Abstract
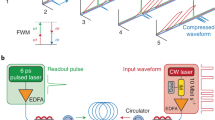
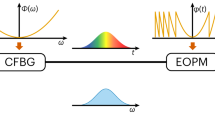
Photonic systems provide access to extremely large bandwidths, which can approach a petahertz1. Unfortunately, full utilization of this bandwidth is not achievable using standard electro-optical technologies, and higher (>100 GHz) performance requires all-optical processing with nonlinear-optical elements. A solution to the implementation of these elements in robust, compact and efficient systems is emerging in photonic integrated circuits, as evidenced by their recent application in various ultrahigh-bandwidth instruments2,3,4. These devices enable the characterization of extremely complex signals by linking the high-speed optical domain with slower speed electronics. Here, we extend the application of these devices beyond characterization and demonstrate an instrument that generates complex and rapidly updateable ultrafast optical waveforms. We generate waveforms with 1.5-ps minimum features by compressing lower-bandwidth replicas created with a 10 GHz electro-optic modulator. In effect, our device allows for ultrahigh-speed direct 270 GHz modulation using relatively low speed devices and represents a new class of ultrafast waveform generators.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dudley, J. M., Genty, G. & Coen, S. Supercontinuum generation is photonic crystal fiber. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1135–1184 (2006).
Foster, M. A. et al. Silicon-chip-based ultrafast optical oscilloscope. Nature 456, 81–84 (2008).
Pelusi, M. et al. Photonic-chip-based radio-frequency spectrum analyser with terahertz bandwidth. Nature Photon. 3, 139–143 (2009).
Salem, R. et al. High-speed optical sampling using a silicon-chip temporal magnifier. Opt. Express 17, 4324–4329 (2009).
Treacy, E. B. Optical pulse compression with diffraction gratings. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 5, 454–458 (1969).
Akhmanov, S. A., Vysloukh, V. A. & Chirkin, A. S. Self-action of wave packets in a nonlinear medium and femtosecond laser pulse generation. Sov. Phys. Usp. 29, 642–677 (1986).
Kolner, B. H. & Nazarathy, M., Temporal imaging with a time lens. Opt. Lett. 14, 630–632 (1989).
Kolner, B. H. Space-time duality and the theory of temporal imaging. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 30, 1951–1963 (1994).
Bennett, C. V. & Kolner, B. H. Principles of parametric temporal imaging—Part I: System configurations. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 36, 430–437 (2000).
Bennett, C. V., Scott, R. P. & Kolner, B. H. Temporal magnification and reversal of 100 Gb/s optical data with an upconversion time microscope. Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 2513–2515 (1994).
Salem, R. et al. Optical time lens based on four-wave mixing on a silicon chip. Opt. Lett. 33, 1047–1049 (2008).
Kauffman, M. T., Banyal, W. C., Godil, A. A. & Bloom, D. M. Time-to-frequency converter for measuring picosecond optical pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 270–272 (1994).
Bennett, C. V. & Kolner, B. H. Upconversion time microscope demonstrating 103x magnification of femtosecond waveforms. Opt. Lett. 24, 783–785 (1999).
Mouradian, L. K., Louradour, F., Messager, V., Barthelemy, A. & Froehly, C. Spectro-temporal imaging of femtosecond events. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 36, 795–801 (2000).
Han, Y., Boyraz, O. & Jalali, B. Tera-sample per second real-time waveform digitizer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 241116 (2005).
Okawachi, Y. et al. High-resolution spectroscopy using a frequency magnifier. Opt. Express 17, 5691–5697 (2009).
Almeida, P. J., Petropoulos, P., Thomsen, B. C., Ibsen, M. & Richardson, D. J. All-optical packet compression based on time-to-wavelength conversion. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16, 1688–1690 (2004).
Weiner, A. M. Femtosecond pulse shaping using spatial light modulators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 1929–1960 (2000).
Dugan, M. A., Tull, J. X. & Warren, W. S. High-resolution acousto-optic shaping of unamplified and amplified femtosecond laser pulses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 14, 2348–2358 (1997).
Leaird, D. E. & Weiner, A. M. Femtosecond direct space-to-time pulse shaping. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 37, 495–504 (2001).
Chou, J., Han, Y. & Jalali, B. Adaptive RF-photonic arbitrary waveform generator. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 15, 581–583 (2003).
Willits, J. T., Weiner, A. M. & Cundiff, S. T. Theory of rapid-update line-by-line pulse shaping. Opt. Express 16, 315–327 (2008).
Foster, M. A. et al. Broad-band optical parametric gain on a silicon photonic chip. Nature 441, 960–963 (2006).
Lin, Q., Zhang, J., Fauchet, P. M. & Agrawal, G. P. Ultrabroadband parametric generation and wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides. Opt. Express 14, 4786–4799 (2006).
Foster, M. A., Turner, A. C., Salem, R., Lipson, M. & Gaeta, A. L. Broad-band continuous-wave parametric wavelength conversion in silicon nanowaveguides. Opt. Express 15, 12949–12958 (2007).
Turner, A. C., Foster, M. A., Gaeta, A. L. & Lipson, M. Ultra-low power parametric frequency conversion in a silicon microring resonator. Opt. Express 16, 4881–4887 (2008).
Dulkeith, E., Xia, F., Schares, L., Green, W. M. J. & Vlasov Y. A. Group index and group velocity dispersion in silicon-on-insulator photonic wires. Opt. Express. 14, 3853–3863 (2006).
Turner, A. C. et al. Tailored anomalous group-velocity dispersion in silicon channel waveguides. Opt. Express 14, 4357–4362 (2006).
Foster, M. A., Turner, A. C., Lipson, M. & Gaeta A. L. Nonlinear optics in photonic nanowires. Opt. Express 16, 1300–1320 (2008).
Bennett, C. V. & Kolner, B. H. Aberrations in temporal imaging. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 37, 20–32 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by DARPA through the optical arbitrary waveform generation program and by the Center for Nanoscale Systems, supported by the NSF and the New York State Office of Science, Technology and Academic Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.A.F., R.S., and Y.O. performed the experiments. M.A.F conceived of the compressor design. A.C.T. and M.A.F. designed the photonic chips. A.C.T. fabricated the photonic chips. M.A.F. and A.L.G prepared the manuscript. A.L.G. and M.L. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, M., Salem, R., Okawachi, Y. et al. Ultrafast waveform compression using a time-domain telescope. Nature Photon 3, 581–585 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.169
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.169
This article is cited by
-
Extreme waveform compression with a nonlinear temporal focusing mirror
Nature Photonics (2022)
-
Front-induced transitions
Nature Photonics (2019)
-
Single-shot real-time femtosecond imaging of temporal focusing
Light: Science & Applications (2018)
-
Bandwidth manipulation of quantum light by an electro-optic time lens
Nature Photonics (2017)
-
Ultrafast and versatile spectroscopy by temporal Fourier transform
Scientific Reports (2014)