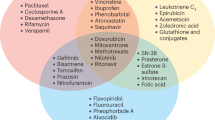
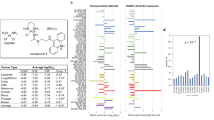
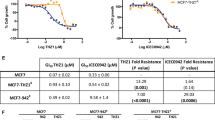
Abstract
Multidrug transporter proteins are best known for their contributions to chemoresistance through the efflux of anticancer drugs from cancer cells. However, a considerable body of evidence also points to their importance in cancer extending beyond drug transport to fundamental roles in tumour biology. Currently, much of the evidence for these additional roles is correlative and definitive studies are needed to confirm causality. We propose that delineating the precise roles of these transporters in tumorigenesis and treatment response will be important for the development of more effective targeted therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottesman, M. M., Fojo, T. & Bates, S. E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nature Rev. Cancer 2, 48–58 (2002).
Dean, M. The genetics of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Methods Enzymol. 400, 409–429 (2005).
Albrecht, C. & Viturro, E. The ABCA subfamily – gene and protein structures, functions and associated hereditary diseases. Pflugers Arch. 453, 581–589 (2007).
Mack, J. T., Brown, C. B. & Tew, K. D. ABCA2 as a therapeutic target in cancer and nervous system disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 12, 491–504 (2008).
Takahashi, K. et al. ABC proteins: key molecules for lipid homeostasis. Med. Mol. Morphol. 38, 2–12 (2005).
Herget, M. & Tampe, R. Intracellular peptide transporters in human – compartmentalization of the “peptidome”. Pflugers Arch. 453, 591–600 (2007).
Deeley, R. G., Westlake, C. & Cole, S. P. Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol. Rev. 86, 849–899 (2006).
Wanders, R. J., Visser, W. F., van Roermund, C. W., Kemp, S. & Waterham, H. R. The peroxisomal ABC transporter family. Pflugers Arch. 453, 719–734 (2007).
Chen, Z. Q. et al. The essential vertebrate ABCE1 protein interacts with eukaryotic initiation factors. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 7452–7457 (2006).
Kerr, I. D. Sequence analysis of twin ATP binding cassette proteins involved in translational control, antibiotic resistance, and ribonuclease L inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 315, 166–173 (2004).
Szakacs, G., Paterson, J. K., Ludwig, J. A., Booth-Genthe, C. & Gottesman, M. M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 219–234 (2006).
Teodori, E., Dei, S., Martelli, C., Scapecchi, S. & Gualtieri, F. The functions and structure of ABC transporters: implications for the design of new inhibitors of Pgp and MRP1 to control multidrug resistance (MDR). Curr. Drug Targets. 7, 893–909 (2006).
Kaye, S. B. Reversal of drug resistance in ovarian cancer: where do we go from here? J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2616–2618 (2008).
Lhomme, C. et al. Phase III study of valspodar (PSC 833) combined with paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with paclitaxel and carboplatin alone in patients with stage IV or suboptimally debulked stage III epithelial ovarian cancer or primary peritoneal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2674–2682 (2008).
Greenberg, P. L. et al. Mitoxantrone, etoposide, and cytarabine with or without valspodar in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: a phase III trial (E2995). J. Clin. Oncol. 22, 1078–1086 (2004).
Ruff, P. et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2 study of docetaxel compared to docetaxel plus zosuquidar (LY335979) in women with metastatic or locally recurrent breast cancer who have received one prior chemotherapy regimen. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 64, 763–768 (2009).
Garraway, L. A. & Chabner, B. MDR1 inhibition: less resistance or less relevance? Eur. J. Cancer 38, 2337–2340 (2002).
Relling, M. V. Are the major effects of P-glycoprotein modulators due to altered pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs? Ther. Drug Monit. 18, 350–356 (1996).
Schinkel, A. H. et al. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77, 491–502 (1994).
Szakacs, G. et al. Predicting drug sensitivity and resistance: profiling ABC transporter genes in cancer cells. Cancer Cell 6, 129–137 (2004).
Randolph, G. J. et al. A physiologic function for p-glycoprotein (MDR-1) during the migration of dendritic cells from skin via afferent lymphatic vessels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6924–6929 (1998).
