Abstract
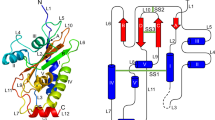
Toxoplasma gondii is a persistent protozoan parasite capable of infecting almost any warm-blooded vertebrate. The surface of Toxoplasma is coated with a family of developmentally regulated glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked proteins (SRSs), of which SAG1 is the prototypic member. SRS proteins mediate attachment to host cells and interface with the host immune response to regulate the virulence of the parasite. The 1.7 Å structure of the immunodominant SAG1 antigen reveals a homodimeric configuration in which the dimeric interface is mediated by an extended β-sheet that forms a deep groove lined with positively charged amino acids. This basic groove seems to be conserved among SRS proteins and potentially serves as a sulfated proteoglycan-binding site on target cell surfaces, thus rationalizing the promiscuous attachment properties of Toxoplasma to a broad range of host cell types.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suzuki, Y., Conley, F.K. & Remington, J.S. J. Infect. Dis. 159, 790–794 (1989).
Luft, B.J. & Remington, J.S. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15, 211–222 (1992).
Grigg, M.E., Ganatra, J., Boothroyd, J.C. & Margolis, T.P. J. Infect. Dis. 184, 633–639 (2001).
Boothroyd, J.C., Hehl, A., Knoll, L.J. & Manger, I.D. Int. J. Parasitol. 28, 3–9 (1998).
Lekutis, C., Ferguson, D.J., Grigg, M.E., Camps, M. & Boothroyd, J.C. Int. J. Parasitol. 31, 1285–1292 (2001).
Lekutis, C., Ferguson, D.J. & Boothroyd, J.C. Exp. Parasitol. 96, 89–96 (2000).
Manger, I.D., Hehl, A.B. & Boothroyd, J.C. Infect. Immun. 66, 2237–2244 (1998).
Cross, G.A. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8, 83–110 (1990).
Jacquet, A. et al. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 116, 35–44 (2001).
Mineo, J.R. et al. J. Immunol. 150, 3951–3964 (1993).
Grimwood, J. & Smith, J.E. Int. J. Parasitol. 26, 169–173 (1996).
Dzierszinski, F., Mortuaire, M., Cesbron-Delauw, M.F. & Tomavo, S. Mol. Microbiol. 37, 574–582 (2000).
Rodriguez, C., Afchain, D., Capron, A., Dissous, C. & Santoro, F. Eur. J. Immunol. 15, 747–749 (1985).
Adman, E.T. Adv. Protein Chem. 42, 145–197 (1991).
Baker, E.N. J. Mol. Biol. 203, 1071–1095 (1988).
Lawrence, M.C. & Colman, P.M. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 946–950 (1993).
Ortega-Barria, E. & Boothroyd, J.C. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1267–1276 (1999).
Pellegrini, L. et al. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26, 545–549 (1998).
Hobbs, M.R. & Boothroyd, J.C. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 43, 1–16 (1990).
Salmon, D. et al. EMBO J. 16, 7272–7278 (1997).
Grigg, M.E., Bonnefoy, S., Hehl, A.B., Suzuki, Y. & Boothroyd, J.C. Science 294, 161–165 (2001).
Hehl, A., Krieger, T. & Boothroyd, J.C. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 89, 271–282 (1997).
Spano, F. et al. Int. J. Parasitol. 32, 121–131 (2002).
Kabsch, W. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 21, 916–924 (1988).
Otwinowski, Z. in Proceedings of the CCP4 Study Weekend (ed. Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, S.) 56–62 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, UK; 1993).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Perrakis, A., Morris, R. & Lamzin, V.S. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 458–463 (1999).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Laskowski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thornton, J.M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Sanchez, R. & Sali, A. Proteins Suppl. 1, 50–58 (1997).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Bacon, D.J. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Nichols, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Proteins 11, 281–296 (1991).
Read, R.J. Acta Crystallogr. A 54, 140–149 (1986).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge M. Martick, D. Chow and D. Alexander for their assistance, G. McDermott for help with MAD data collection and L. Kasper for helpful discussions. This work was funded by the NIH (K.C.G. and J.C.B.), Rita Allen Foundation (K.C.G.), American Heart Association (K.C.G.), RWJ-PRI (K.C.G.) and the California County of Alameda District Attorney's Office (J.C.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xl., Grigg, M., Boothroyd, J. et al. Structure of the immunodominant surface antigen from the Toxoplasma gondii SRS superfamily. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9, 606–611 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb819
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb819
This article is cited by
-
Leishmania mexicana recombinant filamentous acid phosphatase as carrier for Toxoplasma gondii surface antigen 1 expression in Leishmania tarentolae
Journal of Parasitic Diseases (2021)
-
Characterization of a SRS13: a new cyst wall mucin-like domain containing protein
Parasitology Research (2018)