Abstract
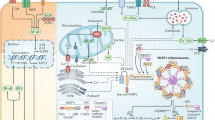
Danger signals are a hallmark of many common inflammatory diseases, and these stimuli can function to activate the cytosolic innate immune signalling receptor NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3). Once activated, NLRP3 nucleates the assembly of an inflammasome, leading to caspase 1-mediated proteolytic activation of the interleukin-1β (IL-1β) family of cytokines, and induces an inflammatory, pyroptotic cell death. Pharmacological inhibition of NLRP3 activation results in potent therapeutic effects in a wide variety of rodent models of inflammatory diseases, effects that are mirrored by genetic ablation of NLRP3. Although these findings highlight the potential of NLRP3 as a drug target, an understanding of NLRP3 structure and activation mechanisms is incomplete, which has hampered the discovery and development of novel therapeutics against this target. Here, we review recent advances in our understanding of NLRP3 activation and regulation, highlight the evolving landscape of NLRP3 modulators and discuss opportunities for pharmacologically targeting NLRP3 with novel small molecules.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 August 2018
A sentence mentioning the authors of reference 122 has been amended to include both corresponding authors.
References
Netea, M. G. et al. Trained immunity: a program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Science 352, 1098–1098 (2016).
Cooper, M. D. & Alder, M. N. The evolution of adaptive immune systems. Cell 124, 815–822 (2006).
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388, 1459–1544 (2016). This study highlights the rise of non-communicable, lifestyle-based diseases on a global scale.
Próchnicki, T., Mangan, M. S. & Latz, E. Recent insights into the molecular mechanisms of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation. F1000Res. 5, 1469 (2016).
Próchnicki, T. & Latz, E. Inflammasomes on the crossroads of innate immune recognition and metabolic control. Cell. Metab. 26, 71–93 (2017).
Lu, A. et al. Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes. Cell 156, 1193–1206 (2014).
Fernandes-Alnemri, T. et al. The pyroptosome: a supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 14, 1590–1604 (2007).
Hoss, F., Rodriguez-Alcazar, J. F. & Latz, E. Assembly and regulation of ASC specks. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74, 1211–1229 (2017).
Keller, M., Rüegg, A., Werner, S. & Beer, H.-D. Active caspase-1 is a regulator of unconventional protein secretion. Cell 132, 818–831 (2008).
Kanneganti, T.-D. et al. Bacterial RNA and small antiviral compounds activate caspase-1 through cryopyrin/Nalp3. Nature 440, 233–236 (2006).
Willingham, S. B. et al. NLRP3 (NALP3, Cryopyrin) facilitates in vivo caspase-1 activation, necrosis, and HMGB1 release via inflammasome-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Immunol. 183, 2008–2015 (2009).
Moltke, von, J. et al. Rapid induction of inflammatory lipid mediators by the inflammasome in vivo. Nature 490, 107–111 (2013).
Sharma, D. & Kanneganti, T.-D. The cell biology of inflammasomes: mechanisms of inflammasome activation and regulation. J. Cell Biol. 213, 617–629 (2016).
Duncan, J. A. et al. Cryopyrin/NALP3 binds ATP/dATP, is an ATPase, and requires ATP binding to mediate inflammatory signaling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 8041–8046 (2007).
Liston, A. & Masters, S. L. Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechansims of inflammasome activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 208–214 (2017).
Bauernfeind, F. G. et al. Cutting edge: NF- B activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J. Immunol. 183, 787–791 (2009). This is the original description (together with reference 17) that NLRP3 priming is a requirement for NLRP3 activation.
Franchi, L., Eigenbrod, T. & Nunez, G. Cutting edge: TNF- mediates sensitization to ATP and Silica via the NLRP3 inflammasome in the absence of microbial stimulation. J. Immunol. 183, 792–796 (2009).
Haneklaus, M. et al. Cutting edge: miR-223 and EBV miR-BART15 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1 production. J. Immunol. 189, 3795–3799 (2012).