Robbiani, D. F. et al. The leukotriene C4 transporter MRP1 regulates CCL19 (MIP-3β, ELC)-dependent mobilization of dendritic cells to lymph nodes. Cell 103, 757–768 (2000).
van de Ven, R. et al. A role for multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4; ABCC4) in human dendritic cell migration. Blood 112, 2353–2359 (2008).
van de Ven, R., Scheffer, G. L., Scheper, R. J. & de Gruijl, T. D. The ABC of dendritic cell development and function. Trends Immunol. 30, 421–429 (2009).
Vander Borght, S. et al. Expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with a more aggressive tumour phenotype and may reflect a progenitor cell origin. Liver Int. 28, 1370–1380 (2008).
Filipits, M. et al. MRP and MDR1 gene expression in primary breast carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2, 1231–1237 (1996).
Zochbauer-Muller, S. et al. P-glycoprotein and MRP1 expression in axillary lymph node metastases of breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 21, 119–124 (2001).
Oevermann, L. et al. Hematopoietic stem cell differentiation affects expression and function of MRP4 (ABCC4), a transport protein for signaling molecules and drugs. Int. J. Cancer 124, 2303–2311 (2009).
Hanada, S. et al. Expression profile of early lung adenocarcinoma: identification of MRP3 as a molecular marker for early progression. J. Pathol. 216, 75–82 (2008).
Konig, J. et al. Expression and localization of human multidrug resistance protein (ABCC) family members in pancreatic carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 115, 359–367 (2005).
Weinstein, R. S. et al. Relationship of the expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human colon carcinoma to local tumor aggressiveness and lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 51, 2720–2726 (1991).
Ohtsuki, S. et al. Correlation of induction of ATP binding cassette transporter A5 (ABCA5) and ABCB1 mRNAs with differentiation state of human colon tumor. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 1144–1146 (2007).
Oda, Y. et al. ATP-binding cassette superfamily transporter gene expression in human soft tissue sarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 114, 854–862 (2005).
Steinbach, D. et al. ABCA3 as a possible cause of drug resistance in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 4357–4363 (2006).
Yoh, K. et al. Breast cancer resistance protein impacts clinical outcome in platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 1691–1697 (2004).
Maris, J. M., Hogarty, M. D., Bagatell, R. & Cohn, S. L. Neuroblastoma. Lancet 369, 2106–2120 (2007).
Haber, M. et al. Association of high-level MRP1 expression with poor clinical outcome in a large prospective study of primary neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 1546–1553 (2006).
Norris, M. D. et al. Expression of multidrug transporter MRP4/ABCC4 is a marker of poor prognosis in neuroblastoma and confers resistance to irinotecan in vitro. Mol. Cancer Ther. 4, 547–553 (2005).
Oberthuer, A. et al. Customized oligonucleotide microarray gene expression-based classification of neuroblastoma patients outperforms current clinical risk stratification. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 5070–5078 (2006).
Mochida, Y. et al. The role of P-glycoprotein in intestinal tumorigenesis: disruption of mdr1a suppresses polyp formation in ApcMin/+ mice. Carcinogenesis 24, 1219–1224 (2003).
Yamada, T. et al. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Mdr1-deficient ApcMin/+ mice. Cancer Res. 63, 895–901 (2003).
Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R. A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100, 57–70 (2000).
Mantovani, A. Cancer: inflaming metastasis. Nature 457, 36–37 (2009).
Lehne, G. & Rugstad, H. E. Cytotoxic effect of the cyclosporin PSC 833 in multidrug-resistant leukaemia cells with increased expression of P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Cancer 78, 593–600 (1998).
Lehne, G., De Angelis, P., den Boer, M. & Rugstad, H. E. Growth inhibition, cytokinesis failure and apoptosis of multidrug-resistant leukemia cells after treatment with P-glycoprotein inhibitory agents. Leukemia 13, 768–778 (1999).
Lehne, G. et al. The cyclosporin PSC 833 increases survival and delays engraftment of human multidrug-resistant leukemia cells in xenotransplanted NOD-SCID mice. Leukemia 16, 2388–2394 (2002).
