Abstract
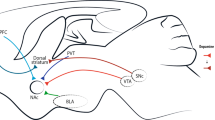
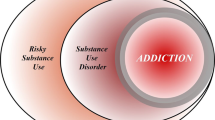
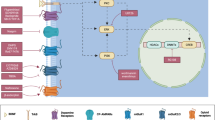
Most advances in addiction treatment to date have addressed the physical dependence and withdrawal that accompany addiction to some drugs of abuse. In contrast, it has proven more difficult to develop medications that effectively treat drug craving and relapse, the core features of addictive disorders. Current efforts focus on developing medications that prevent a drug from getting to its protein target, that mimic drug action and thereby partially alleviate drug craving, or that affect the addiction process per se. The latter approach is the most speculative, but also the most promising in terms of translating basic knowledge of addiction into clinical progress.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Debbie Maizels
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nestler, E.J. Molecular basis of neural plasticity underlying addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 119–128 (2001).
Koob, G.F., Sanna, P.P. & Bloom, F.E. Neuroscience of addiction. Neuron 21, 467–476 (1998).
Wise, R.A. Drug-activation of brain reward pathways. Drug Alcohol Depend. 51, 13–22 (1998).
Everitt, B.J. & Wolf, M.E. Psychomotor stimulant addiction: a neural systems perspective. J. Neurosci. 22, 3312–3320 (2002).
O'Brien, C.P. A range of research-based pharmacotherapies for addiction. Science 278, 66–70 (1997).
Aghajanian, G.K. Tolerance of locus coeruleus neurones to morphine and suppression of withdrawal response by clonidine. Nature 276, 186–188 (1978).
Gold, M.S., Redmond, D.E. Jr., & Kleber, H.D. Clonidine blocks acute opiate-withdrawal symptoms. Lancet 2, 599–602 (1978).
Krystal, J.H., Cramer, J.A., Krol, W.F., Kirk, G.F. & Rosenheck, R.A. Veterans Affairs Naltrexone Cooperative Study 425 Group. Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 1734–1739 (2001).
Kantak, K.M., Collins, S.L., Bond, J. & Fox, B.S. Time course of changes in cocaine self-administration behavior in rats during immunization with the cocaine vaccine IPC-1010. Psychopharmacology 153, 334–340 (2001).
Cohen, P.J. Immunization for prevention and treatment of cocaine abuse: legal and ethical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 48, 167–174 (1997).
National Consensus Development Panel. Effective medical treatment of opiate addiction. JAMA 280, 1936–1943 (1998).
Kreek, M.J. Methadone-related opioid agonist pharmacotherapy for heroin addiction. History, recent molecular and neurochemical research and future in mainstream medicine. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 909, 186–216 (2000).
Ling, W. et al. Buprenorphine maintenance treatment of opiate dependence: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial. Addiction 93, 475–486 (1998).
Silagy, C., Lancaster, T., Stead, L., Mant, D. & Fowler, G. Nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 3, CD000146 (2001).
Pulvirenti, L. & Koob, G.F. Dopamine receptor agonists, partial agonists and psychostimulant addiction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 15, 374–379 (1994).
Self, D.W., Barnhart, W.J., Lehman, D.A. & Nestler, E.J. Opposite modulation of cocaine-seeking behavior by D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptor agonists. Science 271, 1586–1589 (1996).
Hyman, S.E. & Malenka, R.C. Addiction and the brain: the neurobiology of compulsion and its persistence. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 695–703 (2001).
Carlezon, W.A. Jr., Haile, C.N., Neve, R. & Nestler, E.J. Distinct sites of opiate reward and aversion within the midbrain identified using a herpes simplex virus (HSV) vector expressing GluR1. J. Neurosci. 20, RC62 (2000).
Nicola, S.M., Surmeier, J. & Malenka, R.C. Dopaminergic modulation of neuronal excitability in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 185–215 (2000).
Cornish, J.L. & Kalivas, P.W. Cocaine sensitization and craving: differing roles for dopamine and glutamate in the nucleus accumbens. J. Addictive Dis. 20, 43–54 (2001).
Ungless, M.A., Whistler, J.L., Malenka, R.C. & Bonci, A. Single cocaine exposure in vivo induces long-term potentiation in dopamine neurons. Nature, 411, 583–587 (2001).
Self, D.W. Where's the excitement in psychostimulant sensitization? Neuropsychopharmacology 26, 14–17 (2002).
Hutcheson, D.M., Everitt, B.J., Robbins, T.W. & Dickinson, A. The role of withdrawal in heroin addiction: enhances reward or promotes avoidance? Nat. Neurosci. 4, 943–947 (2001).
Shalev, U., Morales, M., Hope, B., Yap, J. & Shaham, Y. Time-dependent changes in extinction behavior and stress-induced reinstatement of drug seeking following withdrawal from heroin in rats. Psychopharmacology 156, 98–107 (2001).
Shaham, Y., Erb, S. & Stewart, J. Stress-induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking in rats: a review. Brain Res. Rev. 33, 13–33 (2000).
Bohn, L.M., Gainetdinov, R.R., Lin, F.T., Lefkowitz, R.J. & Caron, M.G. μ-Opioid receptor desensitization by β-arrestin-2 determines morphine tolerance but not dependence. Nature 408, 720–723 (2000).
Potenza, M.N. & Nestler, E.J. Effects of RGS proteins on the functional response of the μ opioid receptor in a melanophore-based assay. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 291, 482–491 (1999).
Nestler, E.J., Barrot, M. & Self, S.W. ΔFosB: a molecular switch for addiction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11042–11046 (2001).
Acknowledgements
Preparation of this review was supported by grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nestler, E. From neurobiology to treatment: progress against addiction. Nat Neurosci 5 (Suppl 11), 1076–1079 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn945
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn945
This article is cited by
-
The thalamo-cortical resting state functional connectivity and abstinence-induced craving in young smokers
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2018)
-
Hyper-resting brain entropy within chronic smokers and its moderation by Sex
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Repeated Cocaine Administration Decreases 5-HT2A Receptor-Mediated Serotonergic Enhancement of Synaptic Activity in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
-
Development and evaluation of the heroin abstainers’ cue-sensitization questionnaire
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2009)
-
A neuropeptide‐centric view of psychostimulant addiction
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008)