Abstract
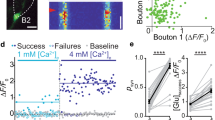
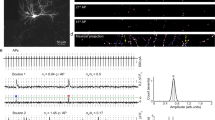
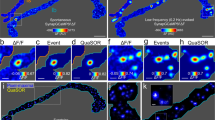
Many synapses can change their strength rapidly in a use-dependent manner, but the mechanisms of such short-term plasticity remain unknown. To understand these mechanisms, measurements of neurotransmitter release at single synapses are required. We probed transmitter release by imaging transient increases in [Ca2+] mediated by synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) in individual dendritic spines of CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat brain slices, enabling quantal analysis at single synapses. We found that changes in release probability, produced by paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) or by manipulation of presynaptic adenosine receptors, were associated with changes in glutamate concentration in the synaptic cleft, indicating that single synapses can release a variable amount of glutamate per action potential. The relationship between release probability and response size is consistent with a binomial model of vesicle release with several (>5) independent release sites per active zone, suggesting that multivesicular release contributes to facilitation at these synapses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katz, B. The Release of Neural Transmitter Substances (Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, 1969).
Harris, K.M. & Sultan, P. Variation in the number, location and size of synaptic vesicles provides an anatomical basis for the nonuniform probability of release at hippocampal CA1 synapses. Neuropharmacology 34, 1387–1395 (1995).
Schikorski, T. & Stevens, C.F. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J. Neurosci. 17, 5858–5867 (1997).
Dobrunz, L.E. & Stevens, C.F. Heterogeneity of release probability, facilitation, and depletion at central synapses. Neuron 18, 995–1008 (1997).
Hanse, E. & Gustafsson, B. Quantal variability at glutamatergic synapses in area CA1 of the rat neonatal hippocampus. J. Physiol. 531, 467–480 (2001).
Auger, C., Kondo, S. & Marty, A. Multivesicular release at single functional synaptic sites in cerebellar stellate and basket cells. J. Neurosci. 18, 4532–4547 (1998).
Tong, G. & Jahr, C.E. Multivesicular release from excitatory synapses of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 12, 51–59 (1994).
Isaac, J.T. et al. An investigation of the expression mechanism of LTP of AMPA receptor–mediated synaptic transmission at hippocampal CA1 synapses using failures analysis and dendritic recordings. Neuropharmacology 37, 1399–1410 (1998).
Wadiche, J.I. & Jahr, C.E. Multivesicular release at climbing fiber-purkinje cell synapses. Neuron 32, 301–313 (2001).
Stevens, C.F. & Wang, Y. Facilitation and depression at single central synapses. Neuron 14, 795–802 (1995).
Redman, S. Quantal analysis of synaptic potentials in neurons of the central nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 70, 165–198 (1990).
Regehr, W.G. & Stevens, C.F. in Synapses (eds. Cowan, W. M., Sudhof, T. C. & Stevens, C. F.) 135–175 (Johns Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore, 2001).
Auger, C. & Marty, A. Quantal currents at single-site central synapses. J. Physiol. 526, 3–11 (2000).
Korn, H., Triller, A., Mallet, A. & Faber, D.S. Fluctuating responses at a central synapse: n of binomial fit predicts number of stained presynaptic boutons. Science 213, 898–901 (1981).
Spruston, N., Jonas, P. & Sakmann, B. Dendritic glutamate receptor channels in rat hippocampal CA3 and CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Physiol. 482, 325–352 (1995).
Faber, D.S., Young, W.S., Legendre, P. & Korn, H. Intrinsic quantal variability due to stochastic properties of receptor–transmitter interactions. Science 258, 1494–1498 (1992).
Magee, J.C. & Cook, E.P. Somatic EPSP amplitude is independent of synapse location in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 895–903 (2000).
Stuart, G. & Spruston, N. Determinants of voltage attenuation in neocortical pyramidal neuron dendrites. J. Neurosci. 18, 3501–3510 (1998).
Williams, S.R. & Stuart, G.J. Dependence of EPSP efficacy on synapse location in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Science 295, 1907–1910 (2002).
Mainen, Z.F., Malinow, R. & Svoboda, K. Synaptic calcium transients in single spines indicate that NMDA receptors are not saturated. Nature 399, 151–155 (1999).
Harris, K.M. & Stevens, J.K. Dendritic spines of CA1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus: serial electron microscopy with reference to their biophysical characteristics. J. Neurosci. 9, 2982–2997 (1989).
Yuste, R. & Denk, W. Dendritic spines as basic functional units of neuronal integration. Nature 375, 682–684 (1995).
Denk, W. & Svoboda, K. Photon upmanship: why multiphoton imaging is more than a gimmick. Neuron 18, 351–357 (1997).
McAllister, A.K. & Stevens, C.F. Nonsaturation of AMPA and NMDA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6173–6178 (2000).