Lopes, E. C. et al. Multidrug resistance modulators PSC 833 and CsA show differential capacity to induce apoptosis in lymphoid leukemia cell lines independently of their MDR phenotype. Leuk. Res. 27, 413–423 (2003).
Robinson, L. J. et al. Human MDR 1 protein overexpression delays the apoptotic cascade in Chinese hamster ovary fibroblasts. Biochemistry 36, 11169–11178 (1997).
Smyth, M. J., Krasovskis, E., Sutton, V. R. & Johnstone, R. W. The drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein, additionally protects drug-resistant tumor cells from multiple forms of caspase-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7024–7029 (1998).
Johnstone, R. W., Cretney, E. & Smyth, M. J. P-glycoprotein protects leukemia cells against caspase-dependent, but not caspase-independent, cell death. Blood 93, 1075–1085 (1999).
Pallis, M. & Russell, N. P-glycoprotein plays a drug-efflux-independent role in augmenting cell survival in acute myeloblastic leukemia and is associated with modulation of a sphingomyelin-ceramide apoptotic pathway. Blood 95, 2897–2904 (2000).
Bezombes, C. et al. Restoration of TNF-α-induced ceramide generation and apoptosis in resistant human leukemia KG1a cells by the P-glycoprotein blocker PSC833. FASEB J. 12, 101–109 (1998).
Tainton, K. M. et al. Mutational analysis of P-glycoprotein: suppression of caspase activation in the absence of ATP-dependent drug efflux. Cell Death Differ. 11, 1028–1037 (2004).
Aleman, C. et al. P-glycoprotein, expressed in multidrug resistant cells, is not responsible for alterations in membrane fluidity or membrane potential. Cancer Res. 63, 3084–3091 (2003).
Peaston, A. E. et al. MRP1 gene expression level regulates the death and differentiation response of neuroblastoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 85, 1564–1571 (2001).
Kuss, B. J. et al. In vitro and in vivo downregulation of MRP1 by antisense oligonucleotides: a potential role in neuroblastoma therapy. Int. J. Cancer 98, 128–133 (2002).
Sassi, Y. et al. Multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 regulates cAMP-dependent signaling pathways and controls human and rat SMC proliferation. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 2747–2757 (2008).
Katoh, S. Y., Ueno, M. & Takakura, N. Involvement of MDR1 function in proliferation of tumour cells. J. Biochem. 143, 517–524 (2008).
Bhattacharya, S., Das, A., Mallya, K. & Ahmad, I. Maintenance of retinal stem cells by Abcg2 is regulated by notch signaling. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2652–2662 (2007).
Dean, M., Fojo, T. & Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nature Rev. Cancer 5, 275–284 (2005).
Zhou, S. et al. Bcrp1 gene expression is required for normal numbers of side population stem cells in mice, and confers relative protection to mitoxantrone in hematopoietic cells in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12339–12344 (2002).
Uchida, N., Leung, F. Y. & Eaves, C. J. Liver and marrow of adult mdr-1a/1b−/− mice show normal generation, function, and multi-tissue trafficking of primitive hematopoietic cells. Exp. Hematol. 30, 862–869 (2002).
Jonker, J. W. et al. The breast cancer resistance protein protects against a major chlorophyll-derived dietary phototoxin and protoporphyria. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15649–15654 (2002).
Zhou, S., Zong, Y., Lu, T. & Sorrentino, B. P. Hematopoietic cells from mice that are deficient in both Bcrp1/Abcg2 and Mdr1a/1b develop normally but are sensitized to mitoxantrone. Biotechniques 35, 1248–1252 (2003).
Wijnholds, J. et al. Increased sensitivity to anticancer drugs and decreased inflammatory response in mice lacking the multidrug resistance-associated protein. Nature Med. 3, 1275–1279 (1997).
Raaijmakers, M. H. ATP-binding-cassette transporters in hematopoietic stem cells and their utility as therapeutical targets in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 21, 2094–2102 (2007).
Bunting, K. D., Galipeau, J., Topham, D., Benaim, E. & Sorrentino, B. P. Transduction of murine bone marrow cells with an MDR1 vector enables ex vivo stem cell expansion, but these expanded grafts cause a myeloproliferative syndrome in transplanted mice. Blood 92, 2269–2279 (1998).
