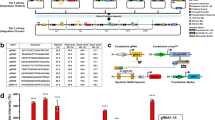
Abstract
Molecular-level information processing1,2 is essential for ‘smart’ in vivo nanosystems. Natural molecular computing, such as the regulation of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis by special proteins called transcription factors3,4, has inspired engineered systems5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 that can control the levels of mRNA with certain combinations of transcription factors. Here, we show an alternative approach to achieving general-purpose control of mRNA and protein levels by logic integration of transcription factor input signals in mammalian cells. The transcription factors regulate synthetic genes coding for small regulatory RNAs (called microRNAs), which, in turn, control the mRNA of interest (the output) via an RNA interference pathway. The simplicity of these modular interactions makes it possible, in theory, to implement any arbitrary logic relation between the transcription factors and the output16. We construct, test and optimize increasingly complex circuits with up to three transcription factor inputs, establishing a platform for in vivo molecular computing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro, E. & Benenson, Y. Bringing DNA computers to life. Sci. Am. 294, 44–51 (2006).
Jungmann, R., Renner, S. & Simmel, F. C. From DNA nanotechnology to synthetic biology. HFSP Journal 2, 99–109 (2008).
Shen-Orr, S. S., Milo, R., Mangan, S. & Alon, U. Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia coli. Nature Genet. 31, 64–68 (2002).
Lee, T. I. et al. Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 298, 799–804 (2002).
Weiss, R., Homsy, G. E. & Knight, T. F. in Evolution as Computation: DIMACS Workshop (eds Landweber, L. F. & Winfree, E.) 275–295 (Springer, 1999).
Guet, C. C., Elowitz, M. B., Hsing, W. H. & Leibler, S. Combinatorial synthesis of genetic networks. Science 296, 1466–1470 (2002).
Basu, S., Gerchman, Y., Collins, C. H., Arnold, F. H. & Weiss, R. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation. Nature 434, 1130–1134 (2005).
Anderson, J. C., Voigt, C. A. & Arkin, A. P. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3, 133 (2007).
Bronson, J. E., Mazur, W. W. & Cornish, V. W. Transcription factor logic using chemical complementation. Mol. Biosystems 4, 56–58 (2008).
Canton, B., Labno, A. & Endy, D. Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices. Nature Biotechnol. 26, 787–793 (2008).
Sayut, D. J., Niu, Y. & Sun, L. H. Construction and enhancement of a minimal genetic AND logic gate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 637–642 (2009).
Ellis, T., Wang, X. & Collins, J. J. Diversity-based, model-guided construction of synthetic gene networks with predicted functions. Nature Biotechnol. 27, 465–471 (2009).
Kramer, B. P., Fischer, C. & Fussenegger, M. BioLogic gates enable logical transcription control in mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 87, 478–484 (2004).
Mayo, A. E., Setty, Y., Shavit, S., Zaslaver, A. & Alon, U. Plasticity of the cis-regulatory input function of a gene. Plos Biol. 4, 555–561 (2006).
Cox, R. S., Surette, M. G. & Elowitz, M. B. Programming gene expression with combinatorial promoters. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3, 145 (2007).
Rinaudo, K. et al. A universal RNAi-based logic evaluator that operates in mammalian cells. Nature Biotechnol. 25, 795–801 (2007).
Fukuda, Y., Kawasaki, H. & Taira, K. Construction of microRNA-containing vectors for expression in mammalian cells. Meth. Mol. Biol. 338, 167–173 (2006).
Buchler, N. E., Gerland, U. & Hwa, T. On schemes of combinatorial transcription logic. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5136–5141 (2003).
Schwake, G. et al. Predictive modeling of non-viral gene transfer. Biotech. Bioeng. 105, 805–813 (2010).
Marguet, P., Balagadde, F., Tan, C. M. & You, L. C. Biology by design: reduction and synthesis of cellular components and behaviour. J. Royal Soc. Interface 4, 607–623 (2007).
An, W. L. & Chin, J. W. Synthesis of orthogonal transcription–translation networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 8477–8482 (2009).
Deans, T. L., Cantor, C. R. & Collins, J. J. A tunable genetic switch based on RNAi and repressor proteins for regulating gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell 130, 363–372 (2007).
Gardner, T. S., Cantor, C. R. & Collins, J. J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 403, 339–342 (2000).
Lu, T. K., Khalil, A. S. & Collins, J. J. Next-generation synthetic gene networks. Nature Biotechnol. 27, 1139–1150 (2009).
Xie, Z., Liu, S. J., Bleris, L. & Benenson, Y. Logic integration of mRNA signals by an RNAi-based molecular computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 2692–2701 (2010).
Valadi, H. et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature Cell Biol. 9, 654–659 (2007).
Gullotti, E. & Yeo, Y. Extracellularly activated nanocarriers: a new paradigm of tumor targeted drug delivery. Mol. Pharmaceutics 6, 1041–1051 (2009).
Broz, P. et al. Toward intelligent nanosize bioreactors: a pH-switchable, channel-equipped, functional polymer nanocontainer. Nano Lett. 6, 2349–2353 (2006).
Lu, Q. Seamless cloning and gene fusion. Trends Biotechnol. 23, 199–207 (2005).
Stegmeier, F., Hu, G., Rickles, R. J., Hannon, G. J. & Elledge, S. J. A lentiviral microRNA-based system for single-copy polymerase II-regulated RNA interference in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 13212–13217 (2005).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for thoughtful comments. M.L. is a recipient of Deutsche Forschungs Gemeinschaft scholarship. The research was funded by the Bauer Fellows program and by the NIGMS grant GM068763 for National Centres of Systems Biology. M.L. acknowledges her father R. Leisner, who passed away as this manuscript was prepared for submission: ‘One learns most from those one loves’ (Goethe).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.B. designed the research and supervised the project. M.L., L.B., J.L., Z.X. and Y.B. performed the research. M.L., Y.B., J.L. and L.B. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have an application pending for a US patent.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 3677 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leisner, M., Bleris, L., Lohmueller, J. et al. Rationally designed logic integration of regulatory signals in mammalian cells. Nature Nanotech 5, 666–670 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.135
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.135
This article is cited by
-
Microneedle biomedical devices
Nature Reviews Bioengineering (2023)
-
A synthetic circuit for buffering gene dosage variation between individual mammalian cells
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Technical Notation as a Tool for Basic Research in Relational Frame Theory
The Psychological Record (2019)
-
Designing cell function: assembly of synthetic gene circuits for cell biology applications
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2018)
-
Mapping the operational landscape of microRNAs in synthetic gene circuits
npj Systems Biology and Applications (2018)