Umemiya, M., Senda, M. & Murphy, T.H. Behavior of NMDA and AMPA receptor-mediated miniature EPSCs at rat cortical neuron synapses identified by calcium imaging. J. Physiol. 521, 113–122 (1999).
Sabatini, B.L., Maravall, M. & Svoboda, K. Ca2+ signaling in dendritic spines. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 349–356 (2001).
Mainen, Z.F. et al. Two-photon imaging in living brain slices. Methods 18, 231–239 (1999).
Bekkers, J.M., Richerson, G.B. & Stevens, C.F. Origins of variability in quantal size in cultured hippocampal neurons and hippocampal slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 5359–5362 (1990).
Zucker, R.S. & Regehr, W.G. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 13–31 (1989).
Wu, L.G. & Saggau, P. Adenosine inhibits evoked synaptic transmission primarily by reducing presynaptic calcium influx in area CA1 of hippocampus. Neuron 12, 1139–1148 (1994).
Wu, L.G. & Saggau, P. Presynaptic inhibition of elicited neurotransmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 20, 204–212 (1997).
Choi, S., Klingauf, J. & Tsien, R.W. Postfusional regulation of cleft glutamate concentration during LTP at 'silent synapses'. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 330–336 (2000).
Clements, J.D. & Westbrook, G.L. Activation kinetics reveal the number of glutamate and glycine binding sites on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Neuron 7, 605–613 (1991).
Neher, E. The use of Fura-2 for estimating Ca buffers and Ca fluxes. Neuropharmacology 34, 1423–1442 (1995).
Sabatini, B.S., Oertner, T.G. & Svoboda, K. The life-cycle of Ca2+ ions in spines. Neuron 33, 439–452 (2002).
Asztely, F., Erdemli, G. & Kullmann, D.M. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron 18, 281–293 (1997).
Arnth-Jensen, N., Jabaudon, D. & Scanziani, M. Cooperation between independent hippocampal synapses is controlled by glutamate uptake. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 325–331 (2002).
Diamond, J.S. Neuronal glutamate transporters limit activation of NMDA receptors by neurotransmitter spillover on CA1 pyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. 21, 8328–8338 (2001).
Barbour, B. An evaluation of synapse independence. J. Neurosci. 21, 7969–7984 (2001).
Rusakov, D.A. & Kullmann, D.M. Extrasynaptic glutamate diffusion in the hippocampus: ultrastructural constraints, uptake, and receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 18, 3158–3170 (1998).
Emptage, N., Bliss, T.V.P. & Fine, A. Single synaptic events evoke NMDA receptor-mediated release of calcium from internal stores in hippocampal dendritic spines. Neuron 22, 115–124 (1999).
Kovalchuk, Y., Eilers, J., Lisman, J. & Konnerth, A. NMDA receptor–mediated subthreshold Ca2+ signals in spines of hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 1791–1799 (2000).
Spacek, J. & Harris, K.M. Three-dimensional organization of smooth endoplasmic reticulum in hippocampal CA1 dendrites and dendritic spines of the immature and mature rat. J. Neurosci. 17, 190–203 (1997).
Patneau, D.K. & Mayer, M.L. Structure–activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J. Neurosci. 10, 2385–2399 (1990).
Bliss, T.V.P. & Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39 (1993).
Renger, J.J., Egles, C. & Liu, G. A developmental switch in neurotransmitter flux enhances synaptic efficacy by affecting AMPA receptor activation. Neuron 29, 469–484 (2001).
Liao, D., Hessler, N.A. & Malinow, R. Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. Nature 375, 400–404 (1995).
Isaac, J.T., Nicoll, R.A. & Malenka, R.C. Evidence for silent synapses: implications for the expression of LTP. Neuron 15, 427–434 (1995).
Sabatini, B.L. & Svoboda, K. Analsyis of calcium channels in single spines using optical fluctuation analysis. Nature 408, 589–593 (2000).
Sather, W., Dieudonne, S., MacDonald, J.F. & Ascher, P. Activation and desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in nucleated outside-out patches from mouse neurons. J. Physiol. 450, 643–672 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank Z. Mainen, R. Malinow, M. Maravall and R. Yasuda for comments on the manuscript, and T. Pologruto for software development. This work was supported by grants from the Swartz Initiative for Computational Neuroscience (to T.G.O.), the Helen Hay Whitney Foundation (to B.L.S.), the Pew and Mathers Foundations and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oertner, T., Sabatini, B., Nimchinsky, E. et al. Facilitation at single synapses probed with optical quantal analysis. Nat Neurosci 5, 657–664 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn867
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn867
This article is cited by
-
Tau in cerebrospinal fluid induces neuronal hyperexcitability and alters hippocampal theta oscillations
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2023)
-
Determinants of synapse diversity revealed by super-resolution quantal transmission and active zone imaging
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Filopodia are a structural substrate for silent synapses in adult neocortex
Nature (2022)
-
Vesicular release probability sets the strength of individual Schaffer collateral synapses
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Structure and function of a neocortical synapse
Nature (2021)