Zhou, S. et al. The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nature Med. 7, 1028–1034 (2001).
Ben-Porath, I. et al. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nature Genet. 40, 499–507 (2008).
Wong, D. J. et al. Module map of stem cell genes guides creation of epithelial cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2, 333–344 (2008).
Steeg, P. S. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nature Med. 12, 895–904 (2006).
Miletti-Gonzalez, K. E. et al. The CD44 receptor interacts with P-glycoprotein to promote cell migration and invasion in cancer. Cancer Res. 65, 6660–6667 (2005).
Colone, M. et al. The multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein: a mediator of melanoma invasion? J. Invest. Dermatol. 128, 957–971 (2008).
Barakat, S. et al. Regulation of brain endothelial cells migration and angiogenesis by P-glycoprotein/caveolin-1 interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 372, 440–446 (2008).
Heimerl, S., Bosserhoff, A. K., Langmann, T., Ecker, J. & Schmitz, G. Mapping ATP-binding cassette transporter gene expression profiles in melanocytes and melanoma cells. Melanoma Res. 17, 265–273 (2007).
Mantovani, A., Allavena, P., Sica, A. & Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454, 436–444 (2008).
Dannenberg, A. J. & Subbaramaiah, K. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 4, 431–436 (2003).
Gasparini, G., Longo, R., Sarmiento, R. & Morabito, A. Inhibitors of cyclo-oxygenase 2: a new class of anticancer agents? Lancet Oncol. 4, 605–615 (2003).
Greenhough, A. et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 30, 377–386 (2009).
Muller, A. J. & Scherle, P. A. Targeting the mechanisms of tumoral immune tolerance with small-molecule inhibitors. Nature Rev. Cancer 6, 613–625 (2006).
Fulton, A. M., Ma, X. & Kundu, N. Targeting prostaglandin E EP receptors to inhibit metastasis. Cancer Res. 66, 9794–9797 (2006).
Chell, S., Kaidi, A., Williams, A. C. & Paraskeva, C. Mediators of PGE2 synthesis and signalling downstream of COX-2 represent potential targets for the prevention/treatment of colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1766, 104–119 (2006).
Tessner, T. G., Muhale, F., Riehl, T. E., Anant, S. & Stenson, W. F. Prostaglandin E2 reduces radiation-induced epithelial apoptosis through a mechanism involving AKT activation and bax translocation. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 1676–1685 (2004).
Vivanco, I. & Sawyers, C. L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 2, 489–501 (2002).
Castellone, M. D., Teramoto, H., Williams, B. O., Druey, K. M. & Gutkind, J. S. Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs-axin-β-catenin signaling axis. Science 310, 1504–1510 (2005).
Tsujii, M. et al. Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer cells. Cell 93, 705–716 (1998).
Gupta, G. P. et al. Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in lung metastasis. Nature 446, 765–770 (2007).
Sombroek, C. C. et al. Prostanoids play a major role in the primary tumor-induced inhibition of dendritic cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 168, 4333–4343 (2002).
Chan, B. S., Satriano, J. A., Pucci, M. & Schuster, V. L. Mechanism of prostaglandin E2 transport across the plasma membrane of HeLa cells and Xenopus oocytes expressing the prostaglandin transporter “PGT”. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 6689–6697 (1998).
Nomura, T., Lu, R., Pucci, M. L. & Schuster, V. L. The two-step model of prostaglandin signal termination: in vitro reconstitution with the prostaglandin transporter and prostaglandin 15 dehydrogenase. Mol. Pharmacol. 65, 973–978 (2004).
Schuster, V. L. Prostaglandin transport. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 633–647 (2002).
Tai, H. H., Ensor, C. M., Tong, M., Zhou, H. & Yan, F. Prostaglandin catabolizing enzymes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 483–493 (2002).
de Waart, D. R., Paulusma, C. C., Kunne, C. & Oude Elferink, R. P. Multidrug resistance associated protein 2 mediates transport of prostaglandin E2. Liver Int. 26, 362–368 (2006).
