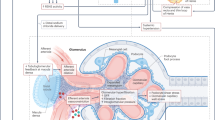
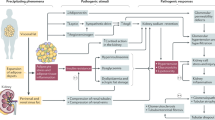
Abstract
The theme of World Kidney Day 2017 is 'kidney disease and obesity: healthy lifestyle for healthy kidneys'. To mark this event, Nature Reviews Nephrology invited five leading researchers to describe changes in the epidemiology of obesity-related kidney disease, advances in current understanding of the mechanisms and current approaches to the management of affected patients. The researchers also highlight new advances that could lead to the development of novel treatments and identify areas in which further basic and clinical studies are needed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson, M. E. et al. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 116, 1094–1105 (2007).
Shaw, K., Gennat, H., O'Rourke, P. & Del Mar, C. Exercise for overweight or obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4, CD003817 (2006).
Knudsen, S. H. et al. Changes in insulin sensitivity precede changes in body composition during 14 days of step reduction combined with overfeeding in healthy young men. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 113, 7–15 (2012).
Allet, L., Knols, R. H., Shirato, K. & de Bruin, E. D. Wearable systems for monitoring mobility-related activities in chronic disease: a systematic review. Sensors (Basel) 10, 9026–9052 (2010).
Wakasugi, M. et al. Association between overall lifestyle changes and the incidence of proteinuria: a population-based, cohort study. Intern. Med. 2017 (in press).
Kuro-o, M. Klotho, phosphate and FGF-23 in ageing and disturbed mineral metabolism. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 9, 650–660 (2013).
Hallan, S. I. et al. Long-term trends with prevalence of chronic kidney disease and the influence of cardiovascular risk factors in Norway. Kidney Int. 90, 665–673 (2016).
Fouque, D. et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 73, 391–398 (2008).
Yamagata, K. et al. Effect of behaviour modification on outcome in early- to moderate-stage chronic kidney disease: a cluster-randomized trial. PLoS ONE 11, e0151422 (2016).
Dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study annual report 2012. DOPPS http://www.dopps.org/annualreport/html/qdialduration_US2011.htm (accessved 9 Dec 2015).
Kaufman, J. S., Durazo-Arvizu, R. A., Rotimi, C. N., McGee, D. L. & Cooper, R. S. Obesity and hypertension prevalence in populations of African origin. The Investigators of the International Collaborative Study on Hypertension in blacks. Epidemiology 7, 398–405 (1996).
Wolf-Maier, K. et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA 289, 2363–2369 (2003).
Stamler, J. The INTERSALT study: background, methods, findings, and implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65 (Suppl. 2), 626S–642S (1997).
Tayo, B. O. et al. Patterns of sodium and potassium excretion and blood pressure in the African diaspora. J. Hum. Hypertens. 26, 315–324 (2012).
Kitiyakara, C. et al. Salt intake, oxidative stress, and renal expression of NADPH oxidase and superoxide dismutase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14, 2775–2782 (2003).
Weir, M. R. & Fink, J. C. Salt intake and progression of chronic kidney disease: an overlooked modifiable exposure? A commentary. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 45, 176–188 (2005).
D'Agati, V. D. et al. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12, 453–471 (2016).
Tahergorabi, Z. et al. From obesity to cancer: a review on proposed mechanisms. Cell Biochem. Funct. 34, 533–545 (2016).
Thomas, M. C., Cooper, M. E. & Zimmet, P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 12, 73–81 (2016).
Zhang, L. et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 905–906 (2016).
Kambham, N. et al. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: an emerging epidemic. Kidney Int. 59, 1498–1509 (2001).
Hsu, C. Y., McCulloch, C. E., Iribarren, C., Darbinian, J. & Go, A. S. Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 144, 21–28 (2006).
Preble, W. Obesity: observations on one thousand cases. Boston Med. Surg. J. 188, 617–621 (1923).
Deji, N. et al. Structural and functional changes in the kidneys of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 296, F118–F126 (2009).
Decleves, A. E., Mathew, A. V., Cunard, R. & Sharma, K. AMPK mediates the initiation of kidney disease induced by a high-fat diet. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 1846–1855 (2011).
Tsukamoto, Y. et al. Report of the Asian Forum of Chronic Kidney Disease Initiative (AFCKDI) 2007. “Current status and perspective of CKD in Asia”: diversity and specificity among Asian countries. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 13, 249–256 (2009).
Chang, A. et al. Lifestyle-related factors, obesity, and incident microalbuminuria: the CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 62, 267–275 (2013).
Ross, W. R. & McGill, J. B. Epidemiology of obesity and chronic kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 13, 325–335 (2006).
