with dexamethasone and melphalan. Clin Cancer Res 13: 621–629.
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S et al. (2008). ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res 68: 3421–3428.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. (2006). The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10: 389–399.
Wagenknecht B, Glaser T, Naumann U, Kugler S, Isenmann S, Bahr M et al. (1999). Expression and biological activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in human malignant glioma. Cell Death Differ 6: 370–376.
Webb JL (ed). (1963). Effect of More Than One Inhibitor; Enzyme and Metabolic Inhibitors, Vol. 1. Academic Press: New York, pp 466–487.
Weiler M, Bahr O, Hohlweg U, Naumann U, Rieger J, Huang H et al. (2006). BCL-xL: time-dependent dissociation between modulation of apoptosis and invasiveness in human malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ 13: 1156–1169.
Weller M, Malipiero U, Aguzzi A, Reed JC, Fontana A . (1995). Protooncogene bcl-2 gene transfer abrogates Fas/APO-1 antibody-mediated apoptosis of human malignant glioma cells and confers resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs and therapeutic irradiation. J Clin Invest 95: 2633–2643.
Zangemeister-Wittke U . (2003). Antisense to apoptosis inhibitors facilitates chemotherapy and TRAIL-induced death signaling. Ann NY Acad Sci 1002: 90–94.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Krebshilfe to WR (German Cancer Aid, Max Eder Program). We thank Ilona Demir, Monika Frank-Stöhr and Sarah Meßnard for expert technical assistance. We thank Manfred Jugold (Molecular Imaging, German Cancer Research Center) for performing magnetic resonance imaging of animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tagscherer, K., Fassl, A., Campos, B. et al. Apoptosis-based treatment of glioblastomas with ABT-737, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 27, 6646–6656 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.259
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.259
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel BH3 mimetic Bcl-2 inhibitor promotes autophagic cell death and reduces in vivo Glioblastoma tumor growth
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Noxa and Mcl-1 expression influence the sensitivity to BH3-mimetics that target Bcl-xL in patient-derived glioma stem cells
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Plasma dilution improves cognition and attenuates neuroinflammation in old mice
GeroScience (2021)
-
Lower expression of Bax predicts poor clinical outcome in patients with glioma after curative resection and radiotherapy/chemotherapy
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2019)
-
Loperamide, pimozide, and STF-62247 trigger autophagy-dependent cell death in glioblastoma cells
Cell Death & Disease (2018)