Reid, G. et al. The human multidrug resistance protein MRP4 functions as a prostaglandin efflux transporter and is inhibited by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 9244–9249 (2003).
Rius, M., Thon, W. F., Keppler, D. & Nies, A. T. Prostanoid transport by multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) localized in tissues of the human urogenital tract. J. Urol. 174, 2409–2414 (2005).
Lin, Z. P. et al. Disruption of cAMP and prostaglandin E2 transport by multidrug resistance protein 4 deficiency alters cAMP-mediated signaling and nociceptive response. Mol. Pharmacol. 73, 243–251 (2008).
Holla, V. R., Backlund, M. G., Yang, P., Newman, R. A. & DuBois, R. N. Regulation of prostaglandin transporters in colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila Pa) 1, 93–99 (2008).
Milne, G. L., Musiek, E. S. & Morrow, J. D. The cyclopentenone (A2/J2) isoprostanes—unique, highly reactive products of arachidonate peroxidation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7, 210–220 (2005).
Musiek, E. S., Milne, G. L., McLaughlin, B. & Morrow, J. D. Cyclopentenone eicosanoids as mediators of neurodegeneration: a pathogenic mechanism of oxidative stress-mediated and cyclooxygenase-mediated neurotoxicity. Brain Pathol. 15, 149–158 (2005).
Negishi, M. & Katoh, H. Cyclopentenone prostaglandin receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 611–617 (2002).
Straus, D. S. & Glass, C. K. Cyclopentenone prostaglandins: new insights on biological activities and cellular targets. Med. Res. Rev. 21, 185–210 (2001).
Michalik, L., Desvergne, B. & Wahli, W. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: complex stories. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 61–70 (2004).
Evers, R. et al. Transport of glutathione prostaglandin A conjugates by the multidrug resistance protein 1. FEBS Lett. 419, 112–116 (1997).
Paumi, C. M., Wright, M., Townsend, A. J. & Morrow, C. S. Multidrug resistance protein (MRP) 1 and MRP3 attenuate cytotoxic and transactivating effects of the cyclopentenone prostaglandin, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14prostaglandin J2 in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochemistry 42, 5429–5437 (2003).
Mezhybovska, M., Wikstrom, K., Ohd, J. F. & Sjolander, A. The inflammatory mediator leukotriene D4 induces β-catenin signaling and its association with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 6776–6784 (2006).
Nielsen, C. K. et al. A novel localization of the G-protein-coupled CysLT1 receptor in the nucleus of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 65, 732–742 (2005).
Ihara, A. et al. Blockade of leukotriene B4 signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses cell proliferation in colon cancer. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 103, 24–32 (2007).
Peters-Golden, M. & Henderson, W. R. Jr. Leukotrienes. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 1841–1854 (2007).
Tazzyman, S., Lewis, C. E. & Murdoch, C. Neutrophils: key mediators of tumour angiogenesis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 90, 222–231 (2009).
Avis, I. M. et al. Growth control of lung cancer by interruption of 5-lipoxygenase-mediated growth factor signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 97, 806–813 (1996).
Hong, S. H. et al. Relationship of arachidonic acid metabolizing enzyme expression in epithelial cancer cell lines to the growth effect of selective biochemical inhibitors. Cancer Res. 59, 2223–2228 (1999).
Boado, R. J., Pardridge, W. M., Vinters, H. V. & Black, K. L. Differential expression of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase transcripts in human brain tumors: evidence for the expression of a multitranscript family. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9044–9048 (1992).
Hennig, R. et al. 5-Lipoxygenase and leukotriene B4 receptor are expressed in human pancreatic cancers but not in pancreatic ducts in normal tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 161, 421–428 (2002).
Tong, W. G., Ding, X. Z., Witt, R. C. & Adrian, T. E. Lipoxygenase inhibitors attenuate growth of human pancreatic cancer xenografts and induce apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1, 929–935 (2002).
Gunning, W. T., Kramer, P. M., Steele, V. E. & Pereira, M. A. Chemoprevention by lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathway inhibitors of vinyl carbamate-induced lung tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 62, 4199–4201 (2002).
