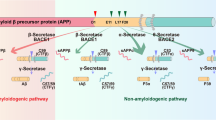
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease is the single biggest unmet medical need in neurology. Current drugs are safe, but of limited benefit to most patients. This review discusses the scientific basis and current status of promising disease-modifying therapies in the discovery and development stages. I describe the major targets of anti-amyloid therapy and the main focus of disease modification approaches. In addition, two new potential treatment approaches supported by retrospective epidemiology are outlined.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, K.L. & Samuels, S.C. in Pharmacological Management of Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders (eds. Enna, S. J. & Coyle, J. T.) 267–316 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1998).
Doody, R.S. Therapeutic standards in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 13, S20–S26 (1999).
Hardy, J. & Allsop, D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Pharmacol. 12, 383–388 (1991).
Joachim, C.L. & Selkoe, D.J. The seminal role of β-amyloid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 6, 7–34 (1992).
Younkin, S.G. The role of A beta 42 in Alzheimer's disease. J. Physiol. (Paris) 92, 289–292 (1998).
Selkoe, D.J. Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 399, A23–A31 (1999).
Leung, D., Abbenante, G. & Fairlie, D.P. Protease inhibitors: current status and future prospects. J. Med. Chem. 43, 305–341 (2000).
Francis, R. et al. Aph-1 and pen-2 are required for Notch pathway signaling, γ-secretase cleavage of APP, and presenilin protein accumulation. Dev. Cell 3, 85–97 (2002).
Sisodia, S.S. & St George-Hyslop, P.H. γ-secretase, Notch, Aβ and Alzheimer's disease: where do the presenilins fit in? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 281–290 (2002).
Vassar, R. et al. β-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286, 735–741 (1999).
Hong, L. et al. Structure of the protease domain of memapsin 2 (β-secretase) complexed with inhibitor. Science 290, 150–153 (2000).
Luo, Y. et al. Mice deficient in BACE1, the Alzheimer's β-secretase, have normal phenotype and abolished β-amyloid generation. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 231–232 (2001).
Citron, M. β-secretase as a target for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. (in press).
Sinha, S. et al. Purification and cloning of amyloid precursor protein β-secretase from human brain. Nature 402, 537–540 (1999).
Hock, B.J. & Lamb, B.T. Transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Genet. 17, S7–S12 (2001).
Soto, C. Plaque busters: strategies to inhibit amyloid formation in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Med. Today 5, 343–350 (1999).
Cherny, R.A. et al. Treatment with a copper-zinc chelator markedly and rapidly inhibits β-amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. Neuron 30, 665–676 (2001).
Bush, A. & Tanzi, R.E. The galvanization of β-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7317–7319 (2002).
Schenk, D. et al. Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400, 173–177 (1999).
Bard, F. et al. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid β-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 6, 916–919 (2000).
DeMattos, R.B. et al. Peripheral anti-Aβ antibody alters CNS and plasma Aβ clearance and decreases brain Aβ burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8850–8855 (2001).
Steinberg, D. Companies halt first Alzheimer vaccine trial. The Scientist 16, 22–23 (2002).
McGeer, P.L. & McGeer, E.G. Inflammation, autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol. Aging 22, 799–809 (2001).
Weggen, S. et al. A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Aβ42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity. Nature 414, 212–216 (2001).
Wolozin, B., Kellman, W., Ruosseau, P., Celesia, G.G. & Siegel, G. Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arch. Neurol. 57, 1439–1443 (2000).
Jick, H., Zornberg, G.L., Jick, S.S., Seshadri, S. & Drachman, D.A. Statins and the risk of dementia. Lancet 356, 1627–1631 (2000).
Fassbender, K. et al. Simvastatin strongly reduces levels of Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptides Aβ42 and Aβ40 in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5856–5861 (2001).
Golde, T.E. & Eckman, C.B. Cholesterol modification as an emerging strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Drug Discov. Today 6, 1049–1055 (2001).
Puglielli, L. et al. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase modulates the generation of the amyloid β-peptide. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 905–912 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Citron, M. Alzheimer's disease: treatments in discovery and development. Nat Neurosci 5 (Suppl 11), 1055–1057 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn940
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn940
This article is cited by
-
The sociodemographic characteristics and dietary and blood plasma fatty acid profiles of elderly Saudi women with Alzheimer disease
Lipids in Health and Disease (2019)
-
Production and enhancement of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, huperzine A, from an endophytic Alternaria brassicae AGF041
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)
-
Enhancement of Neuroprotective Effects of Spirulina maxima by a Low-temperature Extraction Process with Ultrasonic Pretreatment
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2018)
-
Similarity search combined with docking and molecular dynamics for novel hAChE inhibitor scaffolds
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2018)
-
In vivo rapid fluorescence imaging of Alzheimer’s disease through accurate target bio-marking of zinc gluconate
Science Bulletin (2015)