Coward, R. & Fornoni, A. Insulin signaling: implications for podocyte biology in diabetic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 24, 104–110 (2015).
Moraes-Vieira, P. M. et al. Leptin deficiency modulates allograft survival by favoring a Th2 and a regulatory immune profile. [corrected]. Am. J. Transplant. 13, 36–44 (2013).
Anders, H. J., Andersen, K. & Stecher, B. The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney Int. 83, 1010–1016 (2013).
Koppe, L. et al. Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: new lessons from experimental models. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 29, 1666–1674 (2014).
Jose, P. A. et al. Gastrorenal axis. Hypertension 67, 1056–1063 (2016).
Hostetter, T. H., Rennke, H. G. & Brenner, B. M. The case for intrarenal hypertension in the initiation and progression of diabetic and other glomerulopathies. Am. J. Med. 72, 375–380 (1982).
Kasiske, B. L. & Napier, J. Glomerular sclerosis in patients with massive obesity. Am. J. Nephrol. 5, 45–50 (1985).
Griffin, K. A., Kramer, H. & Bidani, A. K. Adverse renal consequences of obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 294, F685–F696 (2008).
Jung, U. J. & Choi, M. S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: the role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 6184–6223 (2014).
Hunley, T. E., Ma, L. J. & Kon, V. Scope and mechanisms of obesity-related renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 19, 227–234 (2010).
Lu, H., Boustany-Kari, C. M., Daugherty, A. & Cassis, L. A. Angiotensin II increases adipose angiotensinogen expression. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292, E1280–E1287 (2007).
Shulman, G. I. Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 2237–2238 (2014).
Wang, Y. et al. Applications of complex systems science in obesity and noncommunicable chronic disease research. Adv. Nutr. 5, 574–577 (2014).
Ruster, C. & Wolf, G. Adipokines promote chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 28 (Suppl. 4), iv8–iv14 (2013).
Sharma, K. The link between obesity and albuminuria: adiponectin and podocyte dysfunction. Kidney Int. 76, 145–148 (2009).
Sharma, K. et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 1645–1656 (2008).
Rutkowski, J. M. et al. Adiponectin promotes functional recovery after podocyte ablation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 24, 268–282 (2013).
Tsioufis, C. et al. Relation of microalbuminuria to adiponectin and augmented C-reactive protein levels in men with essential hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 96, 946–951 (2005).
Yano, Y. et al. Differential impacts of adiponectin on low-grade albuminuria between obese and nonobese persons without diabetes. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 9, 775–782 (2007).
Saraheimo, M. et al. Serum adiponectin is increased in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetes Care 28, 1410–1414 (2005).
Forsblom, C. et al. Serum adiponectin concentration is a positive predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in type 1 diabetes. J. Intern. Med. 270, 346–355 (2011).
Thorburn, A. N., Macia, L. & Mackay, C. R. Diet, metabolites, and “western-lifestyle” inflammatory diseases. Immunity 40, 833–842 (2014).
Vinolo, M. A. et al. Tributyrin attenuates obesity-associated inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 303, E272–E282 (2012).
Vaziri, N. D. et al. High amylose resistant starch diet ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, and progression of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 9, e114881 (2014).
Krishnamurthy, V. M. et al. High dietary fiber intake is associated with decreased inflammation and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 81, 300–306 (2012).
Andrade-Oliveira, V. et al. Gut bacteria products prevent AKI induced by ischemia-reperfusion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 1877–1888 (2015).
Johansen, K. L. Exercise in the end-stage renal disease population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1845–1854 (2007).
Malin, S. K. et al. Metformin modifies the exercise training effects on risk factors for cardiovascular disease in impaired glucose tolerant adults. Obesity (Silver Spring) 21, 93–100 (2013).
Malin, S. K. & Braun, B. Impact of metformin on exercise-induced metabolic adaptations to lower type 2 diabetes risk. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 44, 4–11 (2016).
Christensen, M. et al. Renoprotective effects of metformin are independent of organic cation transporters 1 & 2 and AMP-activated protein kinase in the kidney. Sci. Rep. 6, 35952 (2016).
Nehus, E. J. et al. Kidney outcomes three years after bariatric surgery in severely obese adolescents. Kidney Int. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.031 (2016).
Froeder, L., Arasaki, C. H., Malheiros, C. A., Baxmann, A. C. & Heilberg, I. P. Response to dietary oxalate after bariatric surgery. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 7, 2033–2040 (2012).
Agarwal, V. & Navaneethan, S. D. Bariatric surgery for obesity-associated decline in kidney function: filling the knowledge gap? Kidney Int. 90, 28–30 (2016).