Chen, Y., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Peng, C. & Li, S. Loss of the Alox5 gene impairs leukemia stem cells and prevents chronic myeloid leukemia. Nature Genet. 41, 783–792 (2009).
Belinsky, M. G., Chen, Z. S., Shchaveleva, I., Zeng, H. & Kruh, G. D. Characterization of the drug resistance and transport properties of multidrug resistance protein 6 (MRP6, ABCC6). Cancer Res. 62, 6172–6177 (2002).
Chen, Z. S., Guo, Y., Belinsky, M. G., Kotova, E. & Kruh, G. D. Transport of bile acids, sulfated steroids, estradiol 17-β-D-glucuronide, and leukotriene C4 by human multidrug resistance protein 8 (ABCC11). Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 545–557 (2005).
Chen, Z. S. et al. Characterization of the transport properties of human multidrug resistance protein 7 (MRP7, ABCC10). Mol. Pharmacol. 63, 351–358 (2003).
Cui, Y. et al. Drug resistance and ATP-dependent conjugate transport mediated by the apical multidrug resistance protein, MRP2, permanently expressed in human and canine cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 55, 929–937 (1999).
Jedlitschky, G., Leier, I., Buchholz, U., Center, M. & Keppler, D. ATP-dependent transport of glutathione S-conjugates by the multidrug resistance-associated protein. Cancer Res. 54, 4833–4836 (1994).
Leier, I. et al. The MRP gene encodes an ATP-dependent export pump for leukotriene C4 and structurally related conjugates. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 27807–27810 (1994).
Rius, M., Hummel-Eisenbeiss, J. & Keppler, D. ATP-dependent transport of leukotrienes B4 and C4 by the multidrug resistance protein ABCC4 (MRP4). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 324, 86–94 (2008).
Zeng, H., Liu, G., Rea, P. A. & Kruh, G. D. Transport of amphipathic anions by human multidrug resistance protein 3. Cancer Res. 60, 4779–4784 (2000).
Hannun, Y. A. & Obeid, L. M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 139–150 (2008).
Ishii, I., Fukushima, N., Ye, X. & Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 321–354 (2004).
Spiegel, S. & Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 397–407 (2003).
Kluk, M. J. & Hla, T. Signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate via the S1P/EDG-family of G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1582, 72–80 (2002).
Taha, T. A., Argraves, K. M. & Obeid, L. M. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors: receptor specificity versus functional redundancy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1682, 48–55 (2004).
Lee, M. J. et al. Vascular endothelial cell adherens junction assembly and morphogenesis induced by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cell 99, 301–312 (1999).
Kimura, T. et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates proliferation and migration of human endothelial cells possibly through the lipid receptors, Edg-1 and Edg-3. Biochem. J. 348, 71–76 (2000).
Liu, Y. et al. Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 951–961 (2000).
Mizugishi, K. et al. Essential role for sphingosine kinases in neural and vascular development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 11113–11121 (2005).
Visentin, B. et al. Validation of an anti-sphingosine-1-phosphate antibody as a potential therapeutic in reducing growth, invasion, and angiogenesis in multiple tumor lineages. Cancer Cell 9, 225–238 (2006).
Maceyka, M., Payne, S. G., Milstien, S. & Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1585, 193–201 (2002).
Radeff-Huang, J., Seasholtz, T. M., Matteo, R. G. & Brown, J. H. G protein mediated signaling pathways in lysophospholipid induced cell proliferation and survival. J. Cell Biochem. 92, 949–966 (2004).
Van Brocklyn, J. R., Young, N. & Roof, R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulates motility and invasiveness of human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett. 199, 53–60 (2003).
Xia, P. et al. An oncogenic role of sphingosine kinase. Curr. Biol. 10, 1527–1530 (2000).
Pettus, B. J. et al. The sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate pathway mediates COX-2 induction and PGE2 production in response to TNF-α. FASEB J. 17, 1411–1421 (2003).
Sato, K. et al. Critical role of ABCA1 transporter in sphingosine 1-phosphate release from astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 103, 2610–2619 (2007).
Mitra, P. et al. Role of ABCC1 in export of sphingosine-1-phosphate from mast cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 16394–16399 (2006).