Stutz, A. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome assembly is regulated by phosphorylation of the pyrin domain. J. Exp. Med. 214, 1725–1736 (2017).
Spalinger, M. R. et al. NLRP3 tyrosine phosphorylation is controlled by protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 1783–1800 (2016).
Song, N. et al. NLRP3 phosphorylation is an essential priming event for inflammasome activation. Mol. Cell 68, 185–197 (2017).
Mortimer, L., Moreau, F., MacDonald, J. A. & Chadee, K. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition is disrupted in a group of auto-inflammatory disease CAPS mutations. Nat. Immunol. 17, 1176–1186 (2016).
Zhang, Z. et al. Protein kinase D at the Golgi controls NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Exp. Med. 214, 2671–2693 (2017).
Han, S. et al. Lipopolysaccharide primes the NALP3 inflammasome by inhibiting its ubiquitination and degradation mediated by the SCFFBXL2 E3 ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 18124–18133 (2015).
Yan, Y. et al. Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell 160, 62–73 (2015).
Song, H. et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting proteasomal degradation of NLRP3. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–11 (2016).
Py, B. F., Kim, M.-S., Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H. & Yuan, J. Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 critically regulates inflamamsome activity. Mol. Cell 49, 331–338 (2013).
Rodgers, M. A. et al. The linear ubiquitin assembly complex (LUBAC) is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Exp. Med. 211, 1333–1347 (2014).
Pétrilli, V. et al. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 14, 1583–1589 (2007).
Greaney, A. J., Leppla, S. H. & Moayeri, M. Bacterial exotoxins and the inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 6, 1013 (2015).
Compan, V. et al. Cell volume regulation modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 37, 487–500 (2012).
Daniels, M. J. D. et al. Fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome and protect against Alzheimer's disease in rodent models. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–10 (2016). This is the first paper to demonstrate that the fenamate class of NSAIDs, already approved by the FDA for other treatments, is able to inhibit NLRP3.
Tang, T. et al. CLICs-dependent chloride efflux is an essential and proximal upstream event for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nat. Commun. 8, 202 (2017).
Domingo- Fernández, R., Coll, R. C., Kearney, J., Breit, S. & O'Neill, L. A. J. The intracellular chloride channel proteins CLIC1 and CLIC4 induce IL-1β transcription and activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 12077–12087 (2017).
Muñoz-Planillo, R. et al. K+ efflux is the common trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by bacterial toxins and particulate matter. Immunity 38, 1142–1153 (2013).
Hornung, V. et al. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the NALP3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat. Immunol. 9, 847–856 (2008). This paper identifies the lysosomal damage pathway upstream of NLRP3 activation.
Orlowski, G. M. et al. Multiple cathepsins promote pro-IL-1β synthesis and NLRP3-mediated IL-1β activation. J. Immunol. 195, 1685–1697 (2015).
Riteau, N. et al. ATP release and purinergic signaling: a common pathway for particle-mediated inflammasome activation. Cell Death Dis. 3, e403–e410 (2012).
Martinon, F., Petrilli, V., Mayor, A., Tardivel, A. & Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 440, 237–241 (2006). This is the first report of a crystal that activates the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Duewell, P. et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 464, 1357–1361 (2010).
Dostert, C. et al. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 320, 674–677 (2008).
Halle, A. et al. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-β. Nat. Immunol. 9, 857–865 (2008). This article reports for the first time that aggregate peptides can trigger NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Masters, S. L. et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by islet amyloid polypeptide provides a mechanism for enhanced IL-1β in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Immunol. 11, 897–904 (2010).
Franklin, B. S., Mangan, M. S. & Latz, E. Crystal formation in inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 34, 173–202 (2016).
Sanman, L. E. et al. Disruption of glycolytic flux is a signal for inflammasome signaling and pyroptotic cell death. eLife 5, 1–32 (2016).
Groß, C. J. et al. Efflux-independent NLRP3 inflammasome activation by small molecules targeting mitochondria. Immunity 45, 761–773 (2016).
