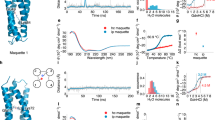
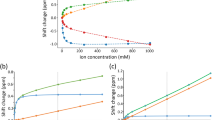
Abstract
The rapid association of barnase and its intracellular inhibitor barstar has been analysed from the effects of mutagenesis and electrostatic screening. A basal association rate constant of 105 M−1 s−1 is increased to over 5×109 M−1s−1 by electrostatic forces. The association between the oppositely charged proteins proceeds through the rate-determining formation of an early, weakly specific complex, which is dominated by long-range electrostatic interactions, followed by precise docking to form the high affinity complex. This mode of binding is likely to be used widely in nature to increase association rate constants between molecules and its principles may be used for protein design.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debye, P. & Hückel, E., Zur Theorie der Elektrolyte. Physik. Z. 24, 185–206 (1923).
Noyes, R.M. Effects of diffusion rates on chemical kinetics. Prog. React. Kinet. 1, 129–160 (1961).
Eigen, M. & Hammes, G.G. Elementary steps in enzyme reactions. Adv. Enzymol. 25, 1–38 (1963).
Berg, O.G. & von Hippel, P.H. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 14, 131–160 (1985).
Stone, R.S., Dennis, S. & Hofsteenge, J. Quantitative evaluation of the contribution of ionic interactions to the formation of the Thrombin-Hirudin complex. Biochemistry 28, 6857–6863 (1989).
von Hippel, P.H. & Berg, O.G. Facilitated target location in biological systems. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 675–678 (1989).
Zhou, H.X. Brownian dynamics study of the influences of electrostatic interaction and diffusion of protein-protein association kenetics. Biophys. J. 64, 1711–1726 (1993).
Pontius, B.W. Close encounters: why unstructured, polymeric domains can increase rates of specific macromolecules association. TIBS. 18, 181–186 (1993).
Northrup, S.H. et al. Effects of charged amino acid mutations on the bimolecular kinetics of reduction of Yeast lso-1-ferricytochrome c by Bovine Ferrocytochrome b5 . >Biochemistry 32, 6613–6623 (1993).
Guillemette, J.G. et al Analysis of the bimolecular reduction of fericytochrome c by ferrocytochrome b5 through mutagenesis and molecular modelling. Biochimie. 76, 592–604 (1994).
Honig, B. & Nicholls, A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science 268, 1144–1149 (1995).
Smoluchowski, M.V. Versuch einer mathematischen Theorie der Koagulationskinetik kolloider Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 92, 129–168 (1918).
Northrup, S.H. & Erickson, H.P. Kinetics of protein-protein association explained by Brownian dynamic computer simulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3338–3342 (1992).
Hartley, R.W. Barnase and Barstar: two small proteins to fold and fit together. Trends Biochem. Sci. 14, 450–454 (1989).
Schreiber, G. & Fersht, A.R. The interaction of barnase with its polypeptide inhibitor barstar studied by protein engineering. Biochemistry. 32, 5145–5150 (1993).
Louie, G.V. & Brayer, G.D. High-resolution refinement of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c and comparisons with other eukaryotic cytochromes c. J. Mol. Biol. 214, 527–555 (1990).
Eltis, L.D., Herbert, R.G., Barker, P.D., Mauk, A.G. & Northrup, S.H. Reduction of horse fericytochrome c by bovine liver ferrocytochrome b 5 . 30, 3663–3674 (1991).
Robinson, R.A. & Stokes, R.H. Electrolyte solutions (Butterworths, London, 1959).
Carter, P.J., Winter, G., Wilkinson, A.J. & Fersht, A.R. The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the Tyrosyl-tRNA Synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell 38, 835–840 (1984).
Horovitz, A. & Fersht, A.R. Co-operative interactions during protein folding. J. Mol. Biol. 224, 733–740 (1992).
Schreiber, G. & Fersht, A.R. Energetics of protein-protein interactions: analysis of the barnase-barstar interface by single mutations and double mutant cycles. J. Mol. Biol. 248, 478–486 (1995).
Nassar, M. et al The 2.2-Angstrom crystal structure of the ras-binding domain of the serine threonine kinase c-raf1 in complex with rap1A and a GTP analog. Nature. 375, 554–560 (1995).
Kobe, B. & Deisenhofer, J. Crystal structure of porcine ribonuclease inhibitor, a protein with leucine-rich repeats. Nature 366, 751–756 (1993).
Rydel, T.J. et al. The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human α-thrombin. Science 245, 277–280 (1990).
Gilson, M.K. & Honig, B.A. Calculation of the total electrostatic energy of a macromolecular system: solvation energies, binding energies, and conformational analysis. Proteins Struct. Fund. Genet. 4, 7–18 (1988).
Schreiber, G., Buckle, A.M. & Fersht, A.R. Stability versus function: two competing forces in the evolution of barstar. Structure 2, 945–951 (1994).
Mossakowska, D.E., Nyberg, K. & Fersht, A.R. Kinetic characterization of the recombinant ribonuclease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (barnase) and investigation of key residues in catalysis by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 28, 3843–3850 (1989).
Horovitz, A., Serrano, L., Avron, B., Bycroft, M. & Fersht, A.R. Strength and cooperativity of contributions of surface salt bridges to protein stability. J. Mol. Biol. 216, 1031–1044 (1990).
Serrano, L., Horovitz, A., Avron, B., Bycroft, M. & Fersht, A.R. Estimating the contribution of engineered surface electrostatic interactions to protein stability using double-mutant cycles. Biochemistry 29, 9343–9352 (1990).
Loewenthal, R., Sancho, J. & Fersht, A.R. Histidine-aromatic interactions in barnase: elevation of histidine pKa and contribution to protein stability. J. Mol. Biol. 224, 759–770 (1992).
Meiering, E.M., Serrano, L. & Fersht, A.R. Effect of active site residues in barnase on activity and stability. J. Mol. Biol. 225, 585–589 (1992).
Hartley, R.W. Directed mutagenesis and Barnase-Barstar recognition. Biochemistry 32, 5978–5984 (1993).
Buckle, M., Schreiber, G. & Fersht, A.R., Protein-Protein Recognition: Crystal structural analysis of a barnase-barstar complex at 2.0-Å resolution. Biochemistry 33 8878–8889 (1994).
Kraulis, P. MolScript, a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Nicholls, A. GRASP. graphical representation and analysis of surface properties. (Columbia University, New York, 1992)
Akerlöf, G. Dielectric constants of some organic solvent-water mixtures at various temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 54, 4125 (1932).
Fersht, A.R. Enzyme Structure and Mechanism (W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, 1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreiber, G., Fersht, A. Rapid, electrostatically assisted association of proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 427–431 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0596-427
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0596-427
This article is cited by
-
Different electrostatic forces drive the binding kinetics of SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV Envelope proteins with the PDZ2 domain of ZO1
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
On the possibility of the existence of orienting hydrodynamic steering effects in the kinetics of receptor–ligand association
European Biophysics Journal (2023)
-
Classification of protein–protein association rates based on biophysical informatics
BMC Bioinformatics (2021)
-
Dynamic conformational flexibility and molecular interactions of intrinsically disordered proteins
Journal of Biosciences (2020)
-
Binding of HasA by its transmembrane receptor HasR follows a conformational funnel mechanism
European Biophysics Journal (2020)