Norris, M. D. et al. Expression of the gene for multidrug-resistance-associated protein and outcome in patients with neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 231–238 (1996).
Meitar, D., Crawford, S. E., Rademaker, A. W. & Cohn, S. L. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastatic disease, N-myc amplification, and poor outcome in human neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 14, 405–414 (1996).
Weiss, W., Aldape, K., Mohapatra, G., Feuerstein, B. & Bishop, J. Targeted expression of MYCN causes neuroblastoma in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 16, 2985–2995 (1997).
Wenk, M. R. The emerging field of lipidomics. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 594–610 (2005).
Norman, B. H. et al. Cyclohexyl-linked tricyclic isoxazoles are potent and selective modulators of the multidrug resistance protein (MRP1). Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 5526–5530 (2005).
O'Connor, R. et al. A phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the multi-drug resistance protein-1 (MRP-1) inhibitor sulindac, in combination with epirubicin in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 59, 79–87 (2007).
Kondratov, R. V., Komarov, P. G., Becker, Y., Ewenson, A. & Gudkov, A. V. Small molecules that dramatically alter multidrug resistance phenotype by modulating the substrate specificity of P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14078–14083 (2001).
de Grouw, E. P. et al. Preferential expression of a high number of ATP binding cassette transporters in both normal and leukemic CD34+CD38- cells. Leukemia 20, 750–754 (2006).
Park, S. et al. Gene expression profiling of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters as a predictor of the pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 99, 9–17 (2006).
Juliano, R. L. & Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455, 152–162 (1976).
Ambudkar, S. V., Kimchi-Sarfaty, C., Sauna, Z. E. & Gottesman, M. M. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 22, 7468–7485 (2003).
Cole, S. P. et al. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 258, 1650–1654 (1992).
Munoz, M., Henderson, M., Haber, M. & Norris, M. Role of the MRP1/ABCC1 multidrug transporter protein in cancer. IUBMB Life 59, 752–757 (2007).
Bunting, K. D. ABC transporters as phenotypic markers and functional regulators of stem cells. Stem Cells 20, 11–20 (2002).
Doyle, L. A. et al. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15665–15670 (1998).
Robey, R. W., Polgar, O., Deeken, J., To, K. W. & Bates, S. E. ABCG2: determining its relevance in clinical drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26, 39–57 (2007).
Dorsam, R. T. & Gutkind, J. S. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 7, 79–94 (2007).
Chen, Z. S., Lee, K. & Kruh, G. D. Transport of cyclic nucleotides and estradiol 17-β-D-glucuronide by multidrug resistance protein 4. Resistance to 6-mercaptopurine and 6-thioguanine. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 33747–33754 (2001).
Wielinga, P. R. et al. Characterization of the MRP4- and MRP5-mediated transport of cyclic nucleotides from intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 17664–17671 (2003).
Jedlitschky, G., Burchell, B. & Keppler, D. The multidrug resistance protein 5 functions as an ATP-dependent export pump for cyclic nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 30069–30074 (2000).
Guo, Y. et al. MRP8, ATP-binding cassette C11 (ABCC11), is a cyclic nucleotide efflux pump and a resistance factor for fluoropyrimidines 2', 3'-dideoxycytidine and 9'-(2'-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) adenine. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 29509–29514 (2003).
de Wolf, C. J. et al. cGMP transport by vesicles from human and mouse erythrocytes. FEBS J. 274, 439–450 (2007).
Borst, P. et al. The potential impact of drug transporters on nucleoside-analog-based antiviral chemotherapy. Antiviral Res. 62, 1–7 (2004).
Raggers, R. J., Vogels, I. & van Meer, G. Multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein (MDR1) secretes platelet-activating factor. Biochem. J. 357, 859–865 (2001).
Heon Seo, K. et al. Platelet-activating factor induces up-regulation of antiapoptotic factors in a melanoma cell line through nuclear factor-κB activation. Cancer Res. 66, 4681–4686 (2006).
Bussolati, B. et al. PAF produced by human breast cancer cells promotes migration and proliferation of tumor cells and neo-angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1713–1725 (2000).