Wolf, A. J. et al. Hexokinase is an innate immune receptor for the detection of bacterial peptidoglycan. Cell 166, 624–636 (2016).
Abais, J. M., Xia, M., Zhang, Y., Boini, K. M. & Li, P.-L. Redox regulation of NLRP3 inflammasomes: ROS as trigger or effector? Antioxid. Redox Signal 22, 1111–1129 (2015).
Shimada, K. et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity 36, 401–414 (2012).
Yu, J. et al. Inflammasome activation leads to caspase-1-dependent mitochondrial damage and block of mitophagy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 111, 15514–15519 (2014).
Iyer, S. S. et al. Mitochondrial cardiolipin is required for Nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 39, 311–323 (2013).
Dudek, J. Role of cardiolipin in mitochondrial signaling pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 5, 8383 (2017).
Greten, F. R. et al. NF-κB is a negative regulator of IL-1β secretion as revealed by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IKKβ. Cell 130, 918–931 (2007).
Lupfer, C. et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase 2–mediated mitophagy regulates inflammasome activation during virus infection. Nat. Immunol. 14, 480–488 (2013).
van der Burgh, R. et al. Defects in mitochondrial clearance predispose human monocytes to interleukin-1 hypersecretion. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 5000–5012 (2014).
Kayagaki, N. et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signaling. Nature 526, 666–671 (2015).
Baker, P. J. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 45, 2918–2926 (2015).
Zanoni, I. et al. An endogenous caspase-11 ligand elicits interleukin-1 release from living dendritic cells. Science 352, 1232–1236 (2016).
Evavold, C. L. et al. The pore-forming protein gasdermin D regulates interleukin-1 secretion from living macrophages. Immunity 48, 35–44.e6 (2018).
Zanoni, I., Tan, Y., Di Gioia, M., Springstead, J. R. & Kagan, J. C. By capturing inflammatory lipids released from dying cells, the receptor CD14 induces inflammasome-dependent phagocyte hyperactivation. Immunity 47, 697–709.e3 (2017).
Gaidt, M. M. et al. Human monocytes engage an alternative inflammasome pathway. Immunity 44, 833–846 (2016). This article is the first description of the alternative inflammasome activation pathway in monocytes.
Humphries, F., Yang, S., Wang, B. & Moynagh, P. N. RIP kinases: key decision makers in cell death and innate immunity. Cell Death Differ. 22, 225–236 (2014).
Conos, S. A. et al. Active MLKL triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome in a cell-intrinsic manner. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 114, 961–969 (2017).
Lawlor, K. E. et al. RIPK3 promotes cell death and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the absence of MLKL. Nat. Commun. 6, 1–19 (2015).
Shi, H. et al. NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component. Nat. Immunol. 17, 250–258 (2015).
He, Y., Zeng, M. Y., Yang, D., Motro, B. & Nuñez, G. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 530, 354–357 (2016).
Schmid-Burgk, J. L. et al. A genome-wide CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) screen identifies NEK7 as an essential component of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 103–109 (2016).
Gurung, P. et al. FADD and caspase-8 mediate priming and activation of the canonical and noncanonical Nlrp3 inflammasomes. J. Immunol. 192, 1835–1846 (2014).
Ito, M. et al. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation and contributes to ischaemic brain injury. Nat. Commun. 6, 1–11 (2015).
Liu, X. et al. Human NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain–containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activity is regulated by and potentially targetable through Bruton tyrosine kinase. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 140, 1054–1067 (2017).
Broderick, L., De Nardo, D., Franklin, B. S., Hoffman, H. M. & Latz, E. The inflammasomes and autoinflammatory syndromes. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 10, 395–424 (2015).
Sarrauste de Menthiere, C. INFEVERS: the Registry for FMF and hereditary inflammatory disorders mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 282–285 (2003).
Brydges, S. D. et al. Divergence of IL-1, IL-18, and cell death in NLRP3 inflammasomopathies. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 4695–4705 (2013). This important paper details the effects of hyperactive NLRP3 activation and its relative dependence on IL-1β, IL-18 and caspase 1.
