Abstract
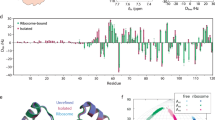
Residual dipolar couplings observed in NMR spectra at very high magnetic fields have been measured to a high degree of accuracy for the paramagnetic protein cyanometmyoglobin. Deviations of these measurements from predictions based on available crystallographic and solution structures are largely systematic and well correlated within a given helix of this highly α-helical protein. These observations can be explained by invoking collective motion and small displacements of representative helices from their reported average positions in the solid state. Thus, the measurements appear to be capable of providing important insights into slower, collective protein motions, which are likely to be important for function, and which have been difficult to study using established experimental techniques.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perutz, M.F. & Mathews, F.S. X-ray study of azide methaemoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 21, 199 (1966).
Karplus, M. & McCammon, J.A. Dynamics of Proteins: Elements and Function. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 53, 263–300 (1983).
Frauenfelder, H., Parak, F. & Young, R.D. Conformational substates in proteins. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 17, 451–479 (1988).
Drenth, J. Principles of Protein X-Ray Crystallography 1–311 (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1994).
Peng, J.W. & Wagner, G. in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Probes of Molecular Dynamics (ed. Tycko, R.) 373–454 (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1994).
Smith, J.C. Protein dynamics: comparison of simulations with inelastic neutron scattering experiments. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 24, 227–291 (1991).
Doster, W., Cusack, S. & Petry, W. Dynamical transition of myoglobin revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Nature 337, 754–756 (1989).
Caspar, D.L.D., Clarage, J., Salunke, D.M. & Clarage, M. Liquid-like movements in crystalline insulin. Nature 332, 659–662 (1988).
Thüne, T. & Badger, J. Thermal diffuse x-ray scattering and its contribution to understanding protein dynamics. Prog. Biophys. Molec. Biol. 63, 251–276 (1995).
Nienhaus, G.U., Heinzl, J., Huenges, E. & Parak, F. Protein crystal dynamics studied by time-resolved analysis of X-Ray diffuse scattering. Nature 338, 665–666 (1989).
Carlson, M.L., Regan, R.M. & Gibson, Q.H. Distal cavity fluctuations in myoglobin: Protein motion and ligand diffusion. Biochemistry 35, 1125–1136 (1996).
Steinbach, P.J. & Brooks, B.R. Hydrated myoglobin's anharmonic fluctuations are not primarily due to dihedral transitions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 55–59 (1996).
Clarage, J.B., Romo, T., Andrews, B.K., Pettitt, B.M. & Phillips Jr., G.N. A sampling problem in molecular dynamics simulations of macromolecules. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3288–3292 (1995).
Chandrasekhar, I., Clore, G.M., Szabo, A., Gronenborn, A.M. & Brooks, B.R. A 500ps molecular dynamics simulation study of interleukin 1b in water. Correlation with nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and crystallography. J. Mol. Biol. 226, 239–250 (1992).
Kneller, G.R. & Smith, J.C. Liquid-like Side-chain Dynamics in Myoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 242, 181–185 (1994).
Elamrani, S., Berry, M.B., Phillips Jr., G.N. & McCammon, J.A. Study of global motions in proteins by weighted masses molecular dynamics: adenylate kinase as a test case. Proteins 25, 79–88 (1996).
Amadei, A., Linssen, A.B.M. & Berendsen, H.J.C. Essential dynamics of proteins. Proteins 17, 412–425 (1993).
Feher, V.A., Baldwin, E.P. & Dahlquist, F.W. Access of ligands to cavities within the core of a protein is rapid. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 516–521 (1996).
Tilton Jr., R.F. & Kuntz Jr., I.D. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of Xenon-129 with myoglobin and hemoglobin. Biochemistry 21, 6850–6857 (1982).
Tolman, J.R., Flanagan, J.M., Kennedy, M.A. & Prestegard, J.H. Nuclear magnetic dipole interactions in field-oriented proteins: Information for structure determination in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9279–9283 (1995).
Tjandra, N., Grzesiek, S. & Bax, A. Magnetic field dependence of nitrogen-proton J splittings in 15N-enriched human ubiquitin resulting from relaxation interference and residual dipolar coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 6264–6272 (1996).
Lohman, J.A.B. & MacLean, C. Alignment effects on high resolution NMR spectra, induced by the magnetic field. Chem. Phys. 35, 269–274 (1978).
Bastiaan, E.W., MacLean, C., Zijl, P.C.M.v. & Bothner-By, A.A. High-resolution NMR of liquids and gases: Effects of magnetic-field-induced molecular alignment. Ann. Rep. NMR Spect. 19, 35–77 (1987).
Rajarathnam, K., LaMar, G.N., Chiu, M.L. & Sligar, S.G. Determination of the orientation of the magnetic axes of the cyano-metMb complexes of point mutants of myoglobin by solution 1H NMR: Influence of His E7-Gly and Arg CD3-Gly substitutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 9048–9058 (1992).
Cheng, X. & Schoenborn, B.P. Neutron diffraction study of carbonmono-xymyoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 220, 381–399 (1991).
Tolman, J.R. & Prestegard, J.H. A quantitative J-Correlation experiment for the accurate measurement of one-bond amide 15N-1H couplings in proteins. J. Magn. Reson. B 112, 245–252 (1996).
Tolman, J.R. & Prestegard, J.H. Measurement of amide 15N-1H one-bond couplings in proteins using accordion heteronuclear-shift-correlation experiments. J. Magn. Reson. B 112, 269–274 (1996).
Kuriyan, J., Wilz, S., Karplus, M. & Petsko, G.A. X-Ray structure and refinement of carbon-monoxy (Fe II)-myoglobin at 1.5 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 192, 133–154 (1986).
Ösapay, K., Theriault, Y., Wright, P.E. & Case, D.A. Solution structure of carbonmonoxy myoglobin determined from nuclear magnetic resonance distance and chemical shift constraints. J. Mol. Biol. 244, 183–197 (1994).
Lipari, G. & Szabo, A. Effect of librational motion on fluorescence depolarization and nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules and membranes. Biophys. J. 30, 489–506 (1980).
Bothner-By, A.A., et al. High-field orientation effects in the high-resolution proton NMR spectra of diverse porphyrins. Magn. Reson. Chem. 23, 935–938 (1985).
Zurcher, R.F. The cause and calculation of proton chemical shifts in non-conjugated organic compounds. Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 2, 205–257 (1967).
Garrett, D.S., Powers, R., Gronenborn, A.M. & Clore, G.M. A common sense approach to peak picking in two-, three-, and four-dimensional spectra using automatic computer analysis of contour diagrams. J. Magn. Reson. 95, 214–220 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolman, J., Flanagan, J., Kennedy, M. et al. NMR evidence for slow collective motions in cyanometmyoglobin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 4, 292–297 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0497-292
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0497-292
This article is cited by
-
Probing conformational dynamics in biomolecules via chemical exchange saturation transfer: a primer
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2017)
-
Integrative, dynamic structural biology at atomic resolution—it's about time
Nature Methods (2015)
-
ORIUM: Optimized RDC-based Iterative and Unified Model-free analysis
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2014)
-
New opportunities for tensor-free calculations of residual dipolar couplings for the study of protein dynamics
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2014)
-
Advances in the REDCAT software package
BMC Bioinformatics (2013)