Abstract
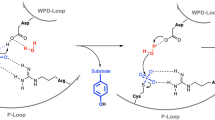
Salmonella SpvC belongs to a new enzyme family designated phosphothreonine lyases that irreversibly inactivate mitogen-activated protein kinases. The crystal structure of SpvC reported here reveals that the two phosphorylated residues in the substrate peptide predominantly mediate its recognition by SpvC. Substrate-induced conformational changes in SpvC sequester the phosphothreonine in a completely solvent-free environment, preventing the hydrolysis of the phosphate group and facilitating the elimination reaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira, S., Uematsu, S. & Takeuchi, O. Cell 124, 783–801 (2006).
Ashwell, J.D. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 532–540 (2006).
Ausubel, F.M. Nat. Immunol. 6, 973–979 (2005).
Tena, G., Asai, T., Chiu, W.L. & Sheen, J. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 392–400 (2001).
Hornef, M.W., Wick, M.J., Rhen, M. & Normark, S. Nat. Immunol. 3, 1033–1040 (2002).
Mukherjee, S. et al. Science 312, 1211–1214 (2006).
Kramer, R.W. et al. PLoS Pathogens [online] 3, e21 (2007).
Arbibe, L. et al. Nat. Immunol. 8, 47–56 (2007).
Li, H. et al. Science 315, 1000–1003 (2007).
Zhang, J. et al. Cell Host & Microbe 1, 175–185 (2007).
Matsui, H. et al. J. Bacteriol. 183, 4652–4658 (2001).
Schubert, H.L., Fauman, E.B., Stuckey, J.A., Dixon, J.E. & Saper, M.A.A. Protein Sci. 4, 1904–1913 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Dong and P. Liu at the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility for assistance with the data collection. This research is funded by Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology '863' grants 2003-AA210090 to J.C. and 2003-AA210080 to J.Z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods (PDF 1747 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Wang, H., Zhang, J. et al. Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism of phosphothreonine lyase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 101–102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1329
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1329
This article is cited by
-
Bacterial virulence mediated by orthogonal post-translational modification
Nature Chemical Biology (2020)