Saberi, M. et al. Hematopoietic cell-specific deletion of Toll-like receptor 4 ameliorates hepatic and adipose tissue insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Cell. Metab. 10, 419–429 (2009).
Shi, H. et al. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid–induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 3015–3025 (2006).
Vandanmagsar, B. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 17, 179–188 (2011).
Ralston, J. C., Lyons, C. L., Kennedy, E. B., Kirwan, A. M. & Roche, H. M. Fatty acids and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in metabolic tissues. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 37, 77–102 (2017).
Youm, Y.-H. et al. Canonical Nlrp3 inflammasome links systemic low-grade inflammationto functional decline in aging. Cell. Metab. 18, 519–532 (2013).
Camell, C. D. et al. Inflammasome-driven catecholamine catabolism in macrophages blunts lipolysis during ageing. Nature 550, 119–123 (2017).
Acosta, J. C. et al. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 978–990 (2013).
Chow, M. T. et al. NLRP3 suppresses NK cell-mediated responses to carcinogen-induced tumors and metastases. Cancer Res. 72, 5721–5732 (2012).
van Deventer, H. W. et al. The inflammasome component NLRP3 impairs antitumor vaccine by enhancing the accumulation of tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 70, 10161–10169 (2010).
Ridker, P. M. et al. Effect of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 390, 1833–1842 (2017).
Cris¸an, T. O. et al. Soluble uric acid primes TLR-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by human primary cells via inhibition of IL-1Ra. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 75, 755–762 (2016).
Kim, T. W. et al. The critical role of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4-mediated NF-kB activation in modified low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammatory gene expression and atherosclerosis. J. Immunol. 186, 2871–2880 (2011).
Mulay, S. R. et al. Calcium oxalate crystals induce renal inflammation by NLRP3-mediated IL-1β secretion. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 236–246 (2012).
Heneka, M. T. et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer's disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493, 674–678 (2014).
Venegas, C. et al. Microglia-derived ASC specks cross- seed amyloid. Nature 552, 355–361 (2017).
Sharp, F. A. et al. Uptake of particulate vaccine adjuvants by dendritic cells activates the NALP3 inflammasome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 106, 870–875 (2009).
Kool, M. et al. Cutting edge: alum adjuvant stimulates inflammatory dendritic cells through activation of the NALP3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 181, 3755–3759 (2008).
Franchi, L. & Nuñez, G. The Nlrp3 inflammasome is critical for aluminium hydroxide-mediated IL-1beta secretion but dispensable for adjuvant activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 2085–2089 (2008).
McKee, A. S. et al. Alum induces innate immune responses through macrophage and mast cell sensors, but these sensors are not required for alum to act as an adjuvant for specific immunity. J. Immunol. 183, 4403–4414 (2009).
Dagenais, M. & Saleh, M. Linking cancer-induced Nlrp3 inflammasome activation to efficient NK cell-mediated immunosurveillance. Oncoimmunology 5, e1129484 (2016).
Pfirschke, C. et al. Immunogenic chemotherapy sensitizes tumors to checkpoint blockade therapy. Immunity 44, 343–354 (2016).
Dietsch, G. N. et al. Coordinated activation of Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) and NLRP3 by the TLR8 agonist, VTX-2337, ignites tumoricidal natural killer cell activity. PLoS ONE 11, 1–18 (2016).
Bahia, M. S., Kaur, M., Silakari, P. & Silakari, O. Interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase inhbitors: potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory- and immune-related disorders. Cell. Signal. 27, 1039–1055 (2015).
Huang, X. & Dixit, V. M. Drugging the undruggables: exploring the ubiquitin system for drug development. Cell Res. 26, 484–498 (2016).
Jesus, A. A. & Goldbach-Mansky, R. IL-1 blockade in autoinflammatory syndromes. Annu. Rev. Med. 65, 223–244 (2014).