Melnikova, V. O., Mourad-Zeidan, A. A., Lev, D. C. & Bar-Eli, M. Platelet-activating factor mediates MMP-2 expression and activation via phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein and contributes to melanoma metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 2911–2922 (2006).
Denizot, Y. et al. Platelet-activating factor and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 113, 503–505 (2005).
Kim, J., Adam, R. M., Solomon, K. R. & Freeman, M. R. Involvement of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in interleukin-6-induced neuroendocrine differentiation of LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Endocrinology 145, 613–619 (2004).
Zhuang, L., Kim, J., Adam, R. M., Solomon, K. R. & Freeman, M. R. Cholesterol targeting alters lipid raft composition and cell survival in prostate cancer cells and xenografts. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 959–968 (2005).
Hughes-Fulford, M., Chen, Y. & Tjandrawinata, R. R. Fatty acid regulates gene expression and growth of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Carcinogenesis 22, 701–707 (2001).
Gillet, J. P., Efferth, T. & Remacle, J. Chemotherapy-induced resistance by ATP-binding cassette transporter genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1775, 237–262 (2007).
Oram, J. F., Wolfbauer, G., Vaughan, A. M., Tang, C. & Albers, J. J. Phospholipid transfer protein interacts with and stabilizes ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and enhances cholesterol efflux from cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 52379–52385 (2003).
Ho, M. M., Ng, A. V., Lam, S. & Hung., J. Y. Side population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched with stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67, 4827–4833 (2007).
Ban, N. et al. ABCA3 as a lipid transporter in pulmonary surfactant biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 9628–9634 (2007).
Hirschmann-Jax, C. et al. A distinct “side population” of cells with high drug efflux capacity in human tumor cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 14228–14233 (2004).
Raaijmakers, M. H. et al. ABCB1 modulation does not circumvent drug extrusion from primitive leukemic progenitor cells and may preferentially target residual normal cells in acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 3452–3458 (2006).
Schatton, T. et al. Identification of cells initiating human melanomas. Nature 451, 345–349 (2008).
Jin, F. et al. Comparison between cells and cancer stem-like cells isolated from glioblastoma and astrocytoma on expression of anti-apoptotic and multidrug resistance-associated protein genes. Neuroscience 154, 541–550 (2008).
Loebinger, M. R. et al. Squamous cell cancers contain a side population of stem-like cells that are made chemosensitive by ABC transporter blockade. Br. J. Cancer 98, 380–387 (2008).
Sager, G., Orbo, A., Pettersen, R. H. & Kjorstad, K. E. Export of guanosine 3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) from human erythrocytes characterized by inside-out membrane vesicles. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 56, 289–293 (1996).
Van Aubel, R. A., Smeets, P. H., van den Heuvel, J. J. & Russel, F. G. Human organic anion transporter MRP4 (ABCC4) is an efflux pump for the purine end metabolite urate with multiple allosteric substrate binding sites. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 288, F327–333 (2005).
Wang, J. et al. c-Myc is required for maintenance of glioma cancer stem cells. PLoS One 3, 3769 (2008).
Zhang, S. et al. Identification and characterization of ovarian cancer-initiating cells from primary human tumors. Cancer Res. 68, 4311–4320 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors were supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia, Cancer Institute New South Wales, Australia, and Cancer Council New South Wales, Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Related links
Related links
DATABASES
National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary
FURTHER INFORMATION
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fletcher, J., Haber, M., Henderson, M. et al. ABC transporters in cancer: more than just drug efflux pumps. Nat Rev Cancer 10, 147–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2789
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2789
This article is cited by
-
Effects of ABCG2 C421A and ABCG2 G34A genetic polymorphisms on clinical outcome and response to imatinib mesylate, in Iranian chronic myeloid leukemia patients
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2023)
-
Advances in the structure, mechanism and targeting of chemoresistance-linked ABC transporters
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
ABCC1 and glutathione metabolism limit the efficacy of BCL-2 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Polymorphic renal transporters and cisplatin’s toxicity in urinary bladder cancer patients: current perspectives and future directions
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
Molecular aspects of ABCB1 and ABCG2 in Gallbladder cancer and its clinical relevance
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)