Vrieze, A. et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 143, 913–916.e7 (2012).
Schulman, G. et al. Randomized placebo-controlled EPPIC trials of AST-120 in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 1732–1746 (2015).
Wanner, C. et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 323–334 (2016).
de Zeeuw, D. et al. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 2492–2503 (2013).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02316821 (2016).
Koury, M. J. & Haase, V. H. Anaemia in kidney disease: harnessing hypoxia responses for therapy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 11, 394–410 (2015).
Arai, S. et al. Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage protein enhances intraluminal debris clearance and ameliorates acute kidney injury in mice. Nat. Med. 22, 183–193 (2016).
Imam, T. H. et al. Estimated GFR before and after bariatric surgery in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.09.020 (2016).
Perkovic, V. et al. Management of patients with diabetes and CKD: conclusions from a “Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes” (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 90, 1175–1183 (2016).
Li, P. K. et al. Asian chronic kidney disease best practice recommendations: positional statements for early detection of chronic kidney disease from Asian Forum for Chronic Kidney Disease Initiatives (AFCKDI). Nephrology 16, 633–641 (2011).
Grimm, E. R. & Steinle, N. I. Genetics of eating behavior: established and emerging concepts. Nutr. Rev. 69, 52–60 (2011).
Dunkler, D. et al. Modifiable lifestyle and social factors affect chronic kidney disease in high-risk individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 87, 784–791 (2015).
Polak, R., Pojednic, R. M. & Phillips, E. M. Lifestyle medicine education. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 9, 361–367 (2015).
Foster-Schubert, K. E. et al. Effect of diet and exercise, alone or combined, on weight and body composition in overweight-to-obese postmenopausal women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20, 1628–1638 (2012).
Vanherweghem, J. L. et al. Rapidly progressive interstitial renal fibrosis in young women: association with slimming regimen including Chinese herbs. Lancet 341, 387–391 (1993).
Navaneethan, S. D. et al. Urinary albumin excretion, HMW adiponectin, and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 20, 308–315 (2010).
Declèves, A.-E. et al. Regulation of lipid accumulation by AMK-activated kinase in high fat diet–induced kidney injury. Kidney Int. 85, 611–623 (2014).
Hainer, V. & Aldhoon-Hainerová, I. Obesity paradox does exist. Diabetes Care 36 (Suppl. 2), S276–S281 (2013).
Luyckx, V. A. & Brenner, B. M. Birth weight, malnutrition and kidney-associated outcomes — a global concern. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 11, 135–149 (2015).
Iseki, K. et al. Body mass index and the risk of development of end-stage renal disease in a screened cohort. Kidney Int. 65, 1870–1876 (2004).
Nagata, M. et al. Trends in the prevalence of chronic kidney disease and its risk factors in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 25, 2557–2564 (2010).
DeFronzo, R. A. et al. Renal, metabolic and cardiovascular considerations of SGLT2 inhibition. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 13, 11–26 (2017).
Kautzky-Willer, A., Harreiter, J. & Pacini, G. Sex and gender differences in risk, pathophysiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 37, 278–316 (2016).
Arora, P. Obesity genetics and epigenetics: dissecting causality. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 7, 395–396 (2016).
Zeevi, D. et al. Personalized nutrition by prediction of glycemic responses. Cell 163, 1079–1094 (2015).
Todd, J. N. et al. Genetic evidence for a causal role of obesity in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes 64, 4238–4246 (2015).
Badran, M., Golbidi, S., Devlin, A., Ayas, N. & Laher, I. Chronic intermittent hypoxia causes endothelial dysfunction in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Sleep Med. 15, 596–602 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank their colleagues in the field and the efforts of the World Kidney Day initiative, for which the focus for 2017 is “kidney disease and obesity: healthy lifestyle for healthy kidneys”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Câmara, N., Iseki, K., Kramer, H. et al. Kidney disease and obesity: epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol 13, 181–190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.191
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.191
This article is cited by
-
Role of polyphenols in remodeling the host gut microbiota in polycystic ovary syndrome
Journal of Ovarian Research (2024)
-
Fine Tuning Mesenchymal Stromal Cells – Code For Mitigating Kidney Diseases
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2024)
-
Being overweight worsens the relationship between urinary sodium excretion and albuminuria: the Wakuya study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023)
-
The Effect of Chronic Kidney Disease or End-stage Kidney Disease on Perioperative Outcomes and Healthcare Utilization in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Obesity Surgery (2023)
-
The programming of kidney injury in offspring affected by maternal overweight and obesity: role of lipid accumulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis in the kidneys of offspring
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2023)