Dinarello, C. A., Simon, A. & van der Meer, J. W. M. Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 633–652 (2012). An important review detailing the development, role, use and future directions of IL-1 inhibitory therapies.
Calabrese, L. H. Anakinra treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Pharmacother. 36, 1204–1209 (2002).
Granowitz, E. V. et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety and immunomodulatory effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in healthy humans. Cytokine 4, 353–360 (1992).
Chakraborty, A. et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of canakinumab, a human anti-interleukin-1β monoclonal antibody. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 51, e1–18 (2012).
Ridker, P. M. et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 1119–1131 (2017). This paper describes the first large-scale clinical trial to assess the effectiveness of IL-1β blockade in reducing atherosclerotic-based diseases.
Moran, A. et al. Interleukin-1 antagonism in type 1 diabetes of recent onset: two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 381, 1905–1915 (2013).
Rossi-Semerano, L. Tolerance and efficacy of off-label anti-interleukin-1 treatments in France: a nationwide survey. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 10, 19 (2015).
Fox, E. et al. The serum and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of anakinra after intravenous administration to non-human primates. J. Neuroimmunol. 223, 138–140 (2010).
Man, S. M. & Kanneganti, T.-D. Regulation of inflammasome activation. Immunol. Rev. 265, 6–21 (2015).
Boxer, M. B. et al. A highly potent and selective caspase 1 inhibitor that utilizes a key 3-cyanopropanoic acid moiety. ChemMedChem 5, 730–738 (2010).
Wannamaker, W. et al. (S)-1-((S)-2- -3,3-dimethyl-butanoyl)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid ((2R,3S)-2-ethoxy-5-oxo-tetrahydro-furan-3-yl)-amide (VX-765), an orally available selective interleukin (IL)-converting enzyme/caspase-1 inhibitor, exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting the release of IL-1beta and IL-18. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 321, 509–516 (2007).
Rudolphi, K., Gerwin, N., Verzijl, N., van der Kraan, P. & van den Berg, W. Pralnacasan, an inhibitor of interleukin-1β converting enzyme, reduces joint damage in two murine models of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11, 738–746 (2003).
MacKenzie, S. H. et al. The potential for caspases in drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 13, 568–576 (2010).
Baldwin, A. G., Brough, D. & Freeman, S. Inhibiting the inflammasome: a chemical perspective. J. Med. Chem. 59, 1691–1710 (2016).
Redondo-Castro, E. et al. Development of a characterised tool kit for the interrogation of NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent responses. Sci. Rep. 8, 5667 (2018).
Jiang, H. et al. Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders. J. Exp. Med. 214, 3219–3238 (2017).
Bowes, J. et al. Reducing safety-related drug attrition: the use of in vitro pharmacological profiling. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 909–922 (2012).
Perregaux, D. G. et al. Identification and characterization of a novel class of interleukin-1 post-translational processing inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299, 187–197 (2001).
Coll, R. C. et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 21, 248–255 (2015). This is the first paper to demonstrate that CP-456,773 is a comprehensive, specific NLRP3 inhibitor.
Ashcroft, F. M. ATP-sensitive potassium channelopathies: focus on insulin secretion. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 2047–2058 (2005).
Lamkanfi, M. et al. Glyburide inhibits the Cryopyrin/Nalp3 inflammasome. J. Cell Biol. 187, 61–70 (2009).
Liao, J. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is critically involved in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Nat. Commun. 6, 8977 (2015).
Marchetti, C. et al. A novel pharmacologic inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome limits myocardial injury after ischemia-reperfusion in the mouse. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 63, 316–322 (2014).
Hill, J. R. et al. Sulfonylureas as concomitant insulin secretagogues and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors. ChemMedChem 12, 1449–1457 (2017).
Guo, C. et al. Development and characterization of a hydroxyl-sulfonamide analogue, 5-chloro-N-[2-(4-hydroxysulfamoyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-2-methoxy-benzamide, as a novel NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor for potential treatment of multiple sclerosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 8, 2194–2201 (2017).
Baldwin, A. G. et al. Boron-based inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Chem. Biol. 24, 1321–1335.e5 (2017).
Liu, W. et al. A novel benzo[d]imidazole derivate prevents the development of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Pharmacol. 85, 1504–1512 (2013).
Zhang, A. H., Liu, W., Jiang, N., Xu, Q. & Tan, R. X. Spirodalesol, an NLRP3 inflammasome activation inhibitor. Org. Lett. 18, 6496–6499 (2016).
Cocco, M. et al. Electrophilic warhead-based design of compounds preventing NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis. J. Med. Chem. 57, 10366–10382 (2014).
Cocco, M. et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of acrylamide derivatives as direct NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors. ChemMedChem 11, 1790–1803 (2016).
Cocco, M. et al. Development of an acrylate derivative targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Med. Chem. 60, 3656–3671 (2017).
He, Y. et al. 3,4-Methylenedioxy-β-nitrostyrene inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by blocking assembly of the inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 1142–1150 (2014).
Marchetti, C. et al. OLT1177, a β-sulfonyl nitrile compound, safe in humans, inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and reverses the metabolic cost of inflammation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 115, E1530–E1539 (2018).
Kim, B.-H. et al. Benzoxathiol derivative BOT-4-one suppresses L540 lymphoma cell survival and proliferation via inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling. Exp. Mol. Med. 43, 313–321 (2011).
Lee, H. G. et al. Immunomodulatory activities of the benzoxathiole derivative BOT-4-One ameliorate pathogenic skin inflammation in mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 136, 107–116 (2016).
Shim, D.-W. et al. BOT-4-one attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation:NLRP3 alkylation leading to the regulation of its ATPase activity and ubiquitination. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–12 (2017).
Juliana, C. et al. Anti-inflammatory compounds Parthenolide and Bay 11–7082 are direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 9792–9802 (2010).
Krishnan, N., Bencze, G., Cohen, P. & Tonks, N. K. The anti-inflammatory compound BAY-11-7082 is a potent inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases. FEBS J. 280, 2830–2841 (2013).
Strickson, S. et al. The anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11–7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system. Biochem. J. 451, 427–437 (2013).
Allen, I. C. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome mediates in vivo innate immunity to influenza A virus through recognition of viral RNA. Immunity 30, 556–565 (2009).
Hise, A. G. et al. An essential role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in host defense against the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe 5, 487–497 (2009).
McNeela, E. A. et al. Pneumolysin activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes proinflammatory cytokines independently of TLR4. PLoS Pathog. 6, 1–16 (2010).
Maltez, V. I. & Miao, E. A. Reassessing the evolutionary importance of inflammasomes. J. Immunol. 196, 956–962 (2016).
Zaki, M. H. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome protects against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during experimental colitis. Immunity 32, 379–391 (2010).
Kanai, T. et al. Interleukin 18 is a potent proliferative factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 119, 1514–1523 (2000).
Hove, Ten, T. et al. Blockade of endogenous IL-18 ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by decreasing local TNF-alpha production in mice. Gastroenterology 121, 1372–1379 (2001).
Nowarski, R. et al. Epithelial IL-18 equilibrium controls barrier function in colitis. Cell 163, 1444–1456 (2015).
Bauer, C. et al. Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut 59, 1192–1199 (2010).
Youm, Y.-H. et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 21, 263–269 (2015). This is the first paper to demonstrate that a molecule produced endogenously in response to fasting conditions is a potent NLRP3 inhibitor, opening the possibility of treating autoinflammatory diseases without pharmaceutical intervention.
Goldberg, E. L. et al. b-Hydroxybutyrate deactivates neutrophil NLRP3 inflammasome to relieve gout flares. Cell Rep. 18, 2077–2087 (2017).
Guarda, G. et al. Type I interferon inhibits interleukin-1 production and inflammasome activation. Immunity 34, 213–223 (2011). This report links type I interferons to inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Inoue, M. et al. Interferon-β therapy against EAE is effective only when development of the disease depends on the NLRP3 inflammasome. Sci. Signal. 5, ra38 (2012).
Malhotra, S. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is associated with the response to IFN-β in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain 138, 644–652 (2015).
Sokolowska, M. et al. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through EP4 receptor and intracellular cyclic AMP in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 194, 5472–5487 (2015).
Song, N. et al. Salmeterol, agonist of beta2-aderenergic receptor, prevents systemic inflammation via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Pharmacol. 150, 245–255 (2018).
Carta, S. et al. Cell stress increases ATP release in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated autoinflammatory diseases, resulting in cytokine imbalance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 2835–2840 (2015).
Di Virgilio, F., Ben, D. D., Sarti, A. C., Giuliani, A. L. & Falzoni, S. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity 47, 15–31 (2017).
Dempsey, C. et al. Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 promotes non-phlogistic clearance of amyloid-beta and cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 61, 306–316 (2017).
van der Heijden, T. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by MCC950 reduces atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice-brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 37, 1457–1461 (2017).
Besnard, A.-G. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is required in murine asthma in the absence of aluminum adjuvant. Allergy 66, 1047–1057 (2011).
Kim, R. Y. et al. Role for NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated, IL-1beta-dependent responses in severe, steroid-resistant asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 196, 283–297 (2017).
Primiano, M. J. et al. Efficacy and pharmacology of the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor CP-456,773 (CRID3) in murine models of dermal and pulmonary inflammation. J. Immunol. 197, 2421–2433 (2016).
Ruiz-Miyazawa, K. W. et al. Quercetin inhibits gout arthritis in mice: induction of an opioid-dependent regulation of inflammasome. Inflammopharmacology https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0356-x (2017).
Neudecker, V. et al. Myeloid-derived miR-223 regulates intestinal inflammation via repression of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Exp. Med. 214, 1737–1752 (2017).
Henao-Mejia, J. et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 482, 179–185 (2012).
Wree, A. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is required for fibrosis development in NAFLD. J. Mol. Med. 92, 1069–1082 (2014).
Mridha, A. R. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 66, 1037–1046 (2017).
Krishnan, S. M. et al. Inflammasome activity is essential for one kidney/deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt-induced hypertension in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 173, 752–765 (2015).
van Hout, G. P. J. et al. The selective NLRP3-inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in a pig model of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 38, 828–836 (2017).
Sandanger, O. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is up-regulated in cardiac fibroblasts and mediates myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 99, 164–174 (2013).
Gris, D. et al. NLRP3 plays a critical role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by mediating Th1 and Th17 responses. J. Immunol. 185, 974–981 (2010).
Ludwig-Portugall, I. et al. An NLRP3-specific inflammasome inhibitor attenuates crystal-induced kidney fibrosis in mice. Kidney Int. 90, 525–539 (2016).
Coates, B. M. et al. Inhibition of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome is protective in juvenile influenza A virus infection. Front. Immunol. 8, 1–12 (2017).
Tate, M. D. et al. Reassessing the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome during pathogenic influenza A virus infection via temporal inhibition. Sci. Rep. 6, 27912 (2016).
Jankovic, D. et al. The Nlrp3 inflammasome regulates acute graft-versus-host disease. J. Exp. Med. 210, 1899–1910 (2013).
Yang, F. et al. NLRP3 deficiency ameliorates neurovascular damage in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 34, 660–667 (2014).
Ren, H. et al. Selective NLRP3 (pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome inhibitor reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 49, 184–192 (2018).
Cassel, S. L. et al. The Nalp3 inflammasome is essential for the development of silicosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 9035–9040 (2008).
Hu, C. et al. NLRP3 deficiency protects from type 1 diabetes through the regulation of chemotaxis into the pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 11318–11323 (2015).
Vande Walle, L. et al. Negative regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by A20 protects against arthritis. Nature 512, 69–73 (2014).
Basiorka, A. A. et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome functions as a driver of the myelodysplastic syndrome phenotype. Blood 128, 2960–2975 (2016).
Sutterwala, F. S. et al. Critical role for NALP3/CIAS1/Cryopyrin in innate and adaptive immunity through its regulation of caspase-1. Immunity 24, 317–327 (2006).
Chen, W. et al. Specific inhibition of NLRP3 in chikungunya disease reveals a role for inflammasomes in alphavirus-induced inflammation. Nat. Microbiol. 2, 1435–1445 (2017).
Irrera, N. et al. Lack of the Nlrp3 inflammasome improves mice recovery following traumatic brain injury. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 459 (2017).
Ismael, S., Nasoohi, S. & Ishrat, T. MCC950, the selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor protects mice against traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 35, 1294–1303 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank L. Franchi for advice during the preparation of this document. E.L. is supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG SFBs 645, 670, 1123; TRRs 83, 57), a grant from the National Institutes of Health (1R01HL112661) and by a European Research Council (ERC) Consolidator grant (InflammAct). E.L. is a member of the excellence cluster ImmunoSensation, which is funded by the DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
E.L. is a consultant to IFM Therapeutics. E.J.O., W.R.R., H.M.S. and G.D.G. are employees of IFM Therapeutics.
Glossary
- Innate immune memory
-
Epigenetic reprogramming of innate immune cells following an initial encounter with a pathogen, leading to changed chromatin accessibility and altered transcriptional responsiveness in response to subsequent stimuli.
- Antagonistically pleiotropic
-
A situation in which one gene controls for more than one trait and at least one of these traits is beneficial to the organism's fitness and at least one is detrimental to the organism's fitness.
- ASC speck
-
Multimeric protein aggregates that result from helical fibril formation of ASC that is initiated by the homo-oligomerization of inflammasome proteins.
- Cathepsins
-
A family of cysteine proteases that reside in the lysosomes of cells.
- Mitophagy
-
The deliberate, specific degradation of mitochondria by an autophagic mechanism.
- Astrogliosis
-
An increase in the number of astrocytes that accompanies the death or damage of nearby neuronal cells. The purpose of astrogliosis is likely to limit damage and remove noxious or infectious agents but can lead to scar formation.
- Atherosclerosis
-
A disease in which the lumen of an artery narrows owing to the build-up of a plaque, which, when it ruptures, occludes the vessel and prevents blood flow.
- APP/PS1 mouse line
-
A double-transgenic mouse line that expresses a chimaeric mouse–human amyloid precursor protein and a mutant human presenilin 1, both of which are expressed in central nervous system neurons.
- M2-like
-
A type of macrophage, also known as an alternatively activated macrophage, that is considered anti-inflammatory and is important in wound healing and tissue repair.
- Adjuvants
-
Substances that enhance the body's immune response to an antigen.
- Delayed-type hypersensitivity
-
A cell-mediated immune response to an antigen that takes several days to develop.
- Michael acceptors
-
The accepting molecules in a Michael reaction. The Michael reaction or Michael addition is the nucleophilic addition of a carbanion or another nucleophile to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
- CEREP
-
A service platform that provides over 630 validated in vitro pharmacological assays that cover a broad range of targets, including receptors, ion channels, transporters, enzymes and second messengers. These assays can be used to identify lead compounds, to define mechanism of action and to identify off-target activities.
- Walker A motif
-
A type of phosphate-binding protein motif.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangan, M., Olhava, E., Roush, W. et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17, 588–606 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.97
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.97
This article is cited by
-
Disordered GPR43/NLRP3 expression in peripheral leukocytes of patients with atrial fibrillation is associated with intestinal short chain fatty acids levels
European Journal of Medical Research (2024)
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in donor and end-stage heart failure patients identifies NLRP3 as a therapeutic target for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
BMC Medicine (2024)
-
METTL14 contributes to acute lung injury by stabilizing NLRP3 expression in an IGF2BP2-dependent manner
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
GSNOR negatively regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome via S-nitrosation of MAPK14
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2024)
-
Pas de deux of NLRP3 and ASC with CD63 on mast cell granules
Nature